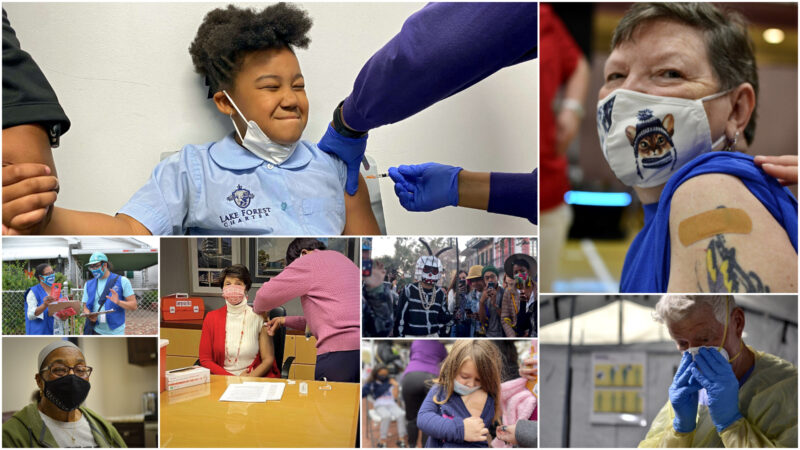
Key COVID moments in the Gulf South 2 years later
Two years ago today, the World Health Organization officially declared COVID-19 a pandemic. Nearly a million people have now died of the disease in the U.S., including approximately 48,000 people across Alabama, Louisiana and Mississippi
Over the last year, the Gulf States Newsroom has chronicled the impact COVID has had on the Gulf South region — from hesitancy during the vaccine rollout to overwhelmed health care systems and burnt-out workers.
Here are some of the key moments we’ve covered:
Vaccine rollout begins, but distribution is uneven

In February 2021, a COVID-19 vaccine had already been out for a couple of months. Demand, however, was already outpacing supply, and snagging a shot in the arm was hard for most people. An NPR analysis of vaccination sites around the country found that in cities like Baton Rouge, access was even more uneven.
Of the 20 official sites providing vaccinations in early February, 15 were located in the southern part of the city, a predominantly white and affluent area. It’s also where the vast majority of medical facilities are located.
“I was getting calls, one or two types of calls,” Clark-Amar, CEO of the East Baton Rouge Council on Aging, said. “One, I’m not going because my grandkids said don’t do it. The second type of call I got is: Where can I get it? How do you get it? How do you sign up? Is there an application?”
We highlighted these issues for a national audience with a roundtable and feature story on NPR.
After this reporting, Baton Rouge Mayor-President Sharon Broome responded and said she would try to address access gaps.
Read more: Uneven Vaccine Rollout Threatens To Leave Black Communities Behind
Black health care workers set the example
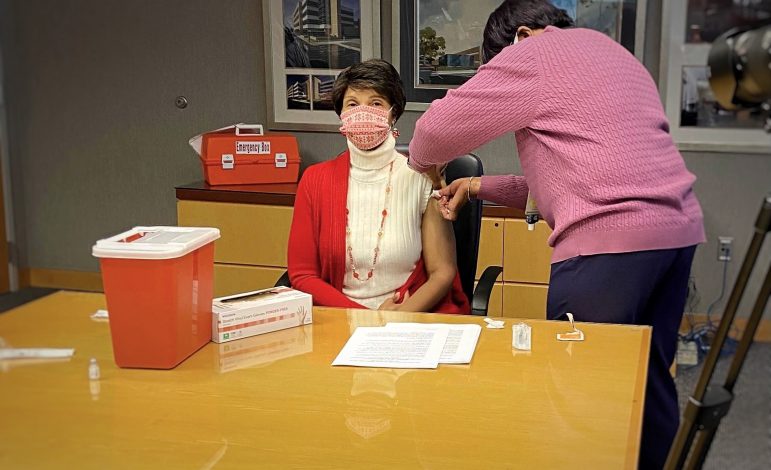
Early in the vaccine rollout, hesitancy within the Black community and among Black health care workers was a major concern for public health officials. In a national survey of 2,500 health care workers in January, 15% of respondents decided not to get the vaccine. And, several Black nurses in Mississippi said they were hesitant as well.
