To Prescribe or Not to Prescribe? Opioid Crisis Presents Ethical Dilemma
Deaths from prescription opioids like oxycodone and hydrocodone have more than quadrupled since 1999. So today, doctors trying to treat pain face a dilemma: to prescribe or not to prescribe? It’s a difficult question for health professionals who want to treat patients without sending them down the path to addiction. For example, at Birmingham’s Phoenix Clinic for homeless or formerly homeless veterans, Dr. Stefan Kertesz is examining Stacey Haley, who’s struggling with a brace and a very arthritic knee.
“So now we’re dealing with pain, right?” asks Kertesz. “And the problem is it’s not been easy to get this knee feeling well? So let’s talk about that.”
And they do talk, in detail, for almost a half an hour. The reasons the course of treatment isn’t an easy call are that Haley is working and doesn’t want to be sidelined by surgery, and there’s a potential red flag when it comes to prescribing opioids: he’s struggled with addiction in the past. But standard meds aren’t working. So Dr. Kertesz starts him on Tramadol.
“As long as they’re non-narcotics, I’m willing to try anything,” says Haley.
Kertesz replies, “I gotta break it to you, Tramadol is partly narcotic.”
But Haley is reassured because Kertesz explains that Tramadol is relatively low-potency. The main reason Kertesz is comfortable giving it to Haley, though, is that he sees Haley regularly.
“So we have to have a pretty careful conversation in the next few weeks about how it’s going,” Kertesz explains. “My expectation is we’re going to converse about whether it made you feel differently, whether you thought you were getting a buzz from it.”
It’s a dilemma doctors face every day: prescribe medicine that could relieve pain and keep patients functional, or withhold it because of potential addiction. Kertesz says taking time to really know patients is the only way to assess those risks. But in recent years, at least five states have limited the doses doctors can prescribe. And that worries him.
“Doctors are being told, ‘get the dose down, no matter what.’ And they’re saying, ‘I have no time, so I’ll just take everybody off, and who knows what happens to those people?’”
Patients who stop taking opioids often seek illegal drugs or suffer debilitating withdrawal.
“It’s usually a complicated situation,” says Kertesz. “That’s why a public policy solution that’s rooted on pill control alone will probably not work.”
At the same time, over-prescription has done tremendous harm. Several states, including Alabama, have more opiate prescriptions than people. And none of it happened overnight. David Juurlink, head of clinical pharmacology and toxicology at the University of Toronto, explains:
“One of the critical things that happened in the 1990s and early 2000s that helped doctors become more comfortable prescribing opioids for chronic pain was the assertion that addiction was rare. And we were told – I remember being taught myself – that less than one percent of people who were on opiates for chronic pain would become addicted.”
But he says it’s actually about five times that. Many trace the misconception to a widely cited one-paragraph letter in the New England Journal of Medicine in 1980, decades before its content could be easily checked online. The letter said the risk of addiction in a very specific, small patient population was low. But drugmakers, lobbyists, and some doctors overgeneralized that letter to quiet wider concerns about addiction. Juurlink just published a paper noting that, while the median number of similar letters’ citations was 11, that letter has been cited 608 times.
“There is a dark element to this, in what I’ll call the pain lobby,” Juurlink says. “There’s money at stake here. If doctors were to suddenly start using opioids less readily, and for shorter durations and at lower doses, the companies that have made tens of billions-with-a-B dollars would be unhappy.”
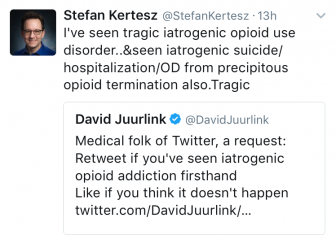
Juurlink is in something of a Twitter battle with Dr. Kertesz: Juurlink emphasizing the harms of over-prescription; Kertesz pointing out that government-imposed dose limits can cause harm too. But they actually agree on a lot. And Juurlink hasn’t stopped prescribing opioids altogether.
“It’s very tough,” he says. “My take is that they have a role … I tend to use them in people in whom other therapies haven’t worked or are too dangerous, but I am extremely judicious with the dosing.”
Juurlink and Kertesz also agree on this: because lives are at stake, there are no easy answers to the question of when to prescribe opioids.
NPR’s Stephen Bisaha contributed to this report.
