Biden to visit Selma for voting rights anniversary
Vice President Joe Biden and U.S. Rep. John Lewis, D-Ga., lead a group across the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma, Ala., Sunday, March 3, 2013.
MONTGOMERY, Ala. (AP) — President Joe Biden will travel to Alabama on Sunday to mark the 58th anniversary of a landmark event of the civil rights movement.
Biden will speak in Selma for the annual remembrance of “Bloody Sunday,” the day in 1965 that white police beat Black civil rights marchers as they attempted to cross the city’s Edmund Pettus Bridge. The White House announced the visit on Tuesday.
The visit comes as the city that served as a crucible of the civil rights movement is fighting to recover from a January tornado. The EF-2 twister, with winds of 130 mph, cut a wide swath and ripped through the city, destroying and severely damaging hundreds of homes.
Biden has twice visited Selma for the annual voting rights commemoration. Three years ago during the 2020 election he spoke at the city’s historic Brown Chapel AME Church hours after strong support from Black voters in South Carolina lifted Biden to his first primary victory. He also visited the city as vice president in 2013. In both stops, Biden warned of erosions to the protections for voting rights won in the city decades ago.
President Barack Obama in 2015 spoke in Selma to mark the 50th anniversary of the 1965 marches.
On March 7, 1965, Alabama state troopers beat and tear-gassed voting-rights demonstrators — including a young John Lewis — as they tried to cross the bridge over the Alabama River. Weeks later, the Rev. Martin Luther King successfully led marchers on the 50-mile march to the state capital of Montgomery.
The marches, and photos of the violent beatings on Bloody Sunday, galvanized Congress to pass the Voting Rights Act of 1965 that struck down impediments to voting by African-Americans and ended all-white rule in the American South.
The annual commemoration has become a regular stop for politicians to pay homage to the fight for voting rights in America and to court Black voters in election years.
Rep. Terri Sewell, the only Democrat in Alabama’s congressional delegation, urged Biden, when she greeted him following his State of the Union address, to visit Selma to see the tornado damage in the city.
“What I asked him was to come to Selma, to see first-hand and to help Selma,” Sewell said earlier this month.
French Champagne-makers wonder: Is it time to move on from the U.S. market?
Amid uncertainty around President Trump's tariffs, some Champagne makers say they're losing trust in the U.S. market.
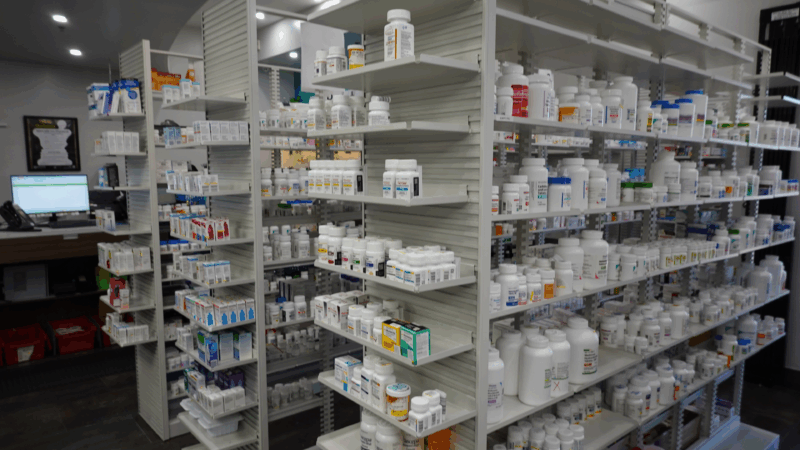
Pharmacists stockpile most common drugs on chance of targeted Trump tariffs
While Big Pharma seems ready to weather the tariff storm, independent pharmacists and makers of generic drugs — which account for 90% of U.S. prescriptions — see trouble ahead for patients.
Why aren’t Americans filling the manufacturing jobs we already have?
Leaders from both political parties have been working to bring back manufacturing. But American manufacturers say they are struggling to fill the manufacturing jobs we already have.
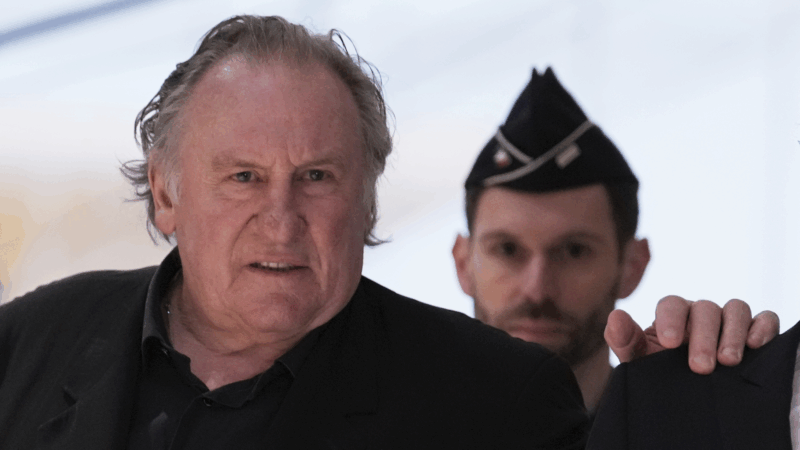
Gérard Depardieu found guilty of sexual assault in landmark French trial
A French court on Tuesday found Gérard Depardieu guilty of sexually assaulting two women on a film set, sentencing the French film icon to an 18-month suspended prison term.
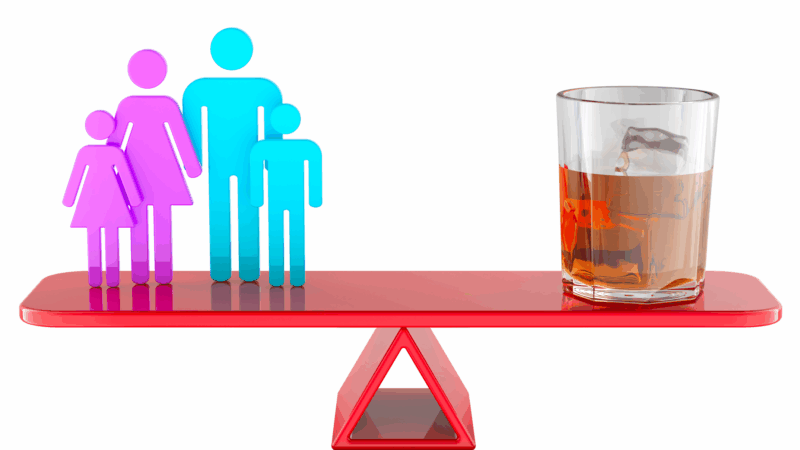
A quarter of children have a parent with substance use disorder, a study finds
A new study estimates that 19 million children in the U.S. have a parent with a substance use disorder and that alcohol is the most commonly used substance by the parents.
This country is slowing climate action. Its capital city is stepping up
As many federal governments slow — or reverse — climate action, Austria's capital, Vienna, wants to show how cities can take the lead.