Alabama wants to speed up medical marijuana growing. Will it be helpful or cause more problems?
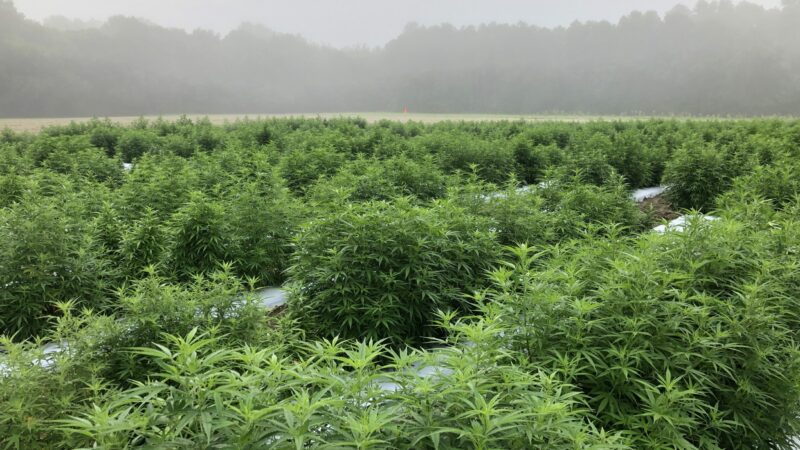
Charlie Decelle is a hemp farmer in Etowah County. He started Dry Creek Hemp three years ago and is planning on applying for a medical marijuana license. Most of his hemp is grown outside, but if he receives a license to grow marijuana, he would grow it in his greenhouse.
“With marijuana they usually want you to grow it in a clean environment and [the greenhouse] is not clean so they would frown upon the state of this greenhouse,” he said. “We would have a lot of upgrades to do.”
With medical marijuana now legal in Alabama, some farmers are eager to get plants in the ground, but licenses to grow marijuana won’t be available until September 2022. That means it wouldn’t be available to patients until 2023. The Alabama Medical Cannabis Commission wants to move up licensing so farmers can plant seeds earlier.
Hemp and marijuana are two types of the same plant—cannabis—but marijuana has a higher concentration of THC, the chemical that causes the feeling of being high. Farmers in Alabama have to make sure their hemp maintains less than a 0.3% concentration of THC by sending samples to the Alabama Department of Agriculture and Industries for testing.
Since they are similar plants, farmers who will be growing marijuana will probably be the ones who are currently growing hemp. There will be a $2500 non-refundable application fee for the licenses. Only 12 will be issued statewide and there will be stricter regulations than there are for hemp, so the licenses will likely go to farmers who are experienced with cannabis like Decelle.
“We’re excited, but we’re not getting too excited. We’re keeping our eyes on the road in front of us and just focusing on hemp at the moment,” he said. “But we are ready. I mean, we could throw these hemp plants out and swap them out in a heartbeat.”
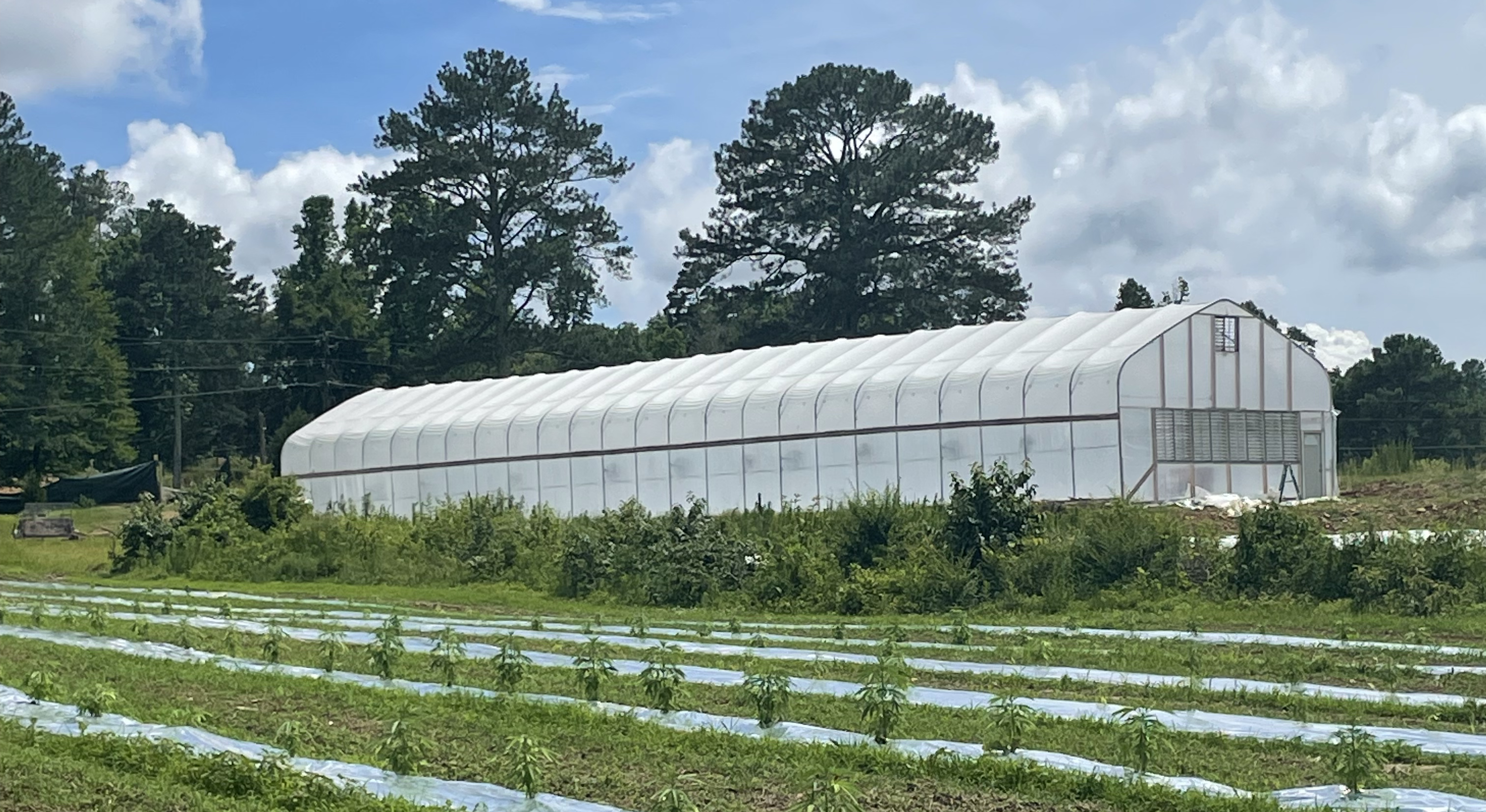

Dry Creek Hemp
Dry Creek Hemp grows most of its hemp outside and some in a greenhouse. Medical marijuana would have to be grown inside.
