UAB Researchers Create Culturally-Based Protocol For Palliative Care
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have created the first culturally based protocol for patients facing end-of-life care. Ronit Elk is a professor in the Division of Gerontology, Geriatrics and Palliative Care at UAB. She has spent her life living in different countries. Once she moved to the U.S., Elk said she noticed the lack of respect for cultural differences for the nation’s sickest minority patients, particularly African Americans.
What was the most notable cultural difference?
For Black patients and their families going through end-of-life care, the concept of hope and miracles is key. Physicians are primarily trained as scientists to read the physical symptoms that are occurring. Black patients and families who believe that there is always hope and it’s in God’s hands, they understand yes, you’re the physician, but you are not the decider. It is God that decides whether my loved one is going to live or die. And it’s caused a lot of clashes with physicians and family members where physicians are often saying to patients’ families, you’re not really accepting that the person is going to die. There’s no way they can live. And the family is saying it’s in God’s hands and a miracle can happen. And somehow that’s a very difficult thing for many physicians to accept.
What are the consequences of treating everyone the same way in palliative care?
Here’s the interesting thing, palliative care physicians and clinicians are probably the most compassionate human beings on this planet. They are taught that you go in and you do exactly what the patient wants. However, what isn’t taught in America is that different people’s culture impacts that. Whenever somebody has a loved one who is very ill, whenever somebody is dying, it is always viewed through their own cultural lens. And that part has never been taught. And so there’s a simple lack of understanding.
Why were minority patients over-looked in models of end-of-life-care?
The model that was developed was based on the white middle-class model. This model is very wonderful if you’re white, middle class and Christian. It is most inappropriate in many cases if you’re not white or you’re not middle class or if you’re not Christian. So why it’s so difficult to understand that different cultures may look at death, life, illness differently; I have no idea. I think maybe in America we’re not taught enough to understand different cultures. But we’re doing a lot of studies with people from other countries, three in Africa and some in other countries, because over there, people know “if a model is for white middle class people, that’s not going to work for my people. I want to see what’s really going to work for our community.”
How do you get hospitals on board with this new protocol?
So the first thing we have to do is to prove that it’s very effective. What we’ve shown is that it’s feasible and it can be done. So we are simultaneously developing trainings so that we can train the physicians who won’t push against it, but will rather embrace it and it will be accepted in hospitals.
Editor’s Note: UAB holds WBHM’s broadcast license, but our news and business departments operate independently.
This interview has been condensed and edited for clarity.
Newly discovered dinosaur species was a fish-eater with a huge horn
The semi-aquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus mirabilis, was discovered by an international team of scientists working in Niger.
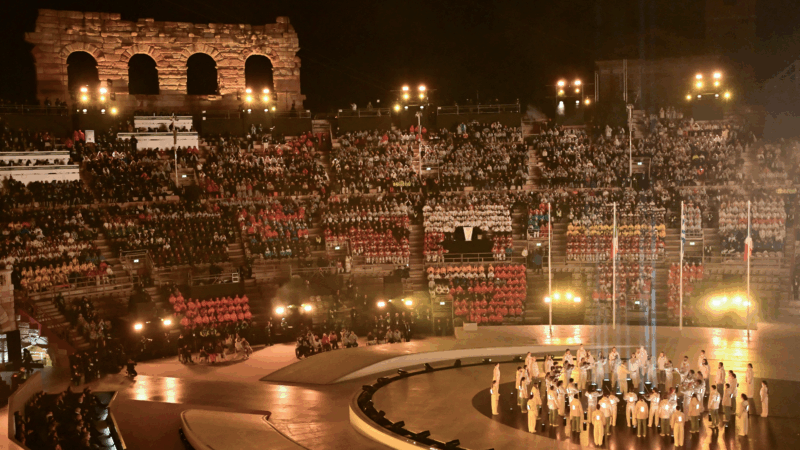
Reporters’ notebook: The Olympics closing ceremony is way more fun than you’d think
Olympics opening ceremonies tend to get more love than their closing counterparts. But a pair of NPR reporters who watched both in Italy left with a newfound appreciation for the latter.
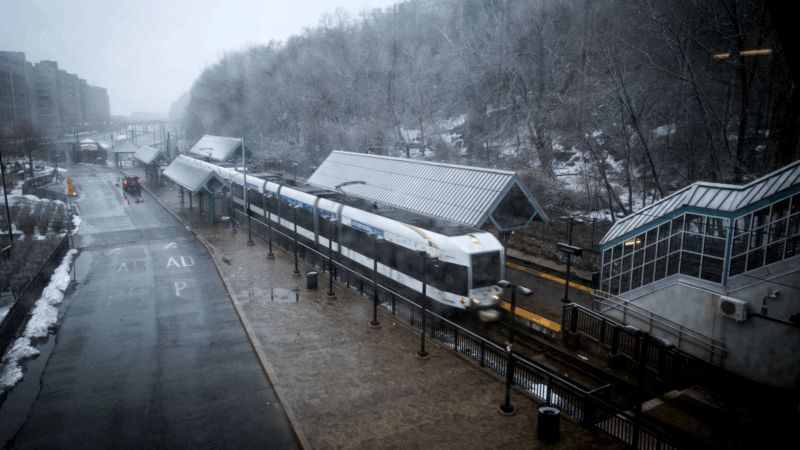
Northeast readies for a major winter storm, with blizzard warnings in effect
New Jersey through Massachusetts could see 2 feet of snow. New York City's mayor said the city had not "seen a storm like this in a decade."
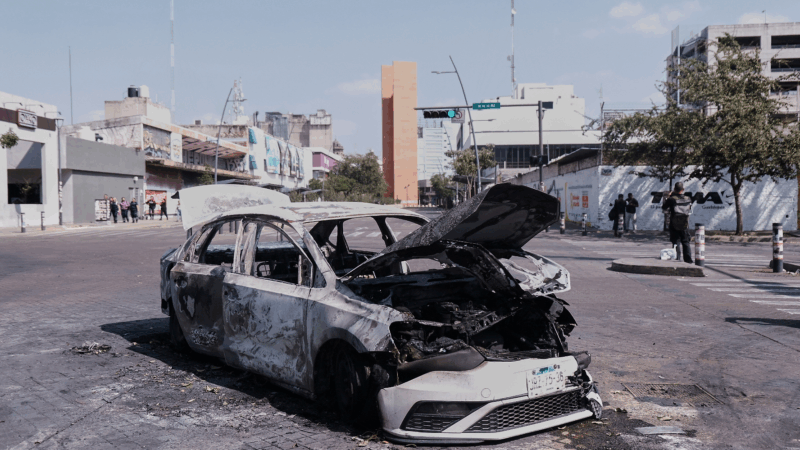
Mexican army kills leader of Jalisco New Generation Cartel, official says
The Mexican army killed the leader of the powerful Jalisco New Generation Cartel, Nemesio Rubén Oseguera Cervantes, "El Mencho," in an operation Sunday, a federal official said.
Ukraine’s combat amputees cling to hope as a weapon of war
Along with a growing number of war-wounded amputees, Mykhailo Varvarych and Iryna Botvynska are navigating an altered destiny after Varvarych lost both his legs during the Russian invasion.
University students hold new protests in Iran around memorials for those killed
Iran's state news agency said students protested at five universities in the capital, Tehran, and one in the city of Mashhad on Sunday.