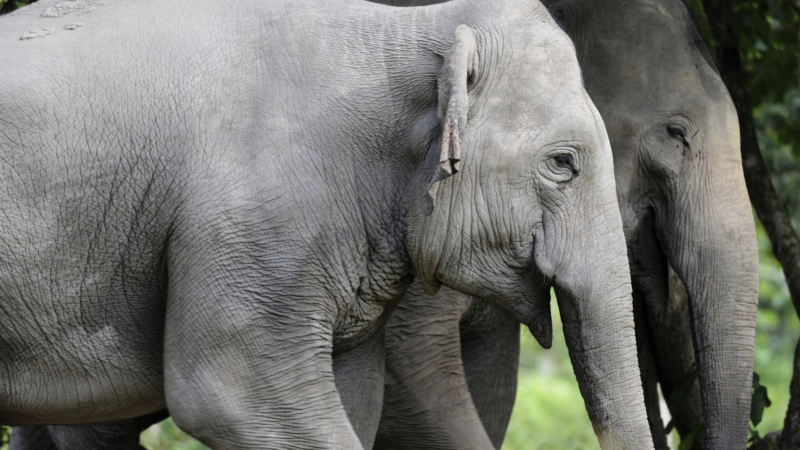
The Asian elephant population in Cambodia is more robust than previously thought
PHNOM PENH, Cambodia — A genetic study of Asian elephants in northern Cambodia published Thursday reveals a larger and more robust population than previously thought, raising hopes the endangered species could slowly recover.
Researchers from the Fauna & Flora conservation group collected samples from elephant dung in Cambodia’s northern plains and extracted DNA. From the DNA they were able to identify individual elephants, estimate population size, and determine the sex of the animals and the overall genetic diversity of the population.
From their work they estimated that there are 51 elephants in the Prey Lang, Preah Roka, and Chhaeb Wildlife Sanctuaries, with greater genetic diversity — a “critical factor for long-term viability,” the researchers said — than in two other areas of the country in which they live.
“With sufficient suitable habitat remaining in the region, the population has the potential to grow if properly protected,” the report concludes.

Overall, some 400 to 600 Asian elephants are believed to remain living in the wild in Cambodia. Researchers said the study’s findings underscore the potential of the northern area studied to become a “national stronghold” for them, contributing to Cambodia’s biodiversity conservation goals.
“Habitat degradation, especially when it leads to fragmentation, continues to be a serious concern,” Pablo Sinovas, director of Fauna & Flora in Cambodia, told The Associated Press.
“This study provides a robust basis on which to base conservation efforts and landscape management.”
The study, supported by USAID funds and Britain’s People’s Postcode Lottery, was conducted in collaboration with the Cambodian Environment Ministry. The genetic testing was done at the Royal University of Phnom Penh with technical support from the Royal Zoological Society of Scotland.
The research was carried out in the 2020-21 dry season, but Sinovas said since elephants reproduce slowly it is not thought that the population size would have changed significantly since then.

Researchers want to replicate the study elsewhere in Cambodia and in other countries, such as neighboring Vietnam where the Asian elephants live in fragmented populations.
“We were very pleasantly surprised by the results of the project,” said Alex Ball, conservation manager for the Royal Zoological Society of Scotland.
“We now hope to expand this methodology across Cambodia and beyond, helping to build a clearer picture of Asian elephant numbers, which will inform how best we can work to help reverse the decline of these spectacular animals.”
Italian fashion designer Valentino dies at 93
Garavani built one of the most recognizable luxury brands in the world. His clients included royalty, Hollywood stars, and first ladies.
Sheinbaum reassures Mexico after US military movements spark concern
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum quelled concerns on Monday about two recent movements of the U.S. military in the vicinity of Mexico that have the country on edge since the attack on Venezuela.
Trump says he’s pursuing Greenland after perceived Nobel Peace Prize snub
"Considering your Country decided not to give me the Nobel Peace Prize… I no longer feel an obligation to think purely of Peace," Trump wrote in a message to the Norwegian Prime Minister.
Trump has rolled out many of the Project 2025 policies he once claimed ignorance about
Some of the 2025 policies that have been implemented include cracking down on immigration and dismantling the Department of Education.
U.S. lawmakers wrap reassurance tour in Denmark as tensions around Greenland grow
A bipartisan congressional delegation traveled to Denmark to try to deescalate rising tensions. Just as they were finishing, President Trump announced new tariffs on the country until it agrees to his plan of acquiring Greenland.
Can exercise and anti-inflammatories fend off aging? A study aims to find out
New research is underway to test whether a combination of high-intensity interval training and generic medicines can slow down aging and fend off age-related diseases. Here's how it might work.