The Ripple Effect When a Giant Iceberg Breaks Away From Antarctica
This week, scientists watched an iceberg the size of Delaware break away from Antarctica’s Larsen C ice shelf. The mass of ice that broke off weighs about a trillion tons. It’ll eventually melt, but as UAB polar biologist and Antarctic explorer Jim McClintock tells WBHM’s Dan Carsen, there are some long-term concerns.
Here are some highlights and an extended interview.
What Happened
“The Larsen C ice shelf just shed a piece of itself that is the size of the state of Delaware. So this is a significant chunk of real estate. The ice sheet is about 1,200 feet thick on average. The piece that broke free is now one of the largest icebergs floating around that has ever been recorded.”
The Good News
“As it melts, it will not contribute to sea level rise because it’s already in the ocean, much as a glass of ice water, when the ice melts, the water doesn’t come over the top of the glass.”
Some of the Bad News
“Ice sheets, as they break up in Antarctica, are essentially barriers to the ice that sits on top of the continent — that two- to three-mile-thick layer of ice where about 70 percent of our freshwater resides on the planet. That ice is flowing towards the ocean from land into the water, and that flow has accelerated in areas where ice sheets have broken out. That is the ice that contributes to sea level rise.”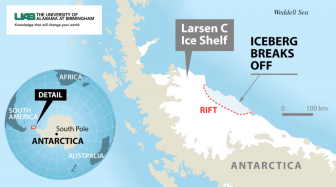
Why it Matters
“We study chemicals produced by sponges and corals that live in Antarctica. And these chemicals are interesting because they defend sponges and corals from predators and things that want to grow on them. They have ecological importance but they also have the potential to fight human disease. And so here in the last 25 years, we’ve come across a compound in an Antarctic tunicate that’s active against melanoma skin cancer … And these changes that are happening — the warming water, the increase in icebergs that are scouring the sea floor because of the ice that is breaking up, all these things are threatening that seafloor community and have an impact on the availability of these potential compounds that fight cancer and different types of human disease.”
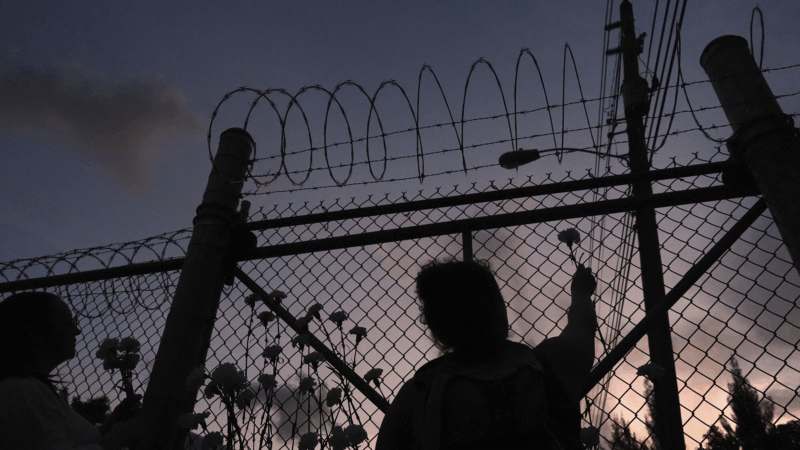
Immigration detention on track for deadliest fiscal year since 2004
Twenty-three people have died since October in ICE custody, as advocates warn about overcrowding and health care access.
