Late Alabama artist Thornton Dial honored with first full-scale retrospective in his home state
By Rachel Parker, WBHM Reflect Alabama Fellow
As a child, Richard Dial can remember hearing his mother on the phone at two or three in the morning with their neighbor, asking him to try and get his father, Thornton Dial, to come inside from the backyard workshop after her own failed attempts. He was still busy creating art.
“Art was a part of his life,” Richard Dial said. “I think he really found his niche in life, his purpose in life,” Richard says.
Some of Thornton Dial’s pieces eventually made it into the nation’s top museums, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. But recognition of the Alabama-born artist by the larger art world did not come through a traditional path. Dial, who died in 2016, had little formal education and no art training.
Now, the University of Alabama at Birmingham’s Abroms-Engle Institute for the Visual Arts presents the first retrospective of Dial’s work in his home state. The exhibit, Thornton Dial: I, Too, Am Alabama, is open through Saturday.
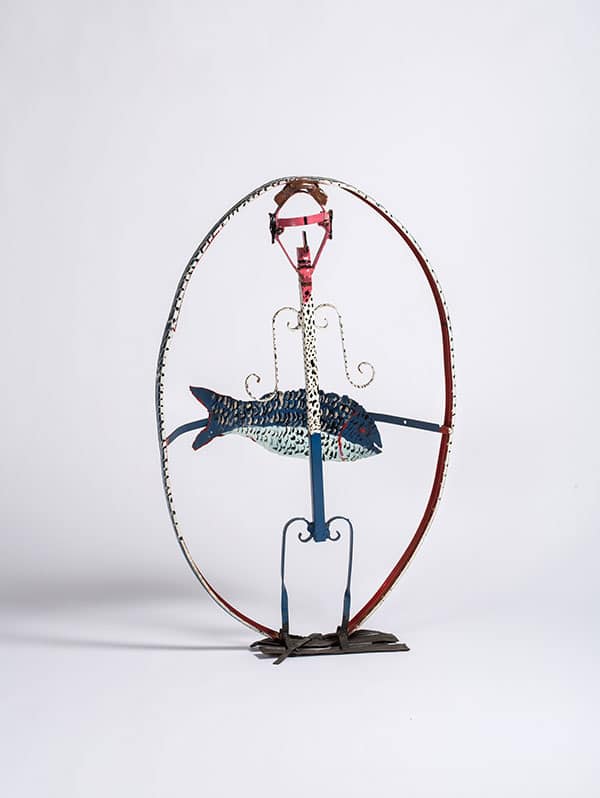

One of the many jobs Dial worked throughout his life was as a metalworker at the Pullman Standard Plant in Bessemer, AL. From his different jobs, he sharpened his artistic skills and used materials he worked with daily, such as rope, wires, metal and fishing lures, to make art.
“I think that is a classic, prime example of some of his best works,” said Brandon Dial, Thornton Dial’s grandson. “When you’re taking things that people consider to be scraps and you’re turning it into something that is truly a treasure.”
In his popular piece called, “How Things Work: The Parade of Life,” two female figures made up of swirling colors – red, orange, black, yellow and white – spread across the canvas. Look closer and there’s a “parade” of children’s toys – cars and legos – lined up and attached to the painting. The objects appear to move through and around the women’s bodies.
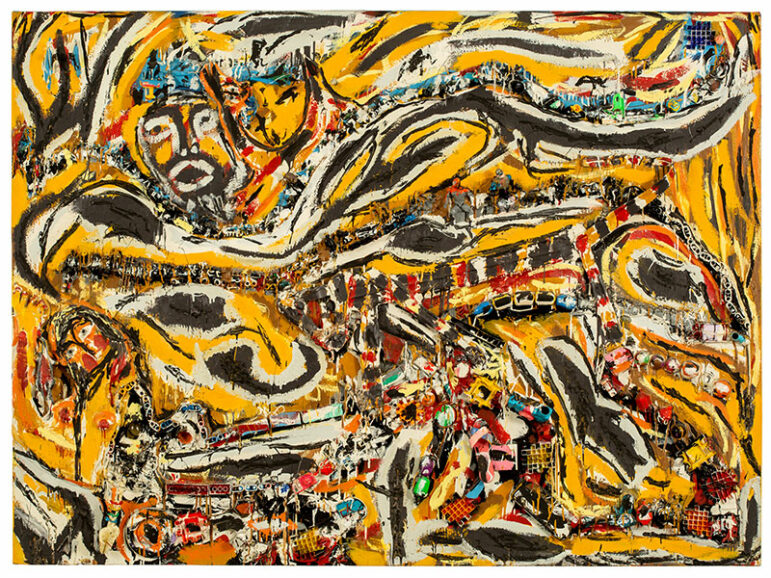

“That’s the power of Mr. Dial’s work is that there is a lot of depth to it. There’s a lot of meaning behind it. Sometimes you can add your own meaning. Sometimes you know what his meaning is. It’s not just what the face value is like, what you see initially,” AEIVA Assistant Curator Tina Ruggieri said.
