Mount Etna erupts, shooting a massive ash cloud into the sky and raising alerts
Italy’s Mount Etna produced a spectacularly explosive eruption Monday morning, sending a ripple of reddish clouds down from its summit. The soaring ash rose to form a mushroom cloud high above Etna, Europe’s highest active volcano, triggering a red alert for aviation crews in the region.
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology’s Etna Observatory in Catania estimated the volcanic cloud’s height at about 21,325 feet. The massive ash cloud was moving in a west-southwest direction, according to the agency, known as INGV.
The dramatic scene at Etna’s southeast crater was caught on multiple webcams, spreading quickly across social media. As seen in a Weather Sicily webcam video, the eruption rapidly grew from a few lava flows to cascades of boiling ash and smoke that rose into a large cloud.
Thankfully, the eruption doesn’t seem to have had any immediate impact on people in the area, other than forcing officials to halt tourists’ visits to the volcano, which is a popular destination and is located on the east coast of Sicily.
Officials believe that a large portion of the crater collapsed, according to the Italian news agency ANSA.
Aviation alerts were eased later on Monday as the INGV said volcanic activity and ash emissions were finally decreasing. With the ash cloud moving toward the west, operations at Vincenzo Bellini Catania Airport, due south of Etna, weren’t affected.
It’s not unusual for Etna to emit lava and gases from its summit craters. Etna is “the most active stratovolcano in the world that has continuously pumped ash and lava” for thousands of years, according to the United Nations. (A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is often steep and conical, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. In contrast, shield volcanoes, like Hawaii’s Mauna Loa, are larger but with a more gradual slope.)
Etna has a long history of frequent eruptions, documented at least to 1500 B.C.
Most of Etna’s eruptions are “Strombolian eruptions” — ejections of cinder, gas and molten lava that result from repeated, but relatively small, explosions.
“The Strombolian activity generally affects a limited area around the vent and is not an agent of risk [to] built up areas” around Etna, according to Italy’s Civil Protection Department. Etna’s lava flows are also normally viscous and slow-moving, often allowing authorities to intervene to redirect flows that threaten communities.
Etna’s eruptions have produced striking scenes over the years, from a vivid nighttime display in 2011 to an outburst that preceded an earthquake in 2018.
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
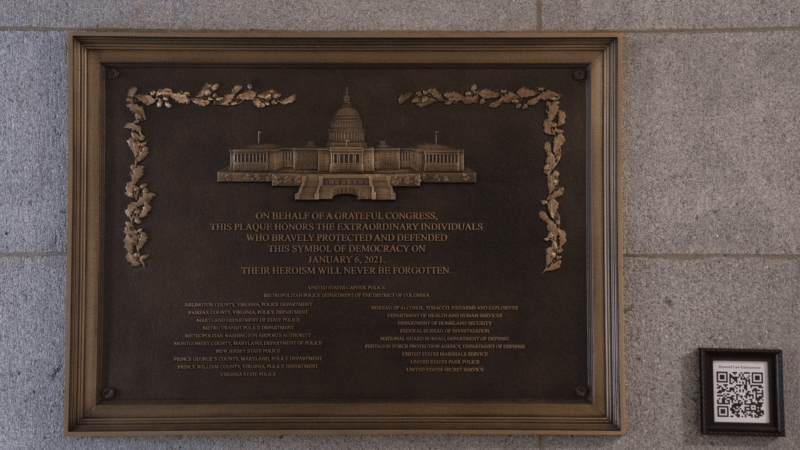
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
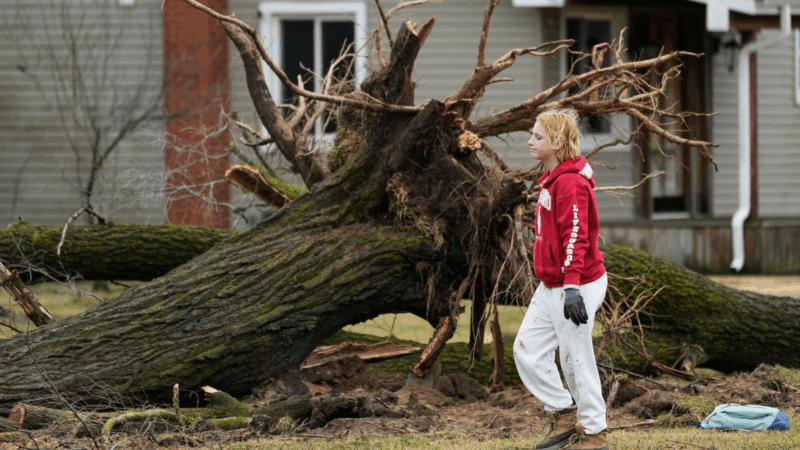
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
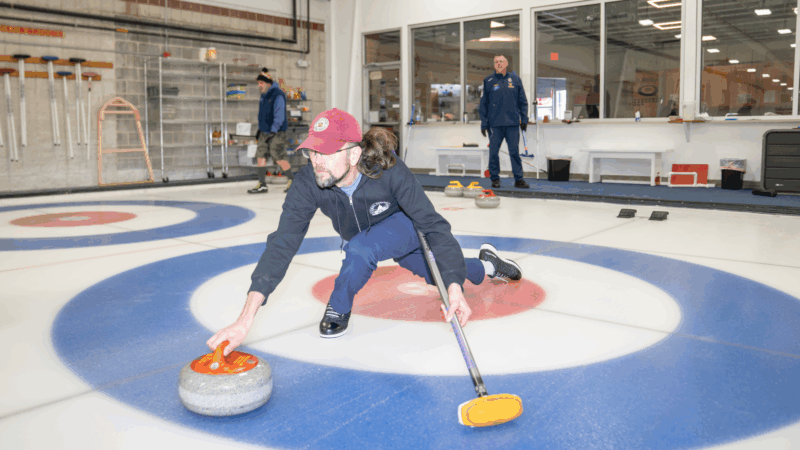
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.