UAB Research Finds Security Risks with Computer Created Voices
What if someone could take a recording of your voice and use it to create a digital version? In other words, he or she could use a computer to make it sound like you’re saying anything. A few weeks ago, the Canadian startup Lyrebird released a computer-generated conversation between some familiar voices.
It’s not the most natural-sounding, but you can probably tell the voices mimic Presidents Donald Trump, Barack Obama, and former Secretary of State Hilary Clinton. The technology has applications beyond parlor tricks. It’s also raising security concerns. That’s because we use our voices to identify ourselves.
Digital assistants such as Apple’s Siri or Amazon’s Alexa are designed to recognize a specific voice. Otherwise anyone shouting “Hey, Siri” could unlock any phone. Beyond that, some banks are now using voice recognition software to allow customers to access financial information by phone. Your voice essentially becomes a password.
But perhaps it’s not a very good password if software can now mimic your voice. Think about how many voices could be collected from YouTube videos or surreptitiously recorded with a smart phone.
So a team with UAB’s SPIES research group, which looks at emerging security and privacy issues, tackled a key question: is this type of security vulnerable to impersonation?
The study looked at two things. First, would a computer recognize and thus reject the fake voice? Turns out, according to this study, the synthesized voice fooled the computer more than 80 percent of the time.
“It’s not secure at all,” says Maliheh Shirvanian, who was part of the research team.
The second part of the study tested humans. Could they tell the difference between a real and fake voice? Test subjects listened to clips of Morgan Freeman and one like this.
Or maybe this…
That’s a fake Oprah Winfrey followed by her real voice.
People got it right only about half the time. Better than the computer but still no better than chance.
When this study came out in 2015, it raised a lot of alarms within the tech community. But Dan Miller says that’s overblown. He’s lead analyst with the firm Opus Research and he follows voice technology. Miller explains there are good procedures and technology in place to prevent fraud. He says outside the lab, banks he’s worked with can reduce that false acceptance rate to less than 2 percent.
“There is always a view that you can defeat these things and indeed you can,” says Miller. “But the safeguards against them being defeated are developing as rapidly as the methods to defeat them.”
Miller says every type of password has vulnerabilities. That’s why security experts recommend multi-factor identification where you need more than just one type of password to access something.
UAB’s Maliheh Shirvanian says the study from 2015 tested speech algorithms. They expect to release a new study in the coming months that tests actual apps which use speech recognition. It’ll be a measure of how quickly the technology is advancing, both to fake voices and to fight the fakes.
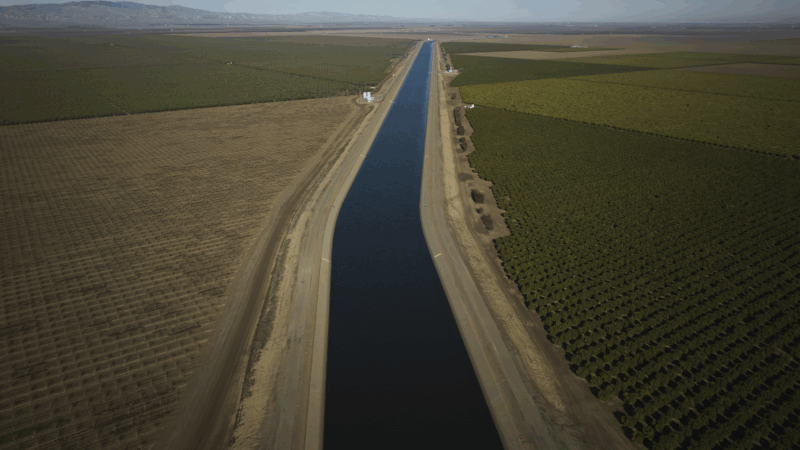
Why farmers in California are backing a giant solar farm
Many farmers have had to fallow land as a state law comes into effect limiting their access to water. There's now a push to develop some of that land… into solar farms.
Every business wants your review. What’s with the feedback frenzy?
Customers want to read reviews and businesses need reviews to attract customers. But the constant demand for reviews could be creating a feedback backlash, experts say.
Can’t get a prescription renewed? Here’s how to cope with prior authorizations
These health care hurdles can stand in the way of getting treatment your doctor says you need. Here's what to know about how to deal with them.
‘Get back to integrity’: Oklahoma’s Kevin Stitt on Republicans after Trump
NPR's Steve Inskeep asks Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt about his spat with President Trump, immigration and the future of the Republican Party.
Civil rights leaders say the racial progress Jesse Jackson fought for is under threat
Activists say racial progress won by the Rev. Jesse Jackson is under threat, as a new generation of leaders works to preserve hard-fought civil rights gains.
Tariffs cost American shoppers. They’re unlikely to get that money back
After the Supreme Court declared the emergency tariffs illegal, the refund process will be messy and will go to businesses first.