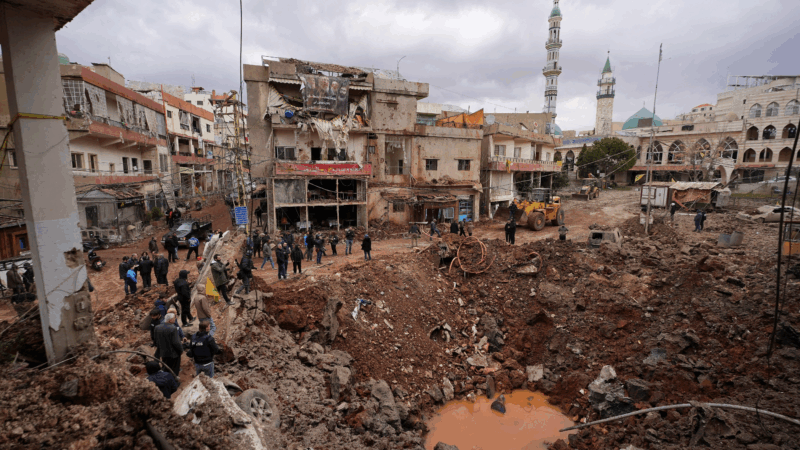
Photos from Iran and across the Middle East as the war enters Week 2
More than a week of the U.S. and Israel's war against Iran has dragged in global powers, upended the world's energy and transport sectors, and brought chaos to usually peaceful areas of the region.
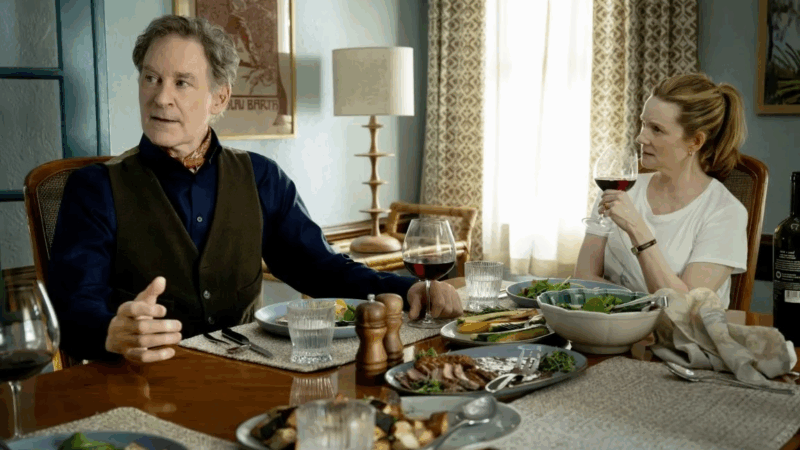
‘American Classic’ is a hidden gem that gets even better as it goes
In this charming TV series, Kevin Kline plays a Shakespearean actor who retreats to his small hometown after a crisis, and gets engaged in an effort to save the local theater.
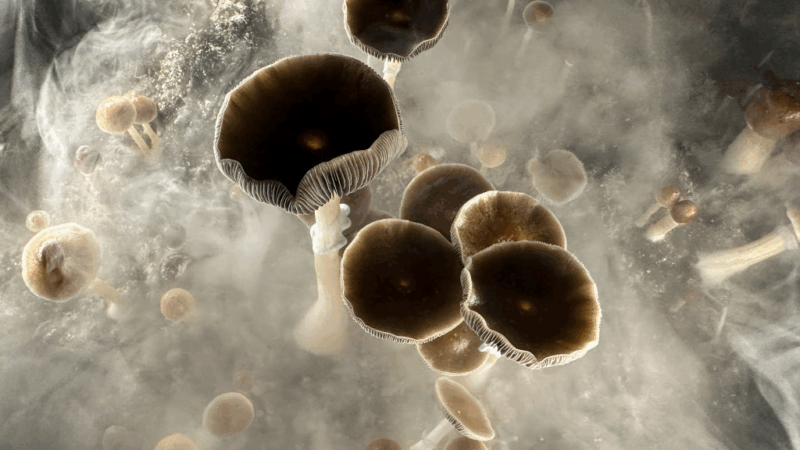
A dose of psilocybin helps smokers quit in new study
The psychoactive substance in magic mushrooms appears to have a powerful effect on people trying to stop smoking.
‘Pro-worker AI,’ streaming fatalities, and other fascinating new economic studies
From artificial intelligence to fatalities from music streaming to the effects of immigrants on elderly health care, the Planet Money newsletter rounds up some interesting new economic studies.
GLP-1s have transformed weight loss and diabetes. Is addiction next?
A large study found that people taking GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic for diabetes were less likely to be diagnosed with substance use disorder.






