Trump administration targets ATF, with plans to cut jobs and ease gun restrictions
The Trump administration has set its sights on restructuring the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, including plans to loosen gun regulations and significantly reduce its budget.
Two weeks ago, the administration sent staff from the Department of Government Efficiency, the administration’s government-slashing initiative, into the agency with a goal of cutting regulations quickly, according to people familiar with the matter who spoke to NPR on the condition of anonymity to avoid retaliation.
As the federal agency responsible for regulating the gun industry, the ATF investigates illegal gun trafficking, inspects gun dealers to ensure they’re following the law, and issues citations and revokes licenses if they’re not.
DOGE has been working with officials at the ATF on changes to around 50 regulations, including making a background check for a firearm purchase valid for 60 days instead of 30, and allowing gun dealers to destroy records after 20 years, rather than keep them indefinitely, according to the people NPR spoke with. Many of the changes might not seem consequential in isolation, but taken together, those people said, a larger picture emerges of a new regime aiming to deregulate the firearms industry.
“The reality is that the ATF plays a critical role in ensuring that gun dealers can operate in a fully, legally compliant manner,” says Kris Brown, president of Brady, a nonprofit that advocates for gun control. “We don’t want to take that sort of critical oversight role away from them because there is no one else out there.”
The proposed regulatory changes are part of a broader effort to transform the ATF. The Department of Justice, which oversees the agency, has proposed a 25% cut to its budget in fiscal year 2026. That includes the loss of more than 500 investigators, who conduct inspections of federally licensed gun dealers. The Justice Department’s own analysis says the cut would reduce the agency’s ability to regulate the firearms and explosives industries by around 40%.
The Justice Department declined NPR’s request for an interview, but ATF said in a statement that the agency is trying to reduce “unnecessary regulatory burdens” so it can focus its “enforcement on violent criminals.”
Pamela Hicks, chief counsel at the agency until she was fired in February, said inspectors ensure gun dealers are keeping accurate records, which is key to solving crime.
“The reason why those [records] are kept is so that crime guns can be traced. And the reason why it’s critical that they be accurate is so that people who shouldn’t have guns don’t have guns,” said Hicks. “And if you can’t trace the gun because of crappy records, then that’s a problem for law enforcement.”
Hicks – who after her firing co-founded the DC Law Collective to ensure federal employees have access to legal advocacy – said if you starve one part of an agency of resources, it will affect the entire operation.
The ATF is the only agency in the country with the ability to trace guns involved in crimes. It keeps a database of the markings left on a bullet or a casing after it has been fired, essentially creating a gun’s fingerprint. Police frequently use that tracing information, provided by the ATF, to solve violent crime.
“The ability to show that a gun was involved in more than one crime, that a gun appeared at this crime scene, then appeared on that rooftop, helps police conduct very effective investigations,” says Brandon del Pozo, former police chief of Burlington, Vt., and an assistant professor at Brown University. “We need that to be well funded. We need that to be a resource available to police everywhere.”
The Trump administration’s cuts to the agency are directly at odds with its claim that it is tough on crime, del Pozo says.
For its part, the administration has said it is not done with its plans to transform the ATF. These changes are also part of a broader dismantling of gun regulations: For instance, the massive tax and spending bill that passed in the Senate Tuesday includes a provision that removes a tax from gun silencers, also known as suppressors, and on certain types of firearms — a move gun-control advocates strongly oppose.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
One week into the Iran war, the fallout is global
The war is no longer just about the U.S., Israel and Iran. More countries are getting caught in the political crossfire or being drawn into the fighting themselves.
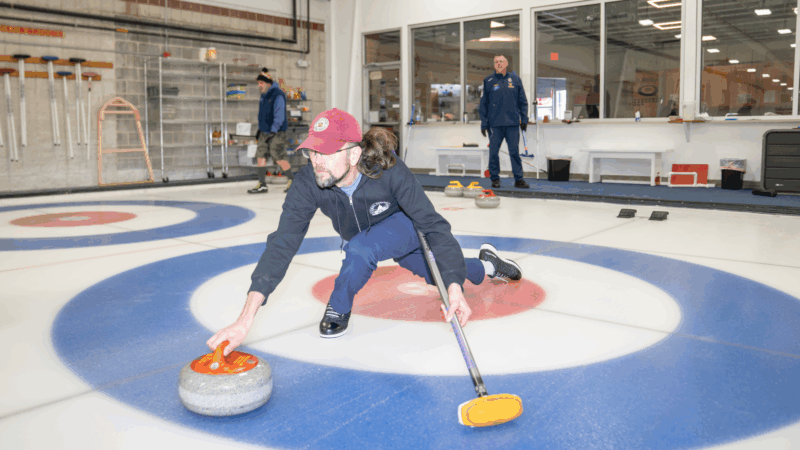
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.
Iran’s president defies U.S. demands while apologizing for strikes on neighbors
President Masoud Pezeshkian said Saturday that a demand by the U.S. for an unconditional surrender is a "dream that they should take to their grave." He also apologized for Iran's attacks on regional countries.
What the Trump administration says about why it went to war with Iran
The Trump administration says it is "laser focused" and mission driven, but the messaging has been varied. The range of cited motivations for striking Iran now are sometimes at odds with each other.