Alabama could use nitrogen hypoxia for executions in death sentences. What is it?
The state approved the method in 2018, but it has not yet been used or tested. A man awaiting a Sep. 22 execution said he opted for nitrogen hypoxia instead of lethal injection due to a fear of needles, but corrections officers lost his paperwork.
Alabama is readying an untried method of execution to carry out its death sentences – nitrogen hypoxia.
The state approved the method in 2018, but it has not yet been used or tested.
The man awaiting a Sep. 22 execution, Alan Eugene Miller, was convicted of killing three men in a workplace shooting in 1999. He said he opted for nitrogen hypoxia instead of lethal injection due to a fear of needles, but corrections officers lost his paperwork.
While the Alabama attorney general’s office found no evidence of that, Miller could receive death by nitrogen hypoxia if a judge blocks the use of lethal injection.
What is nitrogen hypoxia?
Hypoxia is when there is not a sufficient amount of oxygen in the tissues for the body to perform its regular functions. It is different from hypoxemia, which occurs when there is low oxygen in the blood.
Nitrogen hypoxia is a form of inert gas asphyxiation. Nitrogen is safe to breathe – it makes up 78% of what we inhale – but only when mixed with suitable amounts of oxygen.
Inert gas asphyxiation uses gasses that are not typically poisonous, such as nitrogen, methane or helium, as a diluting agent for atmospheric gasses. This then reduces oxygen concentration to fatally low amounts, according to the U.S. Chemical Safety and Hazard Investigation Board.
Once oxygen levels fall below 16%, breathing becomes difficult. At 4% to 6%, a person can enter a coma in as little as 40 seconds.
There are concerns about the method
Oklahoma and Mississippi are the two other states that have authorized the method. Russell Bucklew, a man incarcerated in Missouri tried to get approved for nitrogen hypoxia, but was denied in a lawsuit that went to the U.S. Supreme Court.
Bucklew was initially scheduled for execution in 2014, but sued the director of the Missouri Department of Corrections asking for the use of nitrogen hypoxia instead of lethal injection due to a medical condition he had.
In the opinion of the Court, Justice Neil Gorsuch denied the request, saying that nitrogen hypoxia had been untested and Missouri could not properly prepare it.
Bucklew’s proposal should have included how the nitrogen gas should be administered, in what amounts, how long it would take to work and how to keep the execution team safe, he said.
The Court also ruled there was no evidence to support Bucklew’s claim that hypoxia would be less painful. He was executed in 2019 by lethal injection.
Copyright 2022 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.9(MDA2ODEyMDA3MDEyOTUxNTAzNTI4NWJlNw004))
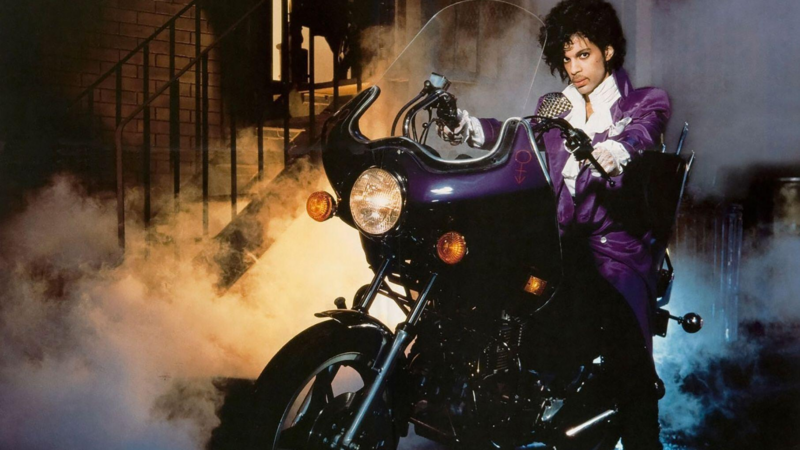
40 years after ‘Purple Rain,’ Prince’s band remembers how the movie came together
Before social media, the film Purple Rain gave audiences a peak into Prince’s musical life. Band members say the true genesis of the title song was much less combative than the version presented in the film.
Park Fire in California could continue growing exponentially, Cal Fire officer says
Cal Fire has confirmed that over a hundred structures have been damaged in the Park Fire, which grew overnight near Chico, Calif. Difficult firefighting conditions are forecast through Friday night.
Checking in with Black voters in Georgia about the election, now that Biden is out
Some voters who could be key to deciding who wins Georgia. What do they think about Vice President Harris becoming the frontrunner in the race to be the Democratic nominee?
Tahiti’s waves are a matter of ‘life and death’ for surfing Olympics
Tahiti's Teahupo'o wave has a slew of riders for the Paris 2024 Olympics. NPR finds out why it's called one of the most dangerous waves.
Researchers are revising botanical names to address troubling connotations
Since the mid-1700s, researchers have classified life with scientific names. But some of them have problematic histories and connotations. The botanical community is trying to tackle this issue.
A spectacular opening ceremony wowed a global audience despite Paris’ on-and-off rain
The Paris Olympics opening ceremony wowed Parisians, fans and most everyone who was able to catch a glimpse of thousands of athletes floating down the Seine to officially begin the Games.