Advocates push for Medicaid expansion in holdout Alabama
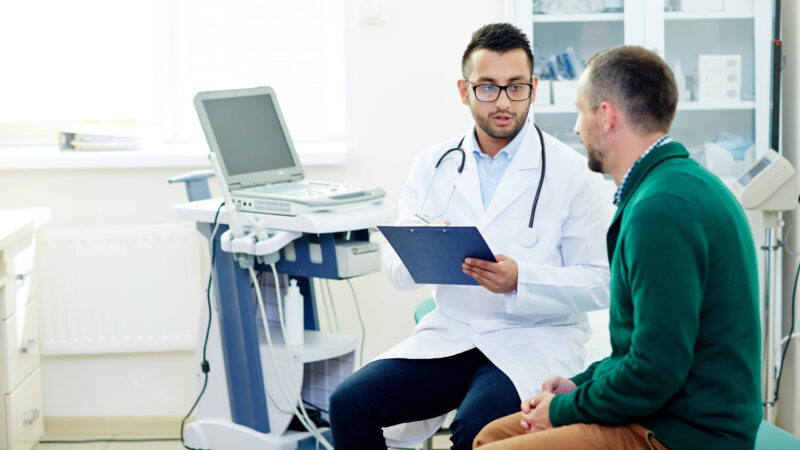
MONTGOMERY, Ala. (AP) — Thirty-year-old Kiana George works at a child care program in Camden, Alabama. She makes too much to qualify for Medicaid and too little to qualify for federal subsidies to help buy health insurance.
Without insurance, she tried to avoid going to the doctor — which eventually landed the mother of a 9-year-old in the hospital for high blood pressure.
“I started getting bills in the mail and that kind of discouraged me from going to the doctor because if I’m already in debt, I can’t pay you. If I don’t have money to get insurance, I don’t have the money to pay you for not having insurance,” George said.
In the 10 states that have not expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, roughly 1.4 million people like George fall in the coverage gap — earning too much to qualify for Medicaid and too little to get federal subsidies to help buy insurance, according to numbers released Tuesday by KFF, a health policy research organization.
Advocates gathered at the Alabama Statehouse Tuesday urging lawmakers to reconsider their long-held reluctance to expand Medicaid, saying the decision is hurting both working families and health care providers. But the push comes at a time there is gathering uncertainty about possible cuts and changes in Washington to Medicaid, the safety net program that provides health care to 80 million U.S. adults and children.
The Affordable Care Act called for states to expand Medicaid programs to cover adults ages 19 to 64 with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level, about $21,597 for a single person or $29,187 for a family of two. But a U.S. Supreme Court decision made expansion optional. People earning more than that are eligible for federal health insurance subsidies through an online marketplace.
The 10 non-expansion states are: Wyoming, Kansas, Wisconsin, Texas, Tennessee, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, South Carolina and Florida. The uninsured rates in states without Medicaid expansion are nearly twice as high as those in expansion states, or 14% to 7.6%, according to KFF.
Angelica McCain, 35, of Hoover, Alabama, was in the coverage gap for years as she worked in the restaurant industry. “You can’t expect workers, when you are not paying them a livable wage, to be able to afford privatized health care because it is upward of $500 a month per person,” she said.
Hospitals, particularly those in rural areas, are feeling the financial pinch of uncompensated care, said Debbie Smith of Cover Alabama, an advocacy group promoting Medicaid expansion. Fifteen hospitals have closed in Alabama since 2011, according to the Alabama Hospital Association.
“When a hospital is closed, it’s not just closed for the uninsured. It’s closed for all of us,” said Dr. Don Williamson, president of the association.
But many Republicans in holdout states have resisted expansion. The uncertainty of what changes might be ahead at the federal level have added to their reluctance.
“Doing anything with Medicaid right now would probably be cost prohibitive,” Republican House Speaker Nathaniel Ledbetter said earlier this month when asked about the outlook for expansion in 2025. “What I’m hearing everybody’s wanting to do is kind of wait and see what the federal government does.”
Mississippi Gov. Tate Reeves last month called for lawmakers in that state to oppose expansion efforts because of the possibility that President Donald Trump’s administration could make changes to Medicaid.
Smith said Alabama’s Medicaid program does not have room for cuts.
“We have a bare-bones program here, only covers children, people with disabilities, pregnant women — very few low-income adults. There is literally nowhere to cut,” Smith said.
She said years of inaction on Medicaid expansion has hurt the state.
“Meanwhile, people are suffering and dying. Hospitals are closing. Alabama is losing billions of dollars that could have been invested in our health care system,” Smith said.
Greetings from Acre, Israel, where an old fortress recalls the time of the Crusades
Far-Flung Postcards is a weekly series in which NPR's international team shares moments from their lives and work around the world.
Can’t decide what to read next? Here are 20 recommendations for your book club
You know that feeling when you finish a book and just have to discuss it with someone? That's a great book club book. Here are 20 tried-and-true titles that are sure to get the conversation started.
The risks of AI in schools outweigh the benefits, report says
A new report warns that AI poses a serious threat to children's cognitive development and emotional well-being.
The death toll from a crackdown on protests in Iran jumps to over 2,500, activists say
The number of dead climbed to at least 2,571 early Wednesday, as reported by the U.S.-based Human Rights Activists News Agency, as Iranians made phone calls abroad for the first time in days.
How have prices changed in a year? NPR checked 114 items at Walmart
We found the effects of tariffs and extreme weather, relief (finally!) in the egg cooler, plus one case of shrinkflation.
How the feud between Trump and Minnesota is impacting the probe into the ICE shooting
The FBI is solely leading the inquiry into the killing of Renee Macklin Good by ICE agent Jonathan Ross without help from Minnesota authorities. Legal experts explain why the move is unusual and why joint investigations are the norm.