EXPLAINER: COVID vaccines for kids under 5: What’s next?
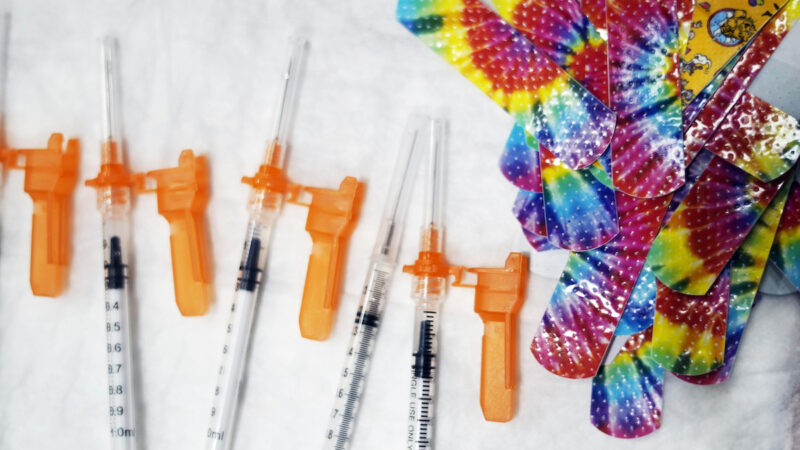
Syringes and colorful bandages are prepared as children from Pittsfield schools visited Morningside School to get COVID-19 vaccines in Pittsfield, Mass., on Monday Dec. 13, 2021. Some of the kids were getting their first shot, a few were getting their second.
By Lauran Neergaard, AP Medical Writer
Parents who thought their children under 5 would have to wait several more months for COVID-19 vaccinations instead just might get them as early as March. Here’s what needs to happen first, and some things to expect if they do become available in the U.S.
Government review
Pfizer has asked the Food and Drug Administration to authorize extra-low doses of its COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 6 months through 4 years. The FDA will review the application and convene a panel of outside advisers in mid-February to debate the data. The FDA will use that advice in deciding whether the new doses are safe and effective enough for the youngest children.
But that’s not the last step. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will gather its own expert panel to help decide if the shots should be recommended for this age group — and if so, for all of them or only those at higher risk from COVID-19.
Special shots
Shots for children in this age group are one-tenth the size of the adult doses. That’s even smaller than the doses given for 5- to 11-year-olds, which are one-third the dose. Pfizer will have to specially bottle the extra-low doses so vaccine providers don’t mix them up with the two other dosages already being used.
Two doses or three?
Here’s where this gets complicated. In December, Pfizer announced a setback: Preliminary study results showed two of the extra-low doses appeared strong enough to protect babies but weren’t strong enough for 2- to 4-year-olds. The company added a third shot to the study, but results are not expected until late March.
Still, the FDA took the highly unusual step of urging Pfizer to apply now for a two-dose series with potentially a third shot added later. During the FDA advisory committee meeting, the public will get its first look at any new evidence of whether two extra-low doses are working better than initially expected among the preschoolers.
If cleared, where would the shots be given?
While the government expanded pharmacists’ ability to vaccinate children during the pandemic, shots for the youngest children primarily are given in pediatricians’ offices.
What about kids younger than 6 months?
There are no plans to test shots in newborns.
Will the shots be in high demand?
Vaccinations have been lower among children than in other age groups, a pattern likely to continue with kids under 5. As of last week, just 20% of kids ages 5 to 11 and just over half of 12- to 17-year-olds were fully vaccinated, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics. Nearly three-quarters of adults are fully vaccinated. While COVID-19 tends to be less severe in children than adults, the omicron wave has caused record numbers of child hospitalizations.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
40 years after ‘Purple Rain,’ Prince’s band remembers how the movie came together
Before social media, the film Purple Rain gave audiences a peak into Prince’s musical life. Band members say the true genesis of the title song was much less combative than the version presented in the film.
Park Fire in California could continue growing exponentially, Cal Fire officer says
Cal Fire has confirmed that over a hundred structures have been damaged in the Park Fire, which grew overnight near Chico, Calif. Difficult firefighting conditions are forecast through Friday night.
Checking in with Black voters in Georgia about the election, now that Biden is out
Some voters who could be key to deciding who wins Georgia. What do they think about Vice President Harris becoming the frontrunner in the race to be the Democratic nominee?
Tahiti’s waves are a matter of ‘life and death’ for surfing Olympics
Tahiti's Teahupo'o wave has a slew of riders for the Paris 2024 Olympics. NPR finds out why it's called one of the most dangerous waves.
Researchers are revising botanical names to address troubling connotations
Since the mid-1700s, researchers have classified life with scientific names. But some of them have problematic histories and connotations. The botanical community is trying to tackle this issue.
A spectacular opening ceremony wowed a global audience despite Paris’ on-and-off rain
The Paris Olympics opening ceremony wowed Parisians, fans and most everyone who was able to catch a glimpse of thousands of athletes floating down the Seine to officially begin the Games.