Advocates hope Alabama’s execution moratorium leads to change but say the blame is misplaced
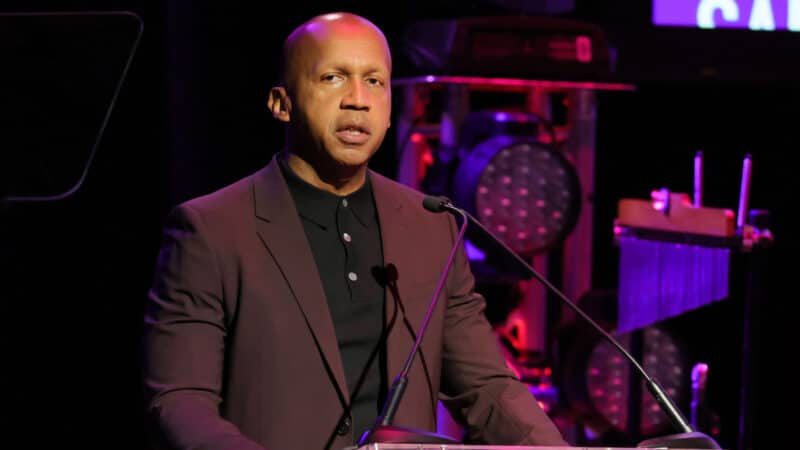
Bryan Stevenson is grateful that Ivey ordered the review, but says that "state officials need to own their own failures with regard to these executions.”
Monday, Gov. Kay Ivey ordered the Alabama Department of Corrections to both pause executions in the state and perform a ”top-to-bottom” review of its execution protocol. Many prison reform advocates praised the decision, while also approaching it with some skepticism.
Equal Justice Initiative Director Bryan Stevenson said, “It is a welcome and huge relief to many of us who see the tragedy that has come out of these recent horrific failed executions.”
However, Stevenson, one of the country’s leading advocates for death row inmates, as well as prison reform more generally, added, “We’re not going to get to a better place if the state’s not prepared to acknowledge its failure in conducting these proceedings legally and responsibly.”
How we got here
The move followed three failed lethal injections of death row inmates: The first was the unsuccessful attempt to execute Doyle Hamm in 2018. The second was of Alan Miller in September of this year, while the third was just last week — a failed attempt to execute Kenneth Eugene Smith.
In all three attempts, prison officials failed to connect either one or both of the intravenous lines Alabama’s protocol requires. According to the Associated Press, a number of other states have had problems carrying out lethal injections, but no other state has had to stop an execution in progress since 2017, the Death Penalty Information Center reports.
The one execution the state did complete recently — of Joe Nathan James, Jr. in July — followed a three-hour delay caused partially by the same problem starting an IV line. And an independent autopsy of James’ body revealed multiple puncture wounds on his hands and wrists, and the possible use of a controversial “cut-down” procedure used to find a vein.
Who’s to blame?
In her announcement of the moratorium and review of the execution process, Ivey said, “I don’t buy for a second the narrative being pushed by activists that these issues are the fault of the folks at Corrections or anyone in law enforcement, for that matter. I believe that legal tactics and criminals hijacking the system are at play here.”
Stevenson disagrees with the governor on that point.
“What’s happened during the executions in Alabama is unconscionable,” he told WBHM. “It’s unnecessary and it was completely avoidable. State officials need to own their own failures with regard to these executions.”
Stevenson continued, saying the executions were “shocking, torturous conduct that provided justice to no one. I don’t think the state is going to get to a better place if they’re looking to blame the imprisoned, blame the condemned, blame the lawyers, blame the court.”
How to fix the system
Stevenson has long advocated for a number of reforms in how states treat their prisoners.
“We’re not going to be judged just by our response to crime and criminality. We’re also going to be judged by how we treat people who are imprisoned, treat people who are condemned. … And what we’ve seen in the last three executions is really quite shocking,” Stevenson said.
“Strapping someone down to a gurney and poking and prodding and threatening and trying to kill them for hours is simply unacceptable.”
What Stevenson hopes comes from this moratorium is real change. He points to what has been done elsewhere.
“I think they’re going to have to call in people who are not just corrections officials in Alabama, if they’re going to get to a better outcome. Other states that have called for these kinds of suspensions have brought in experts to help them create protocols and procedures that are more reliable and more fair.”
Stevenson made it clear that he is grateful Ivey has issued her order to pause executions and to review procedure.
However, he says, “It’s unfortunate that we’ve had to see so much shocking and horrific execution protocols to get to this point. I just hope [the state] has the courage to accept its role and own up to its responsibilities in this review, and that it can yield some different process moving forward.”
40 years after ‘Purple Rain,’ Prince’s band remembers how the movie came together
Before social media, the film Purple Rain gave audiences a peak into Prince’s musical life. Band members say the true genesis of the title song was much less combative than the version presented in the film.
Park Fire in California could continue growing exponentially, Cal Fire officer says
Cal Fire has confirmed that over a hundred structures have been damaged in the Park Fire, which grew overnight near Chico, Calif. Difficult firefighting conditions are forecast through Friday night.
Checking in with Black voters in Georgia about the election, now that Biden is out
Some voters who could be key to deciding who wins Georgia. What do they think about Vice President Harris becoming the frontrunner in the race to be the Democratic nominee?
Tahiti’s waves are a matter of ‘life and death’ for surfing Olympics
Tahiti's Teahupo'o wave has a slew of riders for the Paris 2024 Olympics. NPR finds out why it's called one of the most dangerous waves.
Researchers are revising botanical names to address troubling connotations
Since the mid-1700s, researchers have classified life with scientific names. But some of them have problematic histories and connotations. The botanical community is trying to tackle this issue.
A spectacular opening ceremony wowed a global audience despite Paris’ on-and-off rain
The Paris Olympics opening ceremony wowed Parisians, fans and most everyone who was able to catch a glimpse of thousands of athletes floating down the Seine to officially begin the Games.