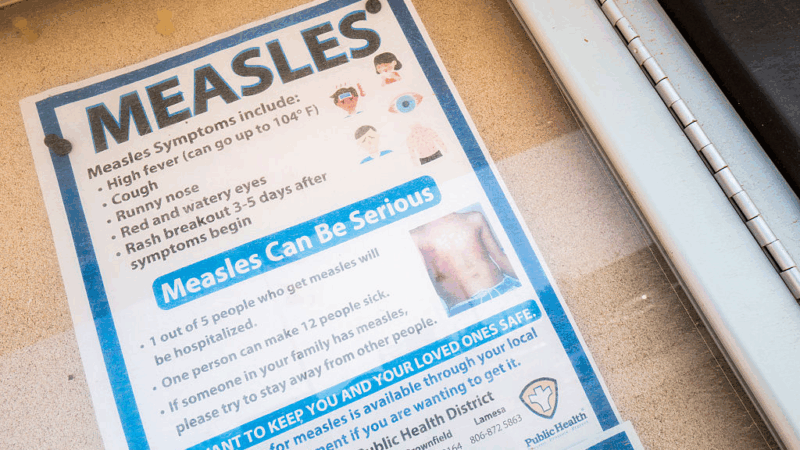
Measles math: What to know about 1,001 measles cases across the country
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports there have been 1,001 confirmed measles cases in the U.S. this year. It’s the second-highest case count in 25 years, topped only by 2019, when more than 1,200 measles cases were detected. The best way to contain measles is two doses of the MMR vaccine (measles, mumps and rubella).
Here are numbers to help you understand how measles is spreading now.
1,001 cases:
The CDC keeps track of confirmed cases and is updating its count on a weekly basis. On May 2, it reported 935 cases. On Friday, it reported cases have ticked past the thousand mark, to 1,001.
31 jurisdictions:
Measles cases have been reported in 31 jurisdictions, up from 30 on May 1. Cases have been reported in more than half of U.S. states this year, but not all of those states have full-fledged outbreaks.
14 outbreaks:
An outbreak is defined as 3 or more related cases. So while the total number of cases is important, the number of outbreaks shows where the virus is spreading. The number of outbreaks went from 12 last week to 14 this week.
By far the largest outbreak is centered in west Texas, where measles has been spreading since January. Reported cases in that outbreak totaled 683 last week and 709 this week.
3 deaths
Two unvaccinated, otherwise healthy children in Texas have died of the disease. One adult in New Mexico was diagnosed with measles posthumously.
18 people
In a population where no one is vaccinated, a single person sick with measles could go on to infect up to 18 others on average. By comparison, when 82% of a population is vaccinated, a sick person would infect about 2 to 3 other unvaccinated people on average.
95% vaccination rate
To prevent outbreaks from spreading within a community, there needs to be a vaccination rate of 95%, according to the CDC. Below that threshold, a community’s herd immunity can begin to erode. In Gaines County, Texas, the epicenter of the outbreak in that state and where measles is still spreading, the kindergarten vaccination rate against measles is just under 82%.
Herd immunity means that enough members of a community are immune to a contagious disease that it is unlikely to keep spreading because there aren’t enough people vulnerable to infection. Herd immunity protects people with weakened immune systems and children who have not yet completed their two-shot series of the measles vaccine.
12 months
It’s an open question how long measles will keep spreading in the U.S. The Texas outbreak, the biggest one, began in January. If any single outbreak continues to result in ongoing transmission for more than 12 months, the U.S. will lose its measles “elimination” status. That’s a technical term in public health for contagions that have been well-controlled for 12 months or more. The U.S. has had that status for about 25 years.
Pentagon says it’s cutting ties with ‘woke’ Harvard, ending military training
Amid an ongoing standoff between Harvard and the White House, the Defense Department said it plans to cut ties with the Ivy League — ending military training, fellowships and certificate programs.
‘Washington Post’ CEO resigns after going AWOL during massive job cuts
Washington Post chief executive and publisher Will Lewis has resigned just days after the newspaper announced massive layoffs.
In this Icelandic drama, a couple quietly drifts apart
Icelandic director Hlynur Pálmason weaves scenes of quiet domestic life against the backdrop of an arresting landscape in his newest film.
After the Fall: How Olympic figure skaters soar after stumbling on the ice
Olympic figure skating is often seems to take athletes to the very edge of perfection, but even the greatest stumble and fall. How do they pull themselves together again on the biggest world stage? Toughness, poise and practice.
They’re cured of leprosy. Why do they still live in leprosy colonies?
Leprosy is one of the least contagious diseases around — and perhaps one of the most misunderstood. The colonies are relics of a not-too-distant past when those diagnosed with leprosy were exiled.
This season, ‘The Pitt’ is about what doesn’t happen in one day
The first season of The Pitt was about acute problems. The second is about chronic ones.