In reversal, Defense Department will continue providing crucial satellite weather data
The Department of Defense has reversed a decision to stop sharing satellite weather data that hurricane forecasters rely on.
In June, the Navy announced that it would stop sharing the crucial information about storms, as peak hurricane season loomed in the Atlantic. In response, scientists and weather forecasters expressed fear that the missing data could lead to less accurate and timely hurricane forecasts.
The Navy’s Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center, which processes and shares the data, “planned to phase out the data as part of a Defense Department modernization effort,” a Navy spokesperson wrote in an email to NPR. “But after feedback from government partners, officials found a way to meet modernization goals while keeping the data flowing until the sensor fails or the program formally ends in September 2026.”
The Defense Department operates satellites that collect information about conditions in the atmosphere and ocean, and for more than 40 years, it has shared that data with scientists and meteorologists.
The information is particularly useful for hurricane forecasters, because it allows them to watch storms in real-time as they form, according to Brian Tang, a hurricane researcher at the University at Albany. Tang says he is happy to hear that the Navy reconsidered its decision. “It’s vital that the data continue to be available through the heart of the Atlantic hurricane season,” he says.
Tracking storms as they gather strength allows forecasters to put out warnings earlier, giving people in harm’s way more time to prepare and evacuate.
The data are also crucial for monitoring sea ice in polar regions. Sea ice coverage affects weather patterns and international shipping, and is also an important source of information about how the planet is responding to climate change.
Before the latest announcement, the Navy had already pushed back the date for ending its data sharing with scientists once. The termination date was originally the end of June, but after an outcry from scientists and forecasters, it was updated to the end of July, according to the Navy. It is unclear what will happen to the satellite data after September 2026.
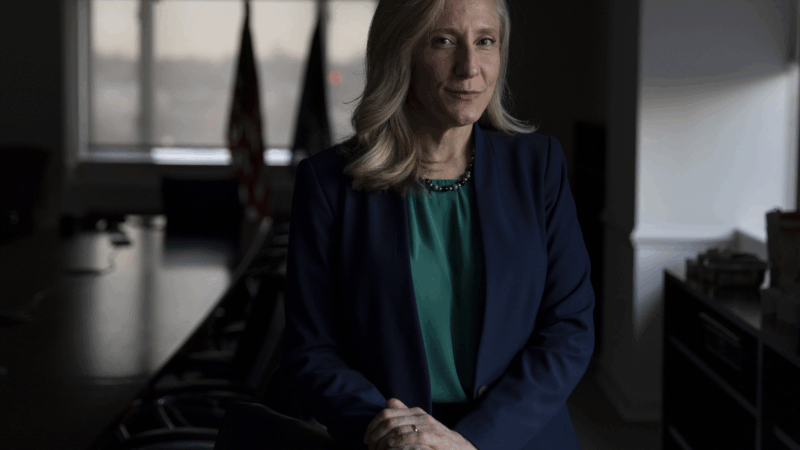
It took 75 governors to elect a woman. Spanberger will soon be at Virginia’s helm
Abigail Spanberger, a former CIA officer and three-term congresswoman, is breaking long-held traditions on inauguration day. She says she wants her swearing-in to showcase the state's modern vibrancy.
For those with addiction, going into and coming out of prison can be a minefield.
Many jails and prisons around the country don't provide medication treatment for opioid use disorder. Studies show that medication makes recovery more likely and reduces the risk of overdose death.
Trump struck deals with 16 drug companies. But they’re still raising prices this year
All 16 drug companies that inked deals with the Trump administration over the past few months still raised some of their prices for 2026.
This hospice has a bold new mission: saving lives
A hospice in Uganda asked itself: Can we do more than ease the pain of dying? Can we actually prevent deaths from cervical and breast cancer?
Ivey releases proposed state budgets
Lawmakers are often running in Montgomery having finished the first week of this year's legislative session. It's a week that saw the announcement of Gov. Kay Ivey's