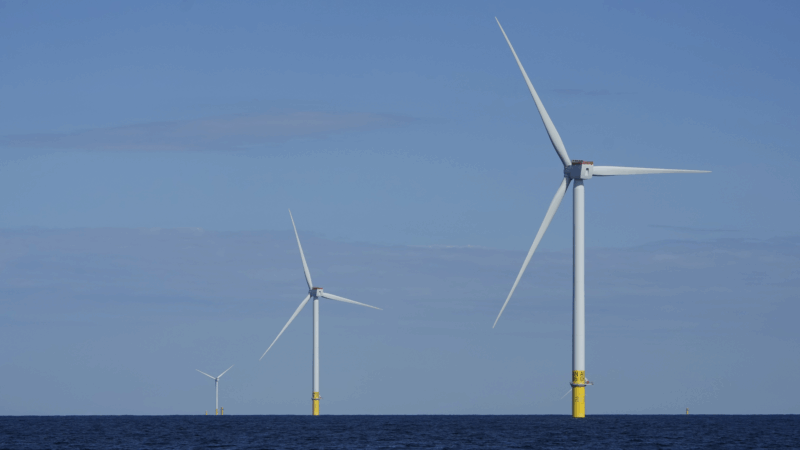
States sue Trump administration for blocking the development of wind energy
A coalition of state attorneys general filed a lawsuit Monday against President Donald Trump’s attempt to stop the development of wind energy.
Attorneys general from 17 states and Washington, D.C., are challenging an executive order Trump signed during his first day in office, pausing approvals, permits and loans for all wind energy projects both onshore and offshore. They say Trump doesn’t have the authority to unilaterally shut down the permitting process, and he’s jeopardizing development of a power source critical to the states’ economic vitality, energy mix, public health and climate goals.
They’re asking a federal judge to declare the order unlawful and stop federal agencies from implementing it.
“This arbitrary and unnecessary directive threatens the loss of thousands of good-paying jobs and billions in investments, and it is delaying our transition away from the fossil fuels that harm our health and our planet,” New York Attorney General Letitia James, who is leading the coalition, said in a statement.
White House spokesperson Taylor Rogers said Democratic attorneys general are “using lawfare to stop the president’s popular energy agenda,” instead of working with him to unleash American energy and lower prices for families.
“The American people voted for the president to restore America’s energy dominance, and Americans in blue states should not have to pay the price of the Democrats’ radical climate agenda,” Rogers said in a statement to The Associated Press.
Trump vowed during the campaign to end the offshore wind industry if he returned to the White House. His order said there were “alleged legal deficiencies underlying the federal government’s leasing and permitting” of wind projects, and it directed the Interior secretary to review wind leasing and permitting practices for federal waters and lands.
The lawsuit was filed in federal court in Massachusetts.
Trump’s order targeted a priority of Biden’s climate plan
The Biden administration saw offshore wind as a climate change solution, setting national goals, holding lease sales and approving nearly a dozen commercial-scale projects. Trump is reversing those energy policies. He’s boosting fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas and coal, which cause climate change, arguing it’s necessary for the U.S. to have the lowest-cost energy and electricity in the world.
The Trump administration took a more aggressive step against wind in April when it ordered the Norwegian company Equinor to halt construction on Empire Wind, a fully permitted project located southeast of Long Island, New York, that is about 30% complete. Interior Secretary Doug Burgum said it appeared the Biden administration rushed the approval.
Equinor went through a seven-year permitting process before starting to build Empire Wind last year to provide power to 500,000 New York homes. Equinor is considering legal options, which would be separate from the complaint filed Monday. The Norwegian government owns a majority stake in Equinor.
Wind provides about 10% of the electricity generated in the United States, making it the nation’s largest source of renewable energy. The attorneys general argue that Trump’s order is at odds with years of bipartisan support for wind energy and contradicts his own declaration of a “national energy emergency,” which called for expanding domestic energy production.
States have already invested large sums to develop wind energy
The coalition includes Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Washington and Washington, D.C. They say they’ve invested hundreds of millions of dollars collectively to develop wind energy and even more on upgrading transmission lines to bring wind energy to the electrical grid.
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul said the executive order sows chaos, when businesses need clear regulations to effectively operate.
Large, ocean-based wind farms are the linchpin of state plans to shift to renewable energy, particularly in populous East Coast states with limited land. The nation’s first commercial-scale offshore wind farm opened a year ago, a 12-turbine wind farm east of Montauk Point, New York. A smaller wind farm operates near Block Island in waters controlled by the state of Rhode Island.
Massachusetts has invested in offshore wind to ensure residents have access to well-paying green jobs and reliable, affordable energy, Massachusetts Attorney General Andrea Campbell said. The state has three offshore wind projects in various stages of development, include Vineyard Wind. The U.S. Supreme Court on Monday denied to hear a case brought by fishermen’s organizations challenging the approval of Vineyard Wind.
