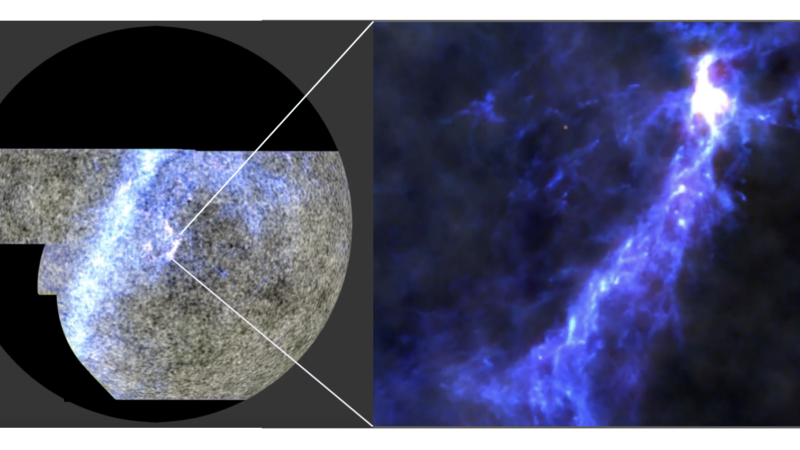
New ‘baby pictures’ of the cosmos show the universe in its infancy
Sure, they’re not your typical baby pictures. But a global team of researchers says new images published this week show some of the clearest visualizations yet of the universe in its infancy.
If our roughly 13 billion-year-old cosmos could be considered middle-aged, the researchers note, these new images captured around its 380,000th birthday represent a snapshot of the universe as a newborn.
The images were created using data from the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), which is located in a remote part of the Chilean Andes and has since been decommissioned. It was the last major data release to come from the project.
ACT had a much higher resolution than the European Space Agency’s Planck space telescope, so strong that it allowed researchers to see the faint polarization of light and create increasingly detailed and far-reaching maps of the universe.
“That means that we can say things about the entire universe at once, such as how mass it has in it, how much hydrogen there is in the entire universe and how much helium there is in the entire universe,” said Suzanne Staggs, director of the ACT.

Some time after the universe burst into existence, according to the Big Bang theory, it became filled with microwave radiation that pervades the cosmos to this day, a phenomenon known as the cosmic microwave background.
That’s what these new maps show — and they’re clearer than ever before, the researchers say. For example, they’re able to see not just how much helium and hydrogen were present billions of years ago, but how the gases were moving, offering hints about what was to come in the universe’s development.
That allows Staggs, who is also a Princeton University professor, and others to test existing mathematical models of the universe. “When we have better and better maps, we can do a better and better job at figuring out that model and figuring out whether it’s correct,” she said.

So far, what we think we know about the universe is checking out. And not only that — the researchers say the new images have helped them measure more precisely the age of the universe (13.8 billion years) and how quickly it’s expanding (67-68 kilometers per second per megaparsec).
“We took this entirely new measurement of the sky, giving us an independent check of the cosmological model, and our results show that it holds up,” Adriaan Duivenvoorden, a lead author of the research with the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, said in a statement.
Some of the researchers were scheduled to present their findings Wednesday at a conference held by the American Physical Society in Anaheim, Calif.
Rideshare union rights, social media limits and other state laws taking effect Jan. 1
Every new year, public media reporters across the country bring us some of the new state laws taking effect where they are. Here are six in 2026.
Guides to help you tackle your New Year’s resolutions
From building your strength to tackling credit card debt, NPR's Life Kit has a newsletter journey to help you tackle your New Year's resolution.
Guides to help you tackle your New Year’s resolutions
From building your strength to tackling credit card debt, NPR's Life Kit has a newsletter journey to help you tackle your New Year's resolution.
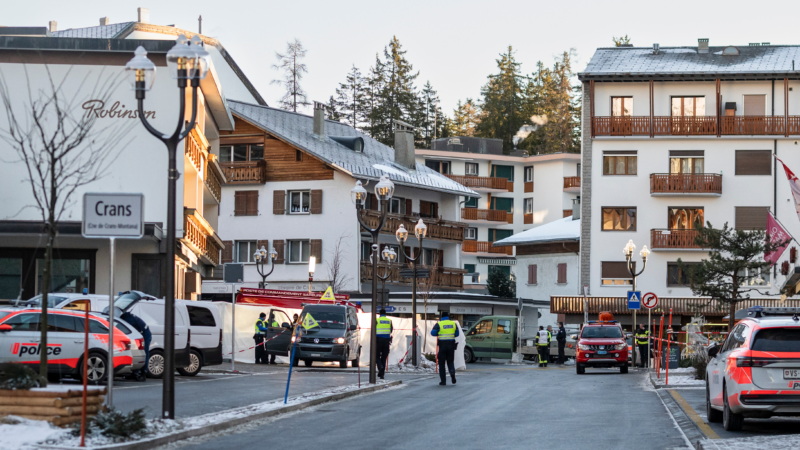
Dozens presumed dead in fire at Swiss Alps bar during New Year’s celebration
Dozens of people are presumed dead and about 100 injured, most of them seriously, following a fire at a Swiss Alps bar during a New Year's celebration, police said Thursday.
Warren Buffett officially retires as Berkshire Hathway’s CEO
The legendary 95-year-old investor spent decades building his company into one of the world's largest and most powerful. Now Greg Abel is taking it over.
Crypto soared in 2025 — and then crashed. Now what?
For most of 2025, cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin surged as President Trump vowed to make the U.S. a crypto leader. But now, a severe sell-off has shaken the sector.