UAB Researchers Create Culturally-Based Protocol For Palliative Care
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have created the first culturally based protocol for patients facing end-of-life care. Ronit Elk is a professor in the Division of Gerontology, Geriatrics and Palliative Care at UAB. She has spent her life living in different countries. Once she moved to the U.S., Elk said she noticed the lack of respect for cultural differences for the nation’s sickest minority patients, particularly African Americans.
What was the most notable cultural difference?
For Black patients and their families going through end-of-life care, the concept of hope and miracles is key. Physicians are primarily trained as scientists to read the physical symptoms that are occurring. Black patients and families who believe that there is always hope and it’s in God’s hands, they understand yes, you’re the physician, but you are not the decider. It is God that decides whether my loved one is going to live or die. And it’s caused a lot of clashes with physicians and family members where physicians are often saying to patients’ families, you’re not really accepting that the person is going to die. There’s no way they can live. And the family is saying it’s in God’s hands and a miracle can happen. And somehow that’s a very difficult thing for many physicians to accept.
What are the consequences of treating everyone the same way in palliative care?
Here’s the interesting thing, palliative care physicians and clinicians are probably the most compassionate human beings on this planet. They are taught that you go in and you do exactly what the patient wants. However, what isn’t taught in America is that different people’s culture impacts that. Whenever somebody has a loved one who is very ill, whenever somebody is dying, it is always viewed through their own cultural lens. And that part has never been taught. And so there’s a simple lack of understanding.
Why were minority patients over-looked in models of end-of-life-care?
The model that was developed was based on the white middle-class model. This model is very wonderful if you’re white, middle class and Christian. It is most inappropriate in many cases if you’re not white or you’re not middle class or if you’re not Christian. So why it’s so difficult to understand that different cultures may look at death, life, illness differently; I have no idea. I think maybe in America we’re not taught enough to understand different cultures. But we’re doing a lot of studies with people from other countries, three in Africa and some in other countries, because over there, people know “if a model is for white middle class people, that’s not going to work for my people. I want to see what’s really going to work for our community.”
How do you get hospitals on board with this new protocol?
So the first thing we have to do is to prove that it’s very effective. What we’ve shown is that it’s feasible and it can be done. So we are simultaneously developing trainings so that we can train the physicians who won’t push against it, but will rather embrace it and it will be accepted in hospitals.
Editor’s Note: UAB holds WBHM’s broadcast license, but our news and business departments operate independently.
This interview has been condensed and edited for clarity.
Alabama prison chief responds to families’ criticism
The department said that a number of changes have been made since Corrections Commissioner John Q. Hamm was appointed in 2022. The department said hiring has increased, and there are ongoing efforts to curb the flow of contraband and improve communications with families.
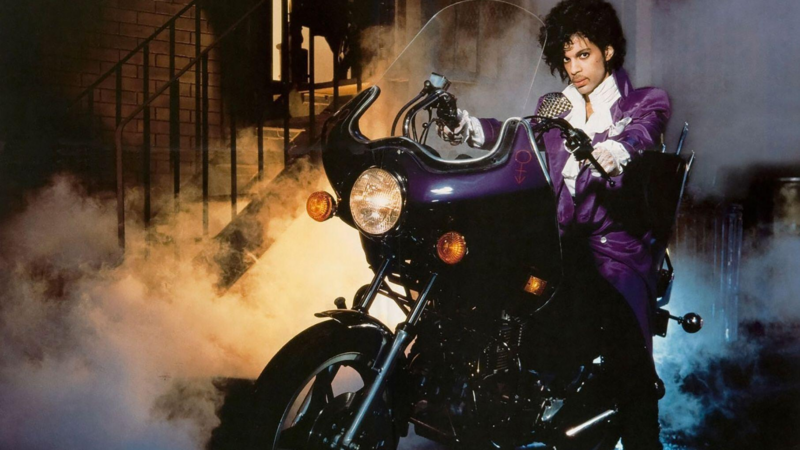
40 years after ‘Purple Rain,’ Prince’s band remembers how the movie came together
Before social media, the film Purple Rain gave audiences a peak into Prince’s musical life. Band members say the true genesis of the title song was much less combative than the version presented in the film.
Park Fire in California could continue growing exponentially, Cal Fire officer says
Cal Fire has confirmed that over a hundred structures have been damaged in the Park Fire, which grew overnight near Chico, Calif. Difficult firefighting conditions are forecast through Friday night.
Checking in with Black voters in Georgia about the election, now that Biden is out
Some voters who could be key to deciding who wins Georgia. What do they think about Vice President Harris becoming the frontrunner in the race to be the Democratic nominee?
Tahiti’s waves are a matter of ‘life and death’ for surfing Olympics
Tahiti's Teahupo'o wave has a slew of riders for the Paris 2024 Olympics. NPR finds out why it's called one of the most dangerous waves.
Researchers are revising botanical names to address troubling connotations
Since the mid-1700s, researchers have classified life with scientific names. But some of them have problematic histories and connotations. The botanical community is trying to tackle this issue.