The European Space Agency will beam the famous ‘Blue Danube’ waltz into space
Johann Strauss II’s popular orchestral piece “By the Beautiful Blue Danube” has been inextricably linked to space since it was used in the 1968 classic film 2001: A Space Odyssey.
The waltz played as a fictional spaceship docks with a space station, with expansive views of the Earth and the distant stars.
This week, the piece will take a more literal place among the stars when the European Space Agency broadcasts it into space.
On Saturday, the Vienna Symphony Orchestra will perform the piece live, while a radio antenna in Spain beams the music out.
The “Blue Danube” broadcast is celebrating the 50th anniversary of the ESA’s creation, as well as 200 years since Strauss’ birth.
The waltz was notably absent when NASA launched 27 pieces of music, as well as other sounds and images, on matching “Golden Records” on the Voyager 1 and 2 missions in 1977. The Voyager 1 probe is the first human-made object to leave the solar system. Both probes are still flying out into deep space today.
The ESA says it aims to rectify that historical overlook.
“The absence of the most famous of all waltzes from the 1977 Voyager Golden Record is a cosmic mistake,” Norbert Kettner, the director of the Vienna Tourist Board, said in a statement.
Strauss was from Austria, and the Vienna Tourist Board is helping the space agency arrange the broadcast.
A piece by another famous Austrian composer, Mozart, was included on the Voyager Golden Record.
Transmitting at the speed of light
The radio antenna in Spain where the piece is being broadcast is about 115 feet across, and is operated by the ESA. It supports uncrewed European missions to study the surface of Mars, create a map of the stars and take up-close pictures of the sun.
On Saturday, it will take a break from that work.
The Vienna Symphony Orchestra’s performance will be livestreamed online. The audio of the performance will be converted into an electromagnetic wave. That wave, which is not audible to humans, will be transmitted into space at the speed of light, in the direction of Voyager 1. The music will be moving so quickly that it will overtake the probe, which was launched in 1977 and left the solar system in 2012, in just 23 hours.
“This demonstrates that our technology can transmit not only scientific data but also human art over long distances,” said Josef Aschbacher, the director general of the ESA, in an announcement about the broadcast.
This is not the first time humans have beamed music deep into space.
Last year, NASA sent the Missy Elliott song “The Rain (Supa Dupa Fly)” to Venus. And in 2008, NASA celebrated its 50th anniversary by sending “Across the Universe” by The Beatles into deep space.
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
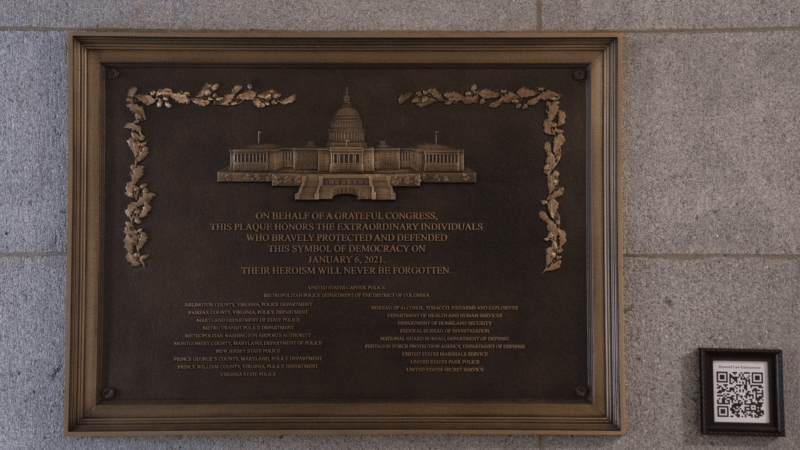
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
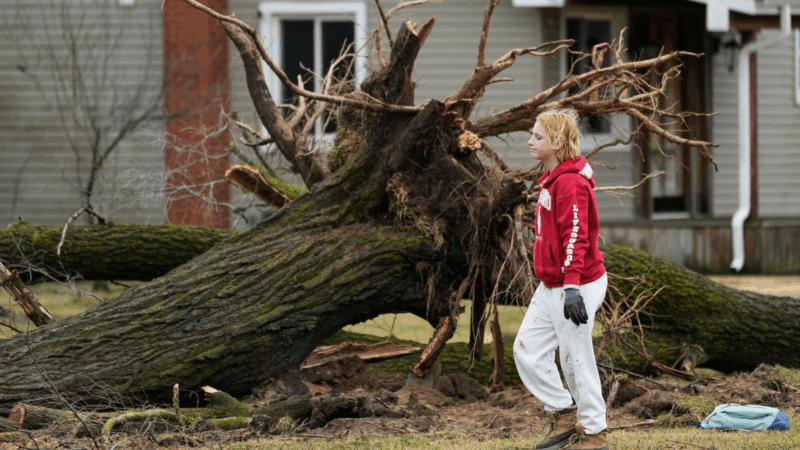
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
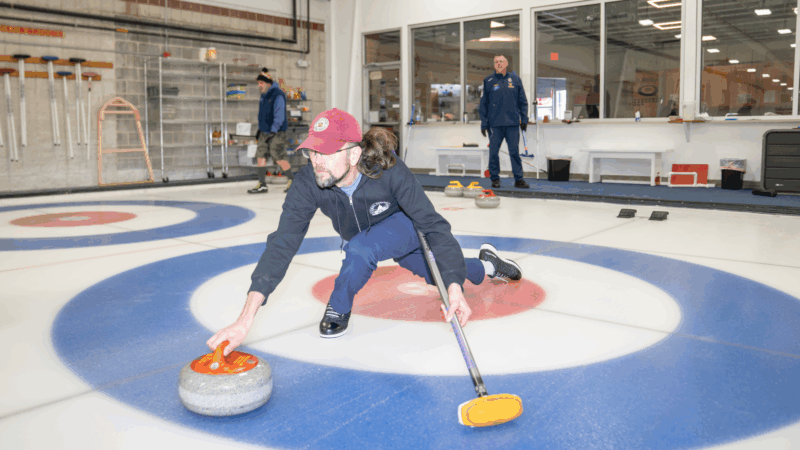
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.