Many Black health care professionals stepped up to be advocates, not only for Black communities in general but specifically for their colleagues. In December 2020, Sonja Fuqua, a nurse and director at the Community Health Center Association of Mississippi, became one of the first five people in Mississippi to get a vaccine.
“Several people responded and said, because I saw you, I’m going to go ahead and do it,” Fuqua said.
One nurse, Mary Williams, who was included in this article was then featured in a Vox Today, Explained episode to talk about why she decided not to take the shot at the time. Williams later did decide to get the vaccine, because she was concerned about the Delta variant.
Read more: To Get The Vaccine Or Not: How These Black Health Care Workers Made The Decision
Trusted providers reach hesitant and underserved patients
There are nearly 1,400 federally-funded urban and rural community health centers serving 30 million people in medically underserved areas across the country regardless of their ability to pay.
In Mississippi, these critical community health centers were left out in the beginning states of the vaccine rollout — harming underserved residents of color that rely on these trusted safety-net providers.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, rural Black southerners faced numerous barriers to health. In April of last year, Black residents accounted for nearly half of all deaths in Alabama and over 70% of deaths in Louisiana and Mississippi. Mississippi’s rural counties, which are over 40% Black, have had some of the highest rates of COVID-19 cases.
Communities get creative to spread vaccine awareness
Later in the vaccine rollout, it became clear that rural white communities showed more hesitancy toward the shot than Black communities.
Public health data from Mississippi, Louisiana, and Alabama showed white residents have lower vaccination rates than Black residents. In particular, national polls showed conservative white men are some of the most hesitant in the nation to take the coronavirus vaccine.
In response, state health officials pivoted their strategy to address these types of concerns — encouraging local leaders, like pastors, to deliver the message that the vaccine is safe and effective.
Read more: Using Pastors And Pints, Gulf States Try to Boost COVID-19 Vaccination Rates In White Communities
Delta variant emerges
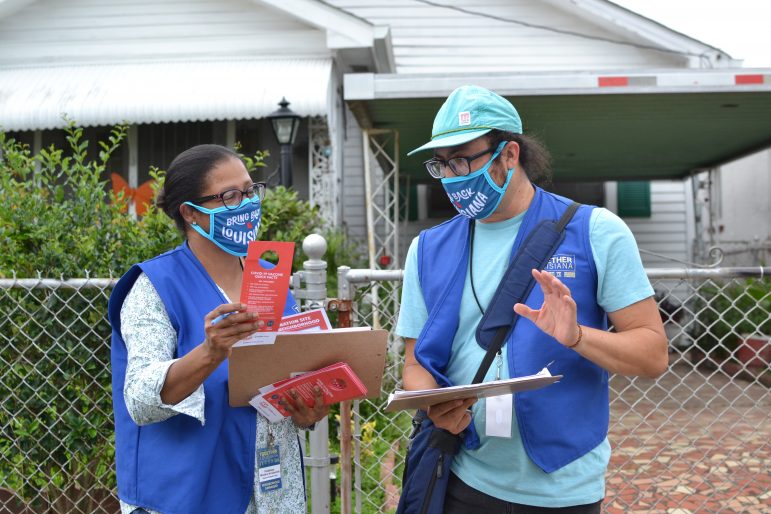

Throughout the vaccine rollout, state health departments tried numerous strategies to get the shot out — including meeting people “where they are.”
But around the time that Louisiana was trying to increase vaccinations through door-to-door campaigns, hyperlocal events in shopping malls and even a million-dollar lottery, the delta variant emerged.
