Gulf South health care systems are failing to equally serve people of color, study says
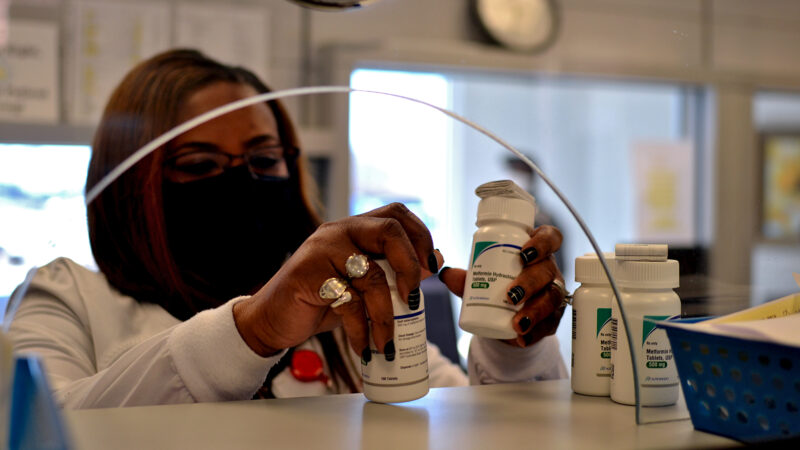
A pharmacist at The Delta Health Center in Mound Bayou, Mississippi talks with a patient about medicine, June 3, 2021.
Health care systems across the United States are failing to equitably serve people of color. But, according to a new analysis, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Alabama are among the states with the worst health outcomes for people of color — Black and Latinx residents, in particular.
The report, which is a state-by-state scoreboard of racial and ethnic disparities in health care, comes from research and grant foundation Commonwealth Fund. Researchers considered indicators like health outcomes, health care access and quality of health care services to come up with a score for each state.
The report also looked at how health systems are serving five different racial and ethnic groups in a majority of states across the country: Black, White, American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian American and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and Hispanic/Latinx.
Researchers found that even in states that have better performing health systems, racial and ethnic disparities persist in terms of health outcomes and access.
Mississippi, Alabama and Louisiana, however, are seeing worse health outcomes and access in all residents than in other states, with Latinx and Black residents facing even more barriers within those states to quality health care. As a result, these states are also seeing larger gaps in health care outcomes and access across racial groups than most other states.
“The [health care] experience of Black individuals in those three states is worse than the experiences of Black people in other states. For example, worse than in New York, Washington, and Virginia,” said David Radley, a co-author of the report. “Even within the state of Louisiana, which is a [Medicaid] expansion state we still see big inequities in the health care experience of Black individuals and of Latinx individuals relative to the experience of white individuals.”
Researchers found that across the region, Black people and American Indian/Alaska Natives are more likely than white people in most other states to die early in life from conditions that would have been treatable if they had access to high-quality health care. Black women are also more likely than white women to be diagnosed with cancer at later stages and to die as a result of that.

Shalina Chatlani,Gulf States Newsroom
