When an earthquake struck San Diego, these elephants formed an ‘alert circle’
When a 5.2 magnitude earthquake hit Southern California on Monday, humans followed the usual drill: drop, cover and hold on.
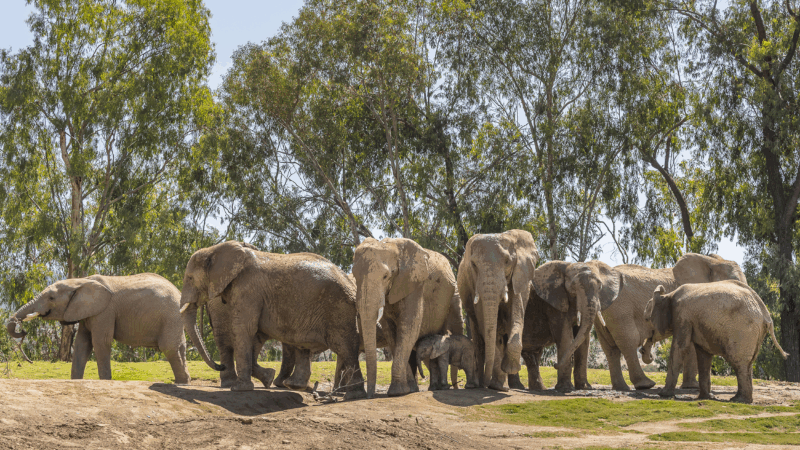
But one herd of elephants at the San Diego Zoo Safari Park in Escondido, Calif. had their own plan — circle up and stand together.
Security footage from the park shows the moment clearly. One minute the elephants were basking in the sun; the next, they were reacting as the ground began to shake.
The three adult females scanned their surroundings and quickly banded together, forming a tight circle around two 7-year-old calves named Zuli and Mkhaya, according to the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance.
Experts call this behavior an “alert circle,” a response matriarch elephants display when they perceive a threat.
“Elephants are highly social, they take care of each other,” says Joshua Plotnik, an associate professor of psychology at Hunter College in New York who studies elephant behavior.
Plotnik says this instinct to protect one another is at the core of the alert circle, a strategy for banding together when danger is near.
“They bunch together, the adults on the outside facing out, and then they’ll push the younger individuals into the middle,” he says.
Elephants can sense seismic vibrations through their feet and ears, Plotnik says, alerting them to potential danger. And earthquakes aren’t the only thing they can detect: Something similar happened during the 2006 Boxing Day Tsunami in southeast Asia, he recalls.
“I’ve heard anecdotes … of elephants responding prior to the large tsunami waves reaching the shores of Thailand, for instance, of elephants retreating up to higher ground with other elephants.”
These fast, coordinated responses reveal the complex social nature of elephants, Plotnik says. But he warns that elephants’ survival in today’s world requires more than just instinct; there’s still much we don’t understand about how they interpret threats.
Learning more, he says, is key to protecting these endangered animals.
“The Asian and African elephants are in imminent danger of going extinct, and it’s crucially important that we continue to learn more about their behavior and cognition if we’re going to come up with ways to protect them and conserve them in the wild,” Plotnik says.
Bernard LaFayette, Selma voting rights organizer, dies at 85
Bernard LaFayette, who died Thursday, laid the foundations of the Selma, Alabama, campaign that culminated in the passage of the Voting Rights Act. He was a Freedom Rider and helped found the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee.
Oil surges to its highest price since 2023, and stocks drop after U.S. jobs report
Stocks fell Friday on worries that the economy could become stuck in a worst-case scenario of stagnating growth and high inflation. Oil prices touched their highest levels since 2023 after surging again because of the Iran war.
No lawsuits required: U.S. Customs is working on a system to refund tariffs
U.S. Customs told the trade court it aims for a streamlined process in 45 days to return importers' money without requiring individual lawsuits.
Poll: A majority of Americans opposes U.S. military action in Iran
Most Americans disapprove of President Trump's handling of Iran, and a majority sees Iran as either only a minor threat or no threat at all, an NPR/PBS News/Marist poll finds.
Your Winter Paralympics primer: What, who and how to watch
Hundreds of para athletes are competing in Italy through March 15. Many Americans are defending past titles, with the U.S. sled hockey team hoping to fend off rival Canada for its fifth straight gold.
After the U.S. sinks an Iranian warship, Sri Lanka takes custody of an Iranian vessel
The move followed Wednesday's sinking of another Iranian warship by a U.S. submarine. Australia confirmed three Australians were on that submarine.