A helping hand
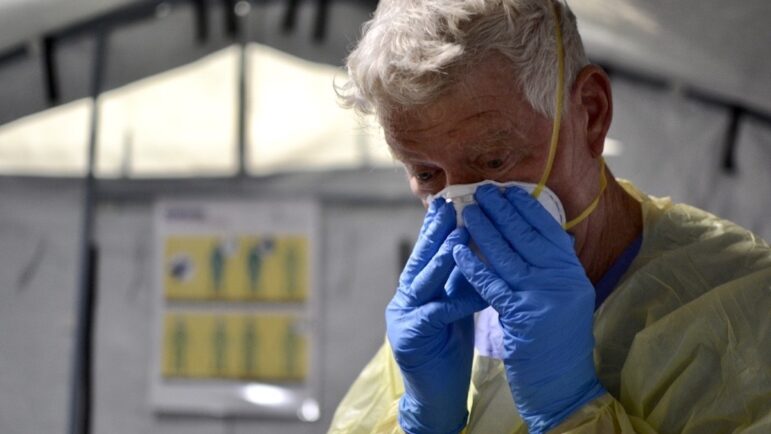

In the fall of 2021, the deadly delta variant caused a massive surge in cases and hospitalizations of people with severe COVID infections.
Health care systems across the country were once again overwhelmed. In response, field hospitals popped up across the region. This story looks at how one field hospital in Mississippi helped the state care for patients that had nowhere else to go.
Read more: As COVID Rages On, Gulf States Hospitals And Their Staff Look For A Helping Hand
Teens and children finally get the vaccine
In November 2021, health providers began rolling out the low-dose Pfizer vaccine for younger children, and appointments and waitlists filled up quickly.
At that point, vaccination rates were still lagging across the Gulf South and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and local health officials recommend the shot for all children ages 5-11.
Read more: Why Black teens are getting vaccinated at higher rates than white teens across the South; First kids ages 5-11 to get COVID shot looking forward to sleepovers, ‘feeling safe’
A bold decision in New Orleans
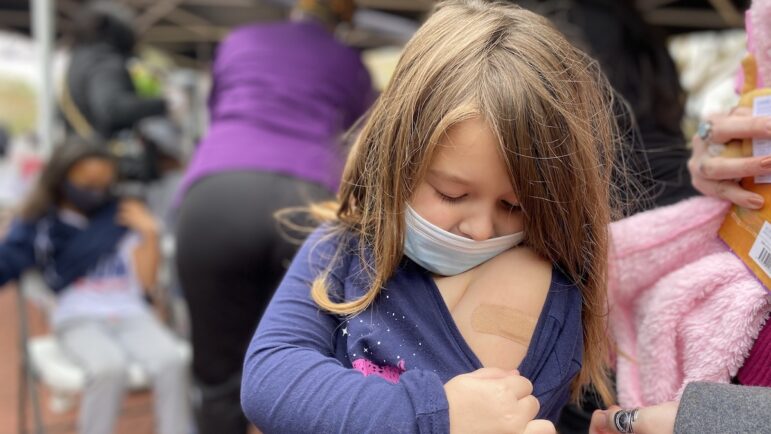

In the two months that children ages 5-11 were eligible for Pfizer’s COVID-19 shot, the pace of vaccine uptake for this age group slowed, and in the Gulf South, it was at a crawl.
By the end of December 2021, only about 10% of young children in the Gulf South had gotten at least one shot, compared to 23% nationally. In a region where rejecting broad vaccine requirements is a source of pride for many state leaders, New Orleans wasn’t afraid to issue a mandate.
New Orleans was already an outlier, having a mandate in place for adults since August. Proof of vaccination or a negative COVID test was required for everything from indoor dining to concerts. In early December, the city expanded the mandate in 2022 to include children 5 and older — including a provision where children would need both shots to stay enrolled in school, unless parents file for a formal exemption.
Read more: As much of the Gulf South remains unvaccinated, New Orleans issues a mandate for kids
Mardi Gras returns
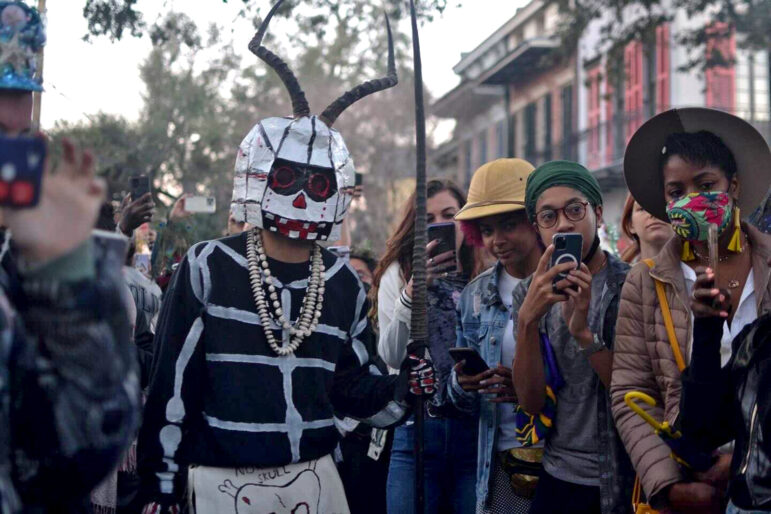

During Mardi Gras 2022, the festivities were back on in New Orleans, signaling a return to normalcy for many.