The Trump administration has also suspended federal funding for floating offshore wind research in Maine and revoked a permit for a proposed offshore wind project in New Jersey.
Elsewhere, political leaders are trying to rapidly increase wind energy. U.K. Prime Minister Keir Starmer announced a major investment in wind power in April while hosting an international summit on energy security. Nova Scotia plans to offer leases for five gigawatts of offshore wind energy by 2030, Nova Scotia Premier Tim Houston said in Virginia last week at an Oceantic Network conference.
A new Nepali party, led by an ex-rapper, is set for a landslide win in parliamentary election
A Nepali political party led by an ex-rapper is set for a landslide victory in the country's first parliamentary election since Gen Z protests ousted the old leadership that has ruled the Himalayan nation for decades.
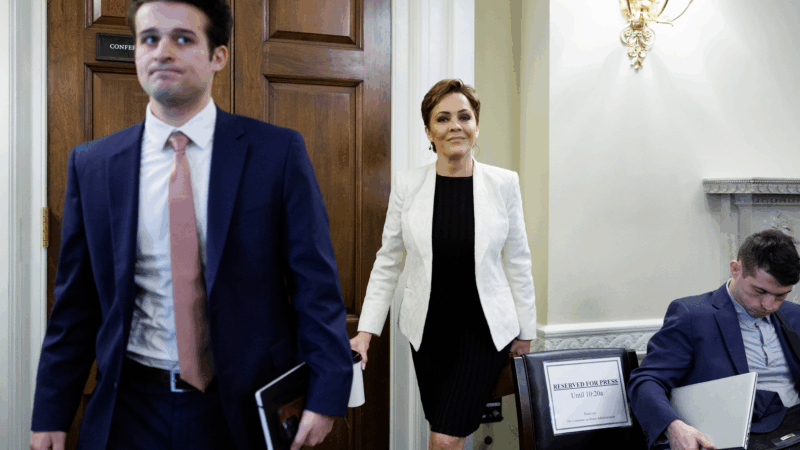
U.S. Judge says Kari Lake broke law in overseeing Voice of America
He declared all of Lake's actions over the past year to be null and void, including the layoffs of more than 1,000 journalists and staffers.
Trump vows to ‘take care of Cuba,’ praises Venezuela cooperation at summit
Trump made the promise in front of an assembled meeting of Latin American leaders.
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
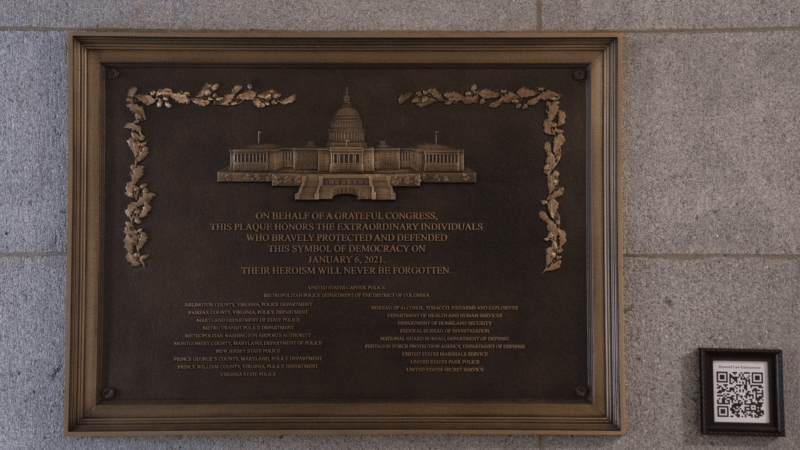
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
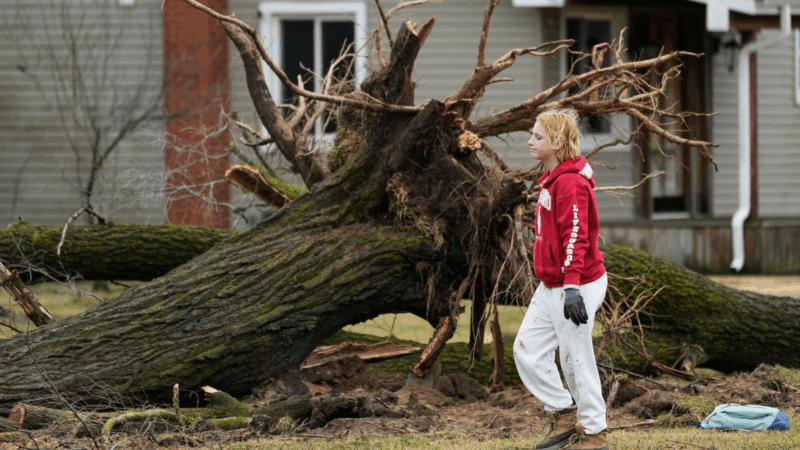
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.