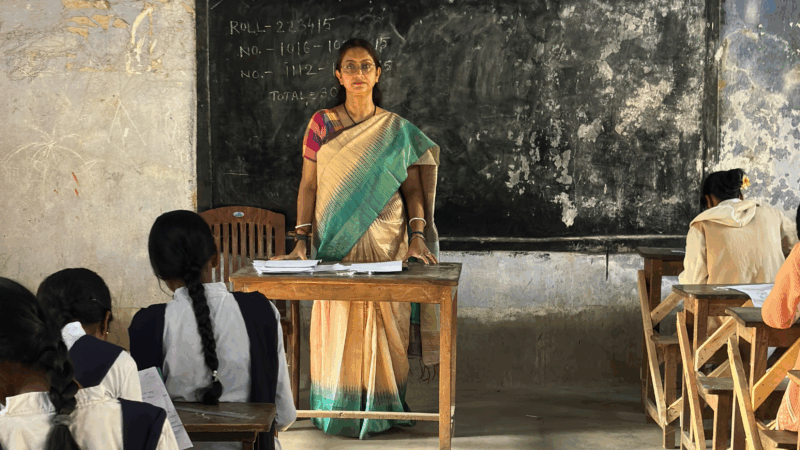Tuskegee Researchers Find Key to Earlier Breast Cancer Diagnosis
A team of researchers at Tuskegee University has developed a new test they say may help detect an aggressive form of breast cancer earlier, especially among African American women.
The breakthrough was published this week in the scientific journal PLOS One. Clayton Yates, a biology professor at Tuskegee University, along with other researchers discovered a new biomarker that can detect a specific type of breast cancer sooner. The discovery will help target cancer treatments toward African American women, who are more likely to be diagnosed later in life.
In African American women, the median age of diagnosis is typically around 55, Yates says. The addition of this biomarker lowered that to around age 49.
Yates says that earlier detection should improve survival rates. Studies show African American women are more likely to die from breast cancer after the initial diagnosis. The additional biomarker will look for specific testosterone receptors and help doctors determine the aggressiveness of the cancer. Yates hopes this discovery will highlight the role ethnicity and genetics play in health disparities among African American women.
-Alexander Richey
Mideast clashes breach Olympic truce as athletes gather for Winter Paralympic Games
Fighting intensified in the Middle East during the Olympic truce, in effect through March 15. Flights are being disrupted as athletes and families converge on Italy for the Winter Paralympics.
A U.S. scholarship thrills a teacher in India. Then came the soul-crushing questions
She was thrilled to become the first teacher from a government-sponsored school in India to get a Fulbright exchange award to learn from U.S. schools. People asked two questions that clouded her joy.
Sunday Puzzle: Sandwiched
NPR's Ayesha Rascoe plays the puzzle with WXXI listener Jonathan Black and Weekend Edition Puzzlemaster Will Shortz.
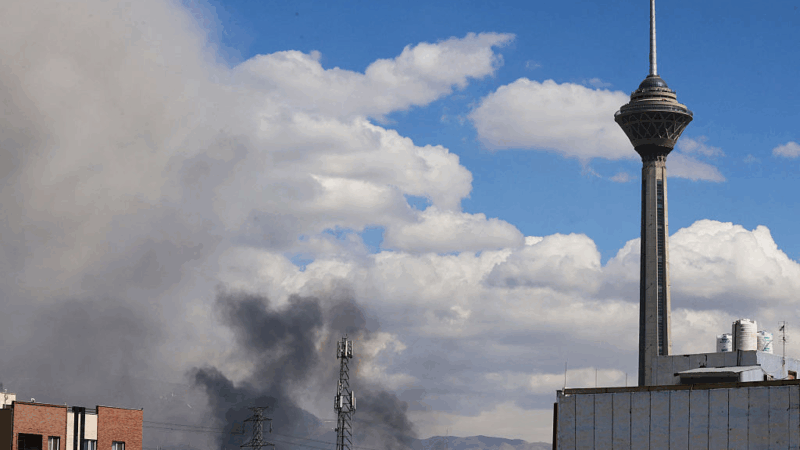
U.S.-Israeli strikes in Iran continue into 2nd day, as the region faces turmoil
Israel said on Sunday it had launched more attacks on Iran, while the Iranian government continued strikes on Israel and on U.S. targets in Gulf states, Iraq and Jordan.
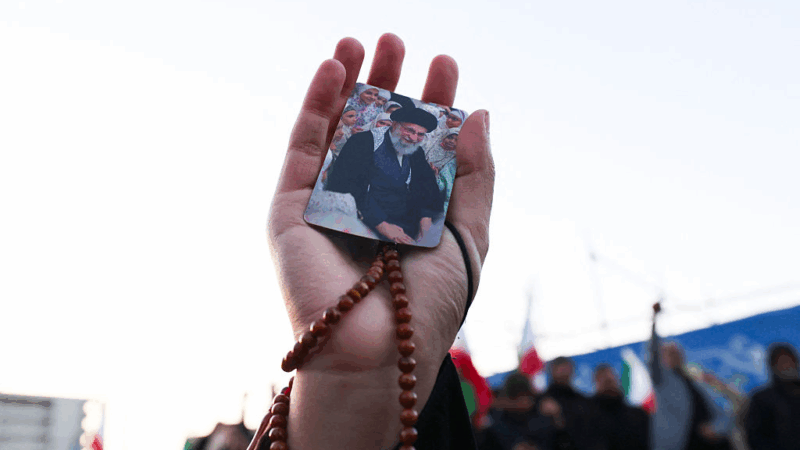
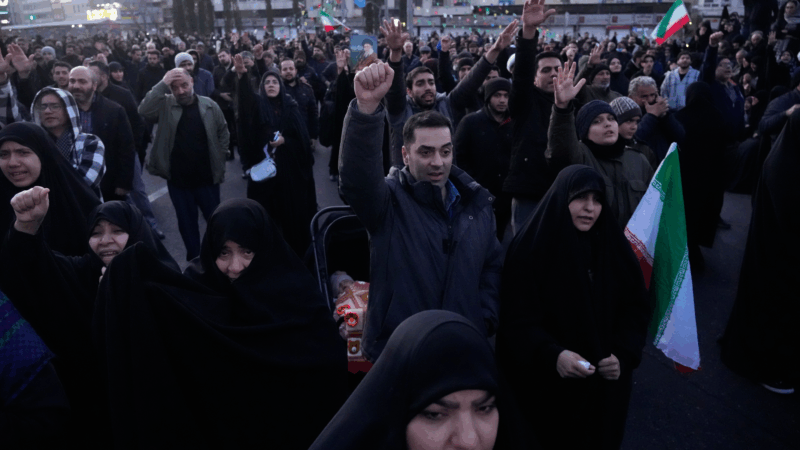
Trump warns Iran not to retaliate after Ayatollah Ali Khamenei is killed
The Iranian government has announced 40 days of mourning. The country's supreme leader was killed following an attack launched by the U.S. and Israel on Saturday against Iran.
Iran fires missiles at Israel and Gulf states after U.S.-Israeli strike kills Khamenei
Iran fired missiles at targets in Israel and Gulf Arab states Sunday after vowing massive retaliation for the killing of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei by the United States and Israel.