At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the event caused a massive surge in COVID-19 cases in the South, so parades were canceled last year.
At the crack of dawn on Fat Tuesday, the Northside Skull & Bone Gang resumed their tradition of waking up residents and reminding them to celebrate the day.
The men in the krewe dressed in skeleton costumes and ghoulish masks, beat their drums and chanted through the streets of New Orleans.
“Mardi Gras is a big relief,” Lorraine Guerin said later that day while enjoying a parade. “We’re having fun, drinking, eating….We really missed it.”
To stem the spread of COVID, city health director Jennifer Avegno said the city continued an indoor mask mandate and a vaccine or negative test requirement for activities like eating at a restaurant. The mask mandate was lifted a few days after Fat Tuesday in March.
This story was produced by the Gulf States Newsroom, a collaboration between Mississippi Public Broadcasting, WBHM in Alabama, WWNO and WRKF in Louisiana and NPR.
From 400-year-old globes to cosmic shrouds: A Maine library brings maps to life
From 400-year-old globes to cosmic funeral shrouds, how the Osher Map Library in Maine shows people that maps aren't just for navigation — but windows into history, culture, and how we see the world.
Benin’s interior minister says a coup announced earlier has been foiled
Earlier, a group of soldiers had appeared on Benin 's state TV Sunday to announce the dissolution of the government in an apparent coup, the latest of many in West Africa.
A fire at a popular nightclub in India’s Goa state kills at least 25, officials say
At least 25 people, including tourists, were killed in a fire at a popular nightclub in India's Goa state, the state's chief minister said Sunday.
National parks fee-free calendar drops MLK Day, Juneteenth and adds Trump’s birthday
The Trump administration, which has railed against what it describes as "woke" policies, removed MLK Day and Juneteenth from next year's list of fare-exempt days for visitors at dozens of national parks.
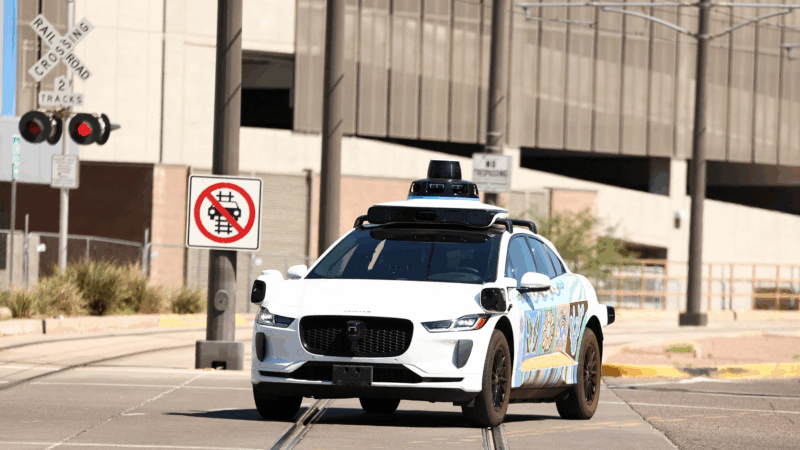
Waymo will recall software after its self-driving cars passed stopped school buses
Waymo is issuing a software recall for its self-driving cars after reports the company's autonomous vehicles failed to stop for school buses.
7 deaths and hundreds of injuries are linked to faulty Abbott glucose monitors
About 3 million glucose monitoring sensors were potentially affected by a production error that caused incorrect low glucose readings.