Alabama health officials seek to eliminate cervical cancer by 2033
Alabama ranks third in the nation for its rates of cervical cancer incidence and mortality, and those rates haven’t changed in 20 years.
“This is not acceptable,” Nancy Wright said during a press conference Monday. “Cervical cancer is preventable. And it’s stoppable.”
Wright, who directs the cancer prevention and control division at the Alabama Department of Public Health (ADPH), is working with a team of providers and experts from across the state to launch “Operation Wipe Out Cervical Cancer Alabama,” a campaign that aims to end cervical cancer by 2033.
ADPH officials plan to achieve the goal by aggressively pursuing three strategies:
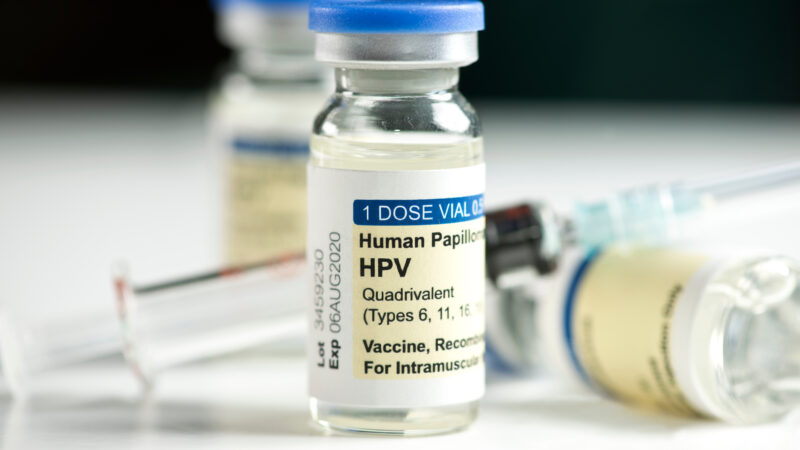
- Vaccinate more kids against the human papilloma virus (HPV), the virus that causes most cases of cervical cancer.
- Increase screenings for cervical cancer among women aged 21-65.
- Connect more women who receive abnormal test results to appropriate follow-up care.
Although HPV vaccination is thought to prevent most cases of cervical cancer, rates of vaccination in Alabama are low. Data from 2022 show that roughly 27% of young adults between the ages of 18 and 26 have completed a full two dose series of the HPV vaccine, which is recommended during childhood and adolescence. Officials hope to significantly increase those numbers through education and outreach.
“This is a historic plan. This is a milestone for us,” state health officer Dr. Scott Harris said. “We really believe that we have the tools and the knowledge to eliminate cervical cancer in our state, and with your help we know that we can do it.”
ADPH officials are working with researchers at UAB Hospital, Auburn University, state and local nonprofits and health care providers to implement “Operation Wipe Out.”
They aim to educate and engage patients through community events and public information campaigns, as well as increase access to vaccination, screenings and follow-up care by adding resources to county health departments and low-income health clinics.
Park Fire in California could continue growing exponentially, Cal Fire officer says
Cal Fire has confirmed that over a hundred structures have been damaged in the Park Fire, which grew overnight near Chico, Calif. Difficult firefighting conditions are forecast through Friday night.
Checking in with Black voters in Georgia about the election, now that Biden is out
Some voters who could be key to deciding who wins Georgia. What do they think about Vice President Harris becoming the frontrunner in the race to be the Democratic nominee?
Tahiti’s waves are a matter of ‘life and death’ for surfing Olympics
Tahiti's Teahupo'o wave has a slew of riders for the Paris 2024 Olympics. NPR finds out why it's called one of the most dangerous waves.
Researchers are revising botanical names to address troubling connotations
Since the mid-1700s, researchers have classified life with scientific names. But some of them have problematic histories and connotations. The botanical community is trying to tackle this issue.
A spectacular opening ceremony wowed a global audience despite Paris’ on-and-off rain
The Paris Olympics opening ceremony wowed Parisians, fans and most everyone who was able to catch a glimpse of thousands of athletes floating down the Seine to officially begin the Games.
Kamala Harris faces racism and sexism as she moves closer to presidential nomination
As Vice President Kamala Harris ramps up her campaign for president, Republicans are trying out new — and old — attacks focused on her race and gender, including calling her a "DEI candidate."