Reporter’s notebook: 8 theories why fentanyl deaths are plummeting
Over the past six months, I’ve been tracking something really cool and mysterious happening on American streets. For the first time in 30 years, drug deaths are plunging at a rate that addiction experts say is hopeful — but also baffling.
In the past, even the most ambitious, well-funded efforts to slow drug deaths only helped a little bit. Reducing fatal overdoses by 8% or 9% was seen as a huge win.
But now, deaths nationwide plunged more than 26% from the peak in June 2023, according to the latest preliminary data gathered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That means roughly 30,000 fewer people a year are dying. Many states are seeing even bigger improvements of 30% to 50%. In some states, progress has been sustained since 2021 and 2022, which suggests this isn’t a temporary blip.
So how did the U.S. finally turn the corner on drug deaths?
What’s going on? No one knows for sure, but here are eight leading theories I hear from experts.
1. Naloxone, also known as Narcan, may be the game-changer. The Biden administration raced to make this medication, a nasal spray that quickly reverses opioid and fentanyl overdoses, far more widely available. People can buy it now over the counter without a prescription. It’s distributed for free in many high-risk communities, and people using drugs often carry it. It’s unclear how many lives naloxone is saving each year, but many front-line public health workers tell me the impact is huge. Learn more here.

2. Weaker fentanyl. Street fentanyl is incredibly potent. But in many parts of the U.S., organizations that test fentanyl doses sold by drug dealers — often in pill form — have found a significant drop in purity. No one’s sure why drug cartels have changed their mixtures. Some researchers believe law enforcement pressure in China, Mexico and the U.S. is disrupting the black market fentanyl supply chain. Learn more here.
3. A dangerous but less lethal street drug supply. In most of the the U.S., gangs are selling complicated “cocktails” of street drugs. The amount of fentanyl appears to be dropping (see above), while the amount of animal tranquilizers, such as medetomidine and xylazine, is rising. These chemicals are highly toxic. They cause skin wounds, severe withdrawal symptoms and other long-term health problems. But doctors and addiction experts generally agree they aren’t as immediately lethal as fentanyl. That could mean more chronic illness but fewer fatal overdoses. Learn more here.

4. Better public health. Thirty years after the U.S. opioid crisis began — and a decade after fentanyl spread nationwide — the U.S. has made strides developing better and more affordable services for people experiencing addiction. Medications that reduce opioid cravings, including buprenorphine and methadone, are more widely available, in part because of insurance coverage provided by Medicaid. In many states, roughly $50 billion in opioid settlement money paid out by corporations is also starting to help. Going forward, it’s unclear how the Trump administration’s deep cuts to public health agencies and grants will affect this new addiction safety net. Learn more here.
5. Many of the most vulnerable people have already died. This theory is discounted by some researchers I talk to, but many addiction experts think it’s a factor. Over the past five years, the U.S. has been losing roughly 110,000 people to fatal drug overdoses every year. It’s possible drug deaths are declining in part because a heartbreaking number of people using fentanyl and other high-risk street drugs simply didn’t survive. Learn more here.
6. Waning effect of the COVID pandemic. The isolation, trauma and disruption of addiction treatment programs that followed the onset of COVID in 2020 overlap with the most devastating years of drug overdose deaths. Many public health experts believe the pandemic deepened the catastrophic impacts of fentanyl. According to this theory, as the impacts of COVID continue to fade, deadly overdoses are also declining to a more “normal” level. Learn more here.
7. People are using fentanyl (and other high risk street drugs) more skillfully. This is a common theory among people who use street drugs. They often tell me they’ve adapted to the risks of fentanyl by smoking rather than injecting the drug, which many addiction experts believe is safer (though still incredibly dangerous). People try to never use fentanyl alone and often carry naloxone or Narcan to reverse overdoses. Many people use test strips to identify unwanted contaminants in their drugs and use smaller fentanyl doses. Learn more here.
8. A decline in young people using drugs. Street fentanyl has emerged as a leading cause of death among young people in the U.S., age 18 to 45. But research suggests far fewer young people and teenagers are using drugs (other than cannabis). This trend matters because new users have low physical tolerance for opioids such as fentanyl, which means they’re more likely to overdose and potentially die. Fewer young users means fewer people taking that risk. Learn more here.
It’s important to emphasize all of these theories are just that — theories. Most researchers, doctors and front-line care providers say they need more data and more time to understand a shift this large.
But there is a growing, tentative consensus that the answer may well be “all of the above.”
A big question going forward is How low will U.S. drug deaths go? We’ve already seen the biggest, fastest drop in U.S. history. So far, there’s no sign the improvement is slowing.
Celebrities wear pins protesting ICE at the Golden Globes
Some celebrities donned anti-ICE pins at the Golden Globes on Sunday in tribute to Renee Good, who was shot and killed by an Immigration and Customs Enforcement officer last week in Minneapolis.
Malaysia, Indonesia become first to block Musk’s Grok over AI deepfakes
Malaysia and Indonesia have become the first countries to block Grok, the artificial intelligence chatbot developed by Elon Musk's xAI, after authorities said it was being misused to generate sexually explicit and non-consensual images.
Death toll from protests in Iran increases as Trump says Iran wants to talk
President Trump said Sunday that Iran proposed negotiations after his threat to strike the Islamic Republic over its crackdown targeting demonstrators. Activists say at least 544 have died.
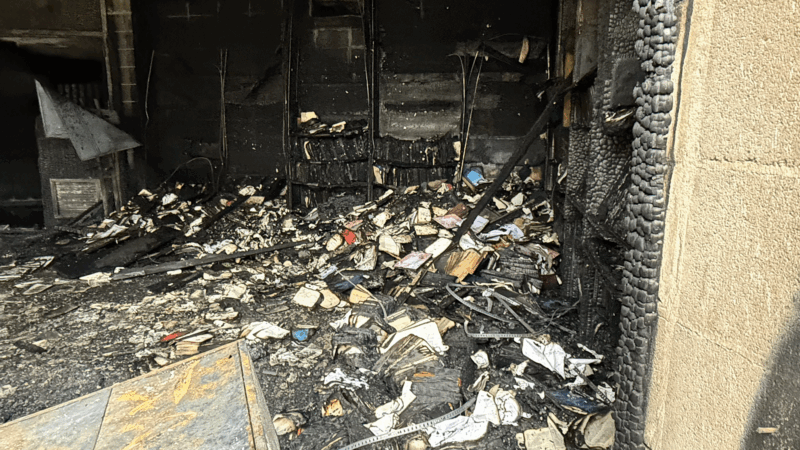
Arson engulfs Mississippi synagogue, a congregation once bombed by Ku Klux Klan
A suspect is charged with arson in a fire that burned through a synagogue in Mississippi. Flames and smoke destroyed its library, housing Torahs.
DOJ subpoenas Federal Reserve in escalating pressure campaign
The Justice Department has subpoenaed the Fed over chair Jerome Powell's testimony over the central bank's headquarters renovation. Powell calls it part of a pressure campaign over interest rates.
The 2026 Golden Globe awards are Sunday. Here’s how to watch
The 2026 Golden Globes air on Sunday night starting at 8 p.m. ET / 5 p.m. PT.