Omicron is less severe, but it’s overwhelming Alabama’s hospitals
Alabama recorded an average of more than 10,000 new coronavirus infections every day this week, more than double the peak for any previous wave.
“It’s just mind boggling and we don’t know how much longer it’s going to go on,” said Alabama Health Officer Dr. Scott Harris during a Facebook live event Thursday afternoon.
Harris said one “silver lining” is that the highly contagious omicron variant is less severe than other strains of the virus, meaning fewer cases lead to hospitalization and death.
According to Dr. Don Williamson, president of the Alabama Hospital Association, about 3% of omicron infections result in hospitalization, compared to 10% of delta cases. And the rate of death with omicron is about half that seen during the delta surge.
But Williamson urged caution saying “less severe” does not mean “no harm.” He said people who are not fully vaccinated face the highest risk of illness, accounting for about 65% of hospitalizations and a vast majority of deaths.
On Friday, officials with the Alabama Department of Public Health warned that a record number of children are hospitalized with COVID-19, with three pediatric patients in the intensive care unit and one child on a ventilator.
This week, Williamson said fewer than 10% of ICU beds were available statewide and some hospitals are canceling non-emergent surgeries.
“Our hospitals are overwhelmed,” said Dr. David Thrasher, a Montgomery-based pulmonologist. “The morale and the stress on our staff is really unbearable.”
Thrasher said many providers are out sick with breakthrough infections, and others are leaving the profession due to burnout.
As of Friday afternoon, Alabama hospitals were caring for roughly 2,100 people with COVID-19, a 30% increase from a week ago.
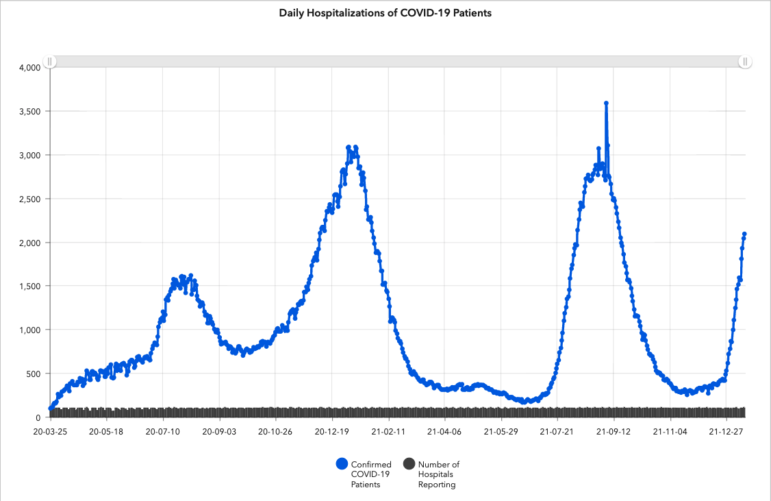
Compared to previous waves, a larger percentage of these hospitalizations are considered “incidentals,” meaning people who are admitted for an unrelated issue but test positive for the virus.
At UAB Hospital, infectious disease specialist Dr. Michael Saag said this group accounts for anywhere from 30 to 40% of COVID hospitalizations. Saag cautions that while these patients may not have severe COVID symptoms, they still require the same infection protocols.
Health experts said it’s difficult to predict the future, but based on data in other states, Alabama’s omicron surge could peak in a few weeks.
They continue to urge people to wear masks indoors and get vaccinated, emphasizing the importance of a third booster shot to offer the strongest protection against omicron.
Pentagon puts Scouts ‘on notice’ over DEI and girl-centered policies
After threatening to sever ties with the organization formerly known as the Boy Scouts, Defense Secretary Hegseth announced a 6-month reprieve
President Trump bans Anthropic from use in government systems
Trump called the AI lab a "RADICAL LEFT, WOKE COMPANY" in a social media post. The Pentagon also ordered all military contractors to stop doing business with Anthropic.
HUD proposes time limits and work requirements for rental aid
The rule would allow housing agencies and landlords to impose such requirements "to encourage self-sufficiency." Critics say most who can work already do, but their wages are low.
Paramount and Warner Bros’ deal is about merging studios, and a whole lot more
The nearly $111 billion marriage would unite Paramount and Warner film studios, streamers and television properties — including CNN — under the control of the wealthy Ellison family.
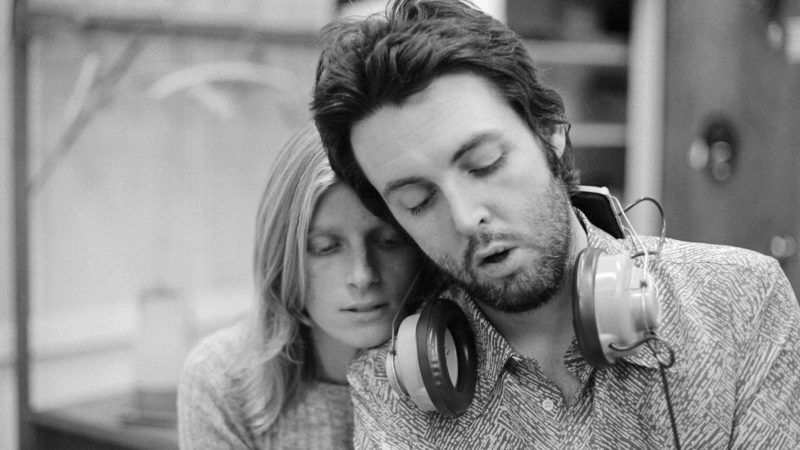
A new film follows Paul McCartney’s 2nd act after The Beatles’ breakup
While previous documentaries captured the frenzy of Beatlemania, Man on the Run focuses on McCartney in the years between the band's breakup and John Lennon's death.
An aspiring dancer. A wealthy benefactor. And ‘Dreams’ turned to nightmare
A new psychological drama from Mexican filmmaker Michel Franco centers on the torrid affair between a wealthy San Francisco philanthropist and an undocumented immigrant who aspires to be a dancer.