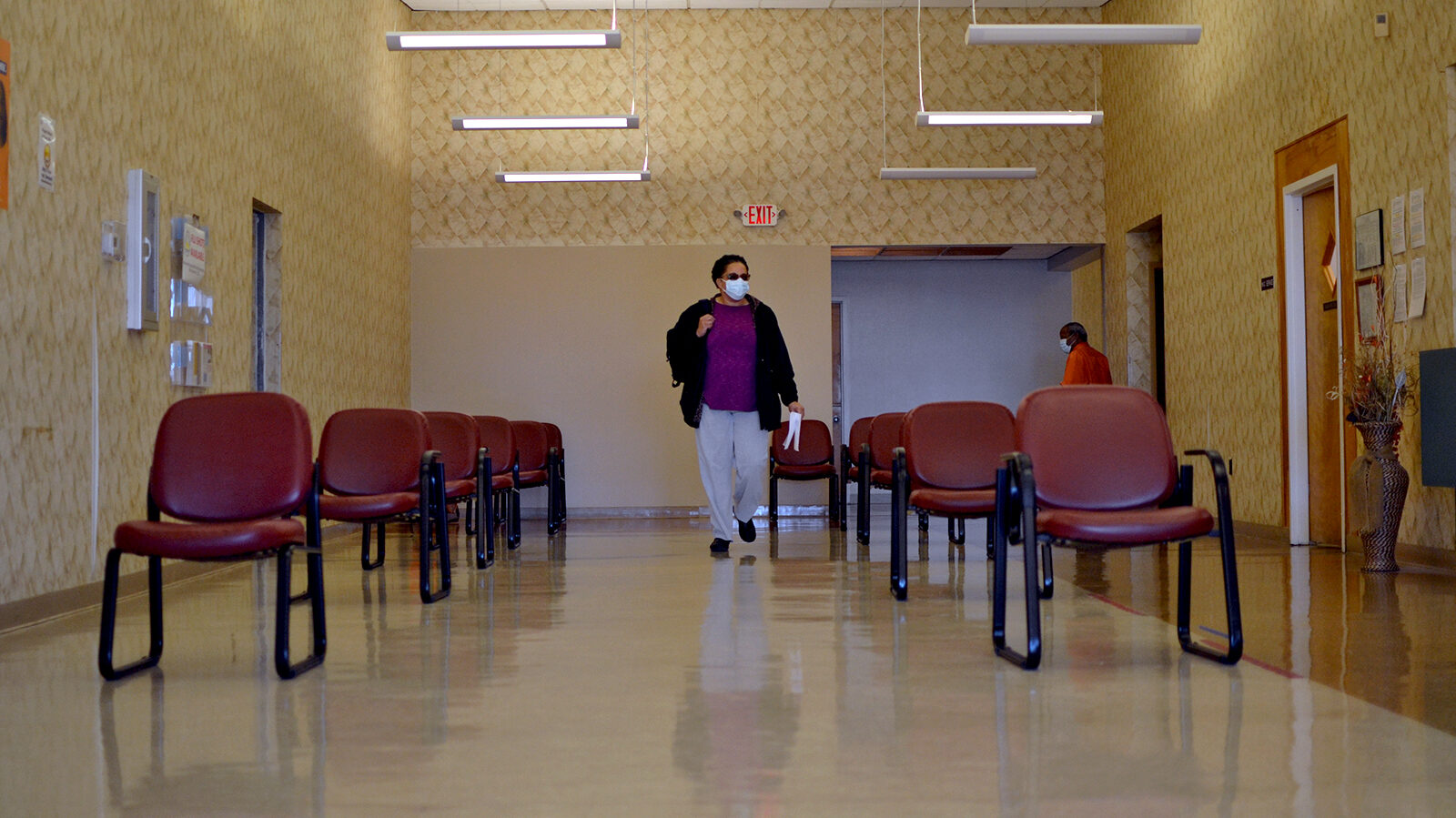
A woman walks through the dental clinic at The Delta Health Center in Mound Bayou, Mississippi, June 3, 2021.
While some of these inequities can be tied to factors like low income and political challenges, such as a failure to expand Medicaid, experts say that lack of social services and racial biases are also to blame.
“People of color are less likely to receive preventative health services irrespective of income, neighborhood, illness or insurance type, and often more likely to receive lower-quality care,” said Laurie Zephyrin, a co-author of the report.
The study authors say state leaders can help reduce inequities by encouraging affordable and comprehensive health insurance options to be available, strengthening primary care options, lowering administrative burdens for patients and investing in social services.
Editor’s note: The Commonwealth Fund supports health equity coverage, but the Gulf States Newsroom operates independently from it.
This story was produced by the Gulf States Newsroom, a collaboration between Mississippi Public Broadcasting, WBHM in Birmingham, Alabama, WWNO in New Orleans and NPR.
U.S. measles cases hit highest level in 33 years, CDC reports
The U.S. has hit an unwelcome milestone in measles cases this year. The CDC is reporting 1,288 cases across the country. The disease was declared eliminated 25 years ago.
10 songs that were hyperpop before the subgenre was born
To commemorate 10 years of SOPHIE's debut, World Cafe put together a mix of "proto-hyperpop" tracks.
What’s on the table for the 5 African Presidents meeting Trump at the White House?
President Trump is hosting 5 African leaders in Washington this week — a mini summit that's raising eyebrows over who was invited, what's on the table, and what it signals about U.S. rivalry with China and BRICS in Africa.
Sean Combs’ sentencing date is set
Last week, a federal jury in Manhattan found Combs guilty of two counts of transportation for prostitution while acquitting him on more serious charges of sex trafficking and racketeering conspiracy.
A battle is unfolding in Europe over the future of wolves
Europe recently downgraded the protected status of wolves, sparking concern among conservationists who warn this may undo decades of progress and lead to the species becoming threatened again.
Greetings from Damascus, Syria, where a crowded bar welcomed post-Assad revelers
Far-Flung Postcards is a weekly series in which NPR's international team shares moments from their lives and work around the world.