UAB Using Whole Blood to Improve Trauma Care
When someone is experiencing severe blood loss, that blood needs to be replaced as soon as possible. Most doctors deliver this transfusion as a “balanced resuscitation,” combining equal amounts of red blood cells, plasma and platelets, which is how blood is separated and delivered to most U.S. hospitals. But a balanced resuscitation is not the same thing as using whole blood that has never been separated, according to Dr. Marisa Marques, medical director of transfusion services at UAB Hospital.
“You’re not able to reconstitute whole blood just mixing the other components,” Marques says, “because each one of them is somewhat diluted with anticoagulant and other substances.”
Most of the research on whole blood transfusions comes from the military and treating injured soldiers in war zones. It suggests that transfusing actual whole blood to care for hemorrhaging patients can lead to better outcomes. Patients may require less blood to be transfused, and they often recover faster. UAB trauma surgeon Dr. Daniel Cox says another advantage of using whole blood, rather than separated components, is that it saves time.
“For the very seriously injured patient, this has the potential to significantly improve the chances of that person surviving,” says Cox.
UAB Hospital recently joined a growing number of hospitals across the country that use whole blood to treat severe trauma patients. Dr. Marques says finding a supply was not easy. It is not available from the local American Red Cross (ARC), where UAB gets most of its blood products. The hospital ended up having to get it from an ARC blood bank in Oklahoma.
Marques says whole blood has to meet strict requirements. To ensure that the product can be used for most patients, she says donors have to be male with low-antigen, type O blood. And timing is key, as whole blood has a shelf life of about three weeks, which is about half that of packed red blood cells.
UAB receives 12 units every week, which is less than 5% of the hospital’s total blood supply. UAB trauma doctors say that since they started receiving the whole blood in August they have used just about every drop.
U.S. has a quarter fewer immigration judges than it did a year ago. Here’s why
The continued drain of personnel from the already strained immigration court system has contributed to depleted staff morale, mounting case backlogs — and floundering due process.
Poll: Most say the state of the union is not strong and the U.S. is worse off
Ahead of the State of the Union address on Tuesday, evidence continues to mount that President Trump is facing political headwinds.
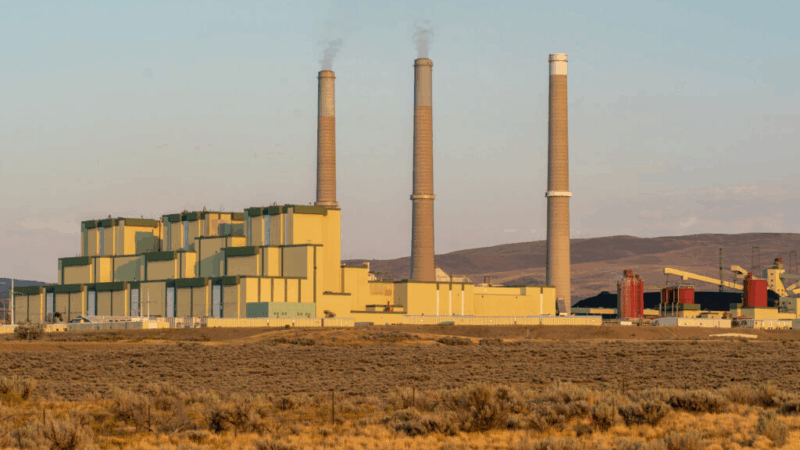
The owners want to close this Colorado coal plant. The Trump administration says no
The Trump administration has ordered several coal plants to keep operating past their planned retirement, part of a larger effort to boost the coal industry. Two Colorado utilities are pushing back.
Influencers are promoting peptides for better health. What’s the science say?
The latest wellness craze involves injecting these molecules for athletic performance, longevity and more. Scientists say the research isn't keeping pace with the health claims.
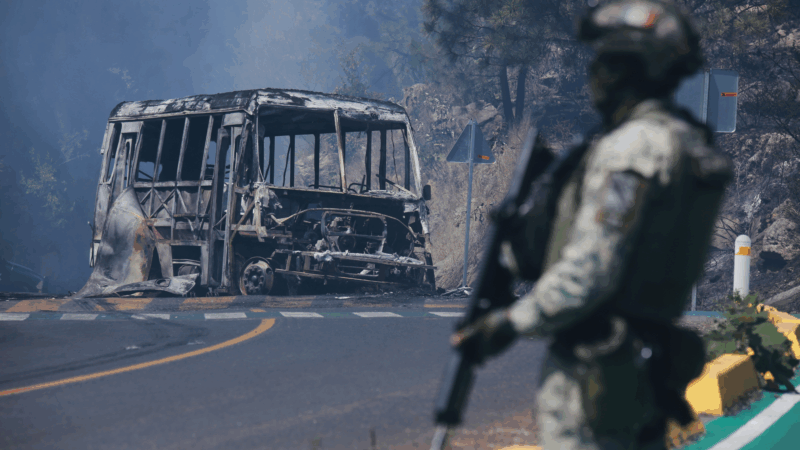
Mexico fears more violence after army kills leader of powerful Jalisco cartel
School was canceled in several Mexican states and local and foreign governments alike warned their citizens to stay inside following the army's killing of the leader of the Jalisco New Generation Cartel, Nemesio Rubén Oseguera Cervantes, "El Mencho," and the violence it spurred
Newly discovered dinosaur species was a fish-eater with a huge horn
The semi-aquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus mirabilis, was discovered by an international team of scientists working in Niger.