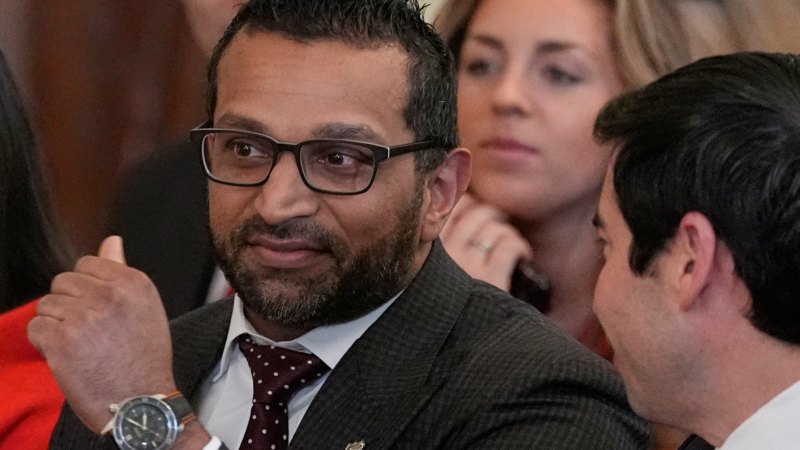
FBI director invites fresh scrutiny over travels with appearance at US men’s hockey team celebration
When the American men's hockey team retreated to their locker room to celebrate their Winter Olympics gold medal win, they were joined by a special guest from the United States: FBI Director Kash Patel.
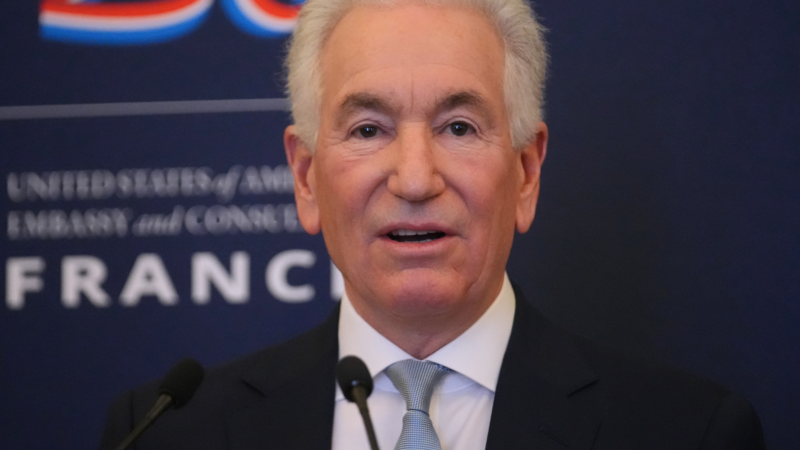
France moves to bar US Ambassador Charles Kushner from direct government access
France's top diplomat has requested that U.S. Ambassador Charles Kushner no longer be allowed direct access to members of the French government. Kushner skipped a meeting Monday to discuss comments by the Trump administration over the beating death of a far-right activist.
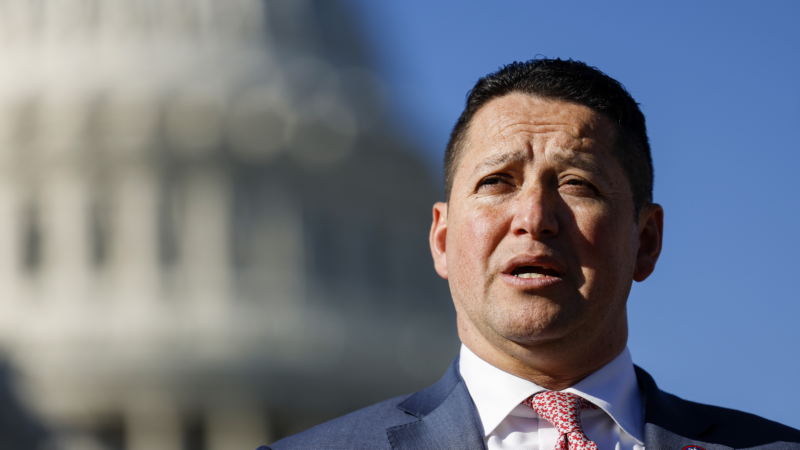
GOP Rep. Tony Gonzales faces pressure from party over affair allegations
The Texas Republican is facing calls from fellow House Republicans to resign, following allegations of an affair with a staffer who later died by suicide.
In pictures: Winter storm slams the east coast
Photos of cities in Connecticut, New York, New Jersey and Massachusetts as they cope with a powerful winter storm.
The FDA creates a quicker path for gene therapies
The Food and Drug Administration aims to evaluate treatments for rare diseases based on plausible evidence that they would work — without requiring a clinical trial first.
BAFTAs apologize after guest with Tourette syndrome uses racial slur during ceremony
A man with Tourette syndrome shouted a racial slur and other offensive remarks during the BAFTA awards ceremony Sunday. The BBC did not edit out his outbursts in its delayed broadcast.