A rose and women were recurring symbols for Dial. They represent his relationship to the women in his life, since he was raised by his grandmother and aunts.
Dial’s artwork also reflects real world, complicated topics including politics, race, class and the environment.
“He would go to work, come home and eat. And he would always, always, every day, he would stop and watch the news. So he knew what was going on in the world,” Richard Dial said.
A timeline made up of plaques in the exhibit connects Dial’s life to contemporary historical events. For instance, the birth of his first child in 1953 is followed by the lynching of Emmett Till in 1955.
Dial wanted his art to be a force for change. He said to make that happen we should focus on the “little man,” which he described as people in the minority and lower class who are often forgotten, and their ideas.
“I see a lot of optimism in a lot of Thornton Dial’s work, even when he’s dealing with very difficult subject matter,.” said Paul Barrett, curator of the UAB exhibit.
While Dial gained widespread acclaim, Barrett says a show like this in Alabama is overdue.
“The fact that Thornton Dial’s work was not just recognized but celebrated in museums in New Orleans and Atlanta for many years before he was celebrated in his hometown, I think was a historic injustice that we were very happy to address,” Barrett said.
The University of Alabama at Birmingham holds WBHM’s broadcast license, but our news and businesses department operate independently.
Editor’s note: Story updated to attribute quote to AEIVA Assistant Curator Tina Ruggieri
‘One year of failure.’ The Lancet slams RFK Jr.’s first year as health chief
In a scathing review, the top US medical journal's editorial board warned that the "destruction that Kennedy has wrought in 1 in office might take generations to repair."
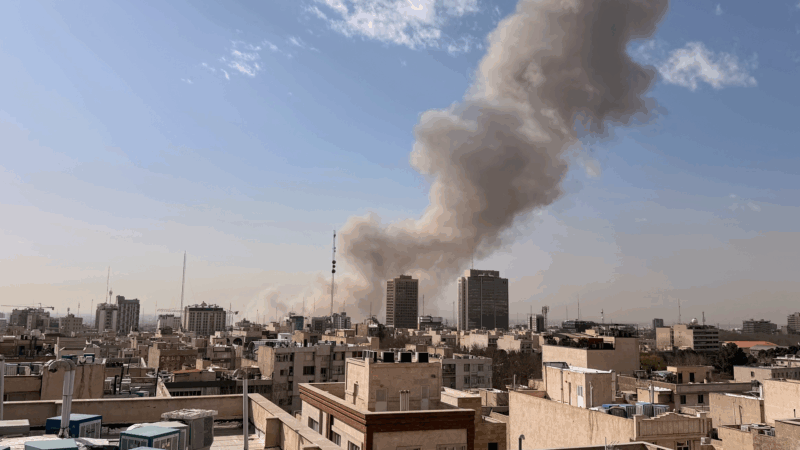
Here’s how world leaders are reacting to the US-Israel strikes on Iran
Several leaders voiced support for the operation – but most, including those who stopped short of condemning it, called for restraint moving forward.
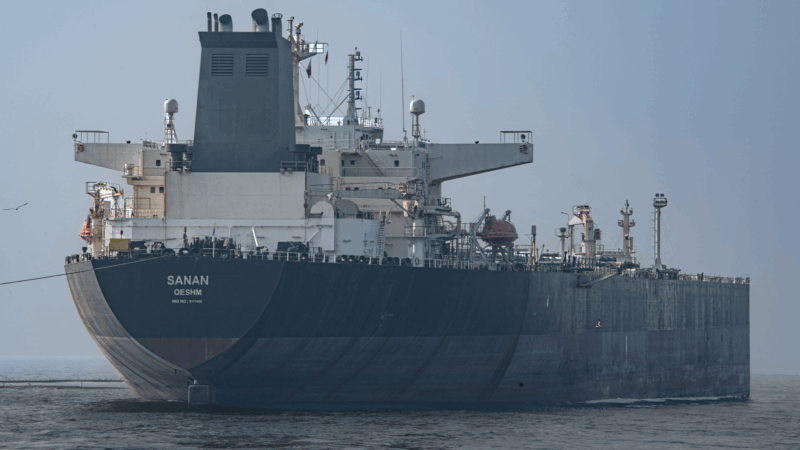
How could the U.S. strikes in Iran affect the world’s oil supply?
Despite sanctions, Iran is one of the world's major oil producers, with much of its crude exported to China.
Why is the U.S. attacking Iran? Six things to know
The U.S. and Israel launched military strikes in Iran, targeting Khamenei and the Iranian president. "Operation Epic Fury" will be "massive and ongoing," President Trump said Saturday morning.
Sen. Tim Kaine calls on the Senate to vote on the war powers resolution
NPR's Scott Simon talks to Sen. Tim Kaine, D-Va., about the U.S. strikes on Iran.
Iran strikes were launched without approval from Congress, deeply dividing lawmakers
Top lawmakers were notified about the operation shortly before it was launched, but the White House did not seek authorization from Congress to carry out the strikes.