There are benefits to issuing licenses earlier.
“The earlier we start, the more we can figure out best management practices to have a successful crop,” said Katelyn Kesheimer, a researcher at Auburn University and the Alabama Cooperative Extension System.
Because Alabama legalized medical marijuana much later than other states, farmers have missed out on learning the best practices for the state’s climate.
“It’s hot, it’s humid. We got a long growing season, so things do thrive, but we need to find that right mix of genetics,” said Kesheimer. “Currently a lot of the cannabis genetics are coming out of Canada or the Pacific Northwest or overseas, and we need to test them here in Alabama again.”
The state will probably require that medical marijuana is grown in a greenhouse to keep it clean for medical use. This will also help keep away insects and pathogens, which is important because the growers will likely not be allowed to use pesticides. Keeping it inside also allows farmers to lock it down to keep it from being stolen. In fact, both Decelle and Kesheimer already have problems with people stealing their hemp.
“They’ll try to smoke it, but it doesn’t have enough THC, so they’re not going to get that psychoactive feeling they’re looking for,” said Kesheimer.
Kesheimer is also eager to get her hands on a license earlier and start growing medical marijuana for research, so she can answer questions from farmers and help them put out their best crop.
“As a scientist, I just want to make sure that we’re utilizing the best science and research-based information, especially since these plants will be ingested by people who have ailments that can benefit from marijuana,” she said.
Another hemp farmer in Anniston, Jon Hegeman, is not worried about challenges with growing. He owns Greenway Plants, where he grows hemp and is also planning on growing medical marijuana if he is able to get a license. His greenhouse is completely controlled and automated.
“We have computer models, and the computer is always sensing what the plants need. If the sun comes out the shades might close,” he said. “It’s always checking the environmental controls.”

Eva Tesfaye,WBHM
Jon Hegeman grows his hemp among other plants in a controlled greenhouse.
Not only does he feel that trying to issue licenses sooner is unnecessary, Hegeman believes it could cause more problems than it’s worth.
“Speeding up the timeline is not going to get us anywhere but create a disaster,” he said. “Let’s do it right the first time.”
He worries that the medical marijuana law could be renegotiated and is particularly concerned that the section that only allows Alabama residents to grow the plant could change. Currently, cultivators are required to have lived in Alabama for at least 15 years continuously.
“I hope that’s not going to happen,” said Dr. Steve Stokes, an oncologist and the chairman of the Alabama Medical Cannabis Commission. “I want this to benefit the farmers of Alabama and the patients of Alabama.
Stokes prescribes medical marijuana to some of his cancer patients in Florida. He does want the licenses out faster. And even though that would require a change to the law, he’s optimistic the commission can speed up the timeline without affecting other parts of the measure.
“They just didn’t think that the commission, our commission would move as fast as we’ve moved. We’ve gotten organized. We’ve selected a director,” he said.
Proponents of quicker licensing hoped it could be brought up during a special session on prisons but it was not. Another special session on redistricting is expected before the end of the year. Otherwise it’ll be next year before any changes to the medical marijuana law could be made.
Frederick Wiseman, who captured the weirdness and wonder of everyday life, dies at 96
The prolific, pioneering filmmaker made dozens of documentaries and chronicled the inner workings of institutions. His 1967 film, Titicut Follies, revealed appalling conditions at a prison facility.
Two U.S. moms in their 40s rocketed to gold and bronze in Olympic bobsled showdown
American sliders Elana Meyers Taylor, 41, and Kaillie Humphreys, 40, secure gold and bronze medals. Meyers-Taylor built on her record as the Black athlete with the most Winter Olympics medals.
The U.S. women’s hockey team is dominating the Olympics. Now they will play for gold
The Americans, whose captain Hilary Knight is leading a generation of thrilling young talent, are undefeated through six games at the Olympics — and they're outscoring their opponents 31 to 1.
A Curling Scandal Rocks Olympic Ice
Allegations of cheating, and swearing, on the curling ice have rocked the wholesome sport after the Swedes accused the Canadians of "double touching" in a match on Friday. What happened then, and what's happened since?
The U.S. ready to make up, Europe ready to break up in Munich
Secretary of State Marco Rubio tried to reassure Europe at the Munich Security Conference, but European leaders are skeptical.
Actor Robert Duvall has died — he brought a compassionate center to edgy hard roles
Duvall appeared in over 90 films over the course of his career, imbuing stock Hollywood types — cowboys, cops, soldiers — with a nuanced sense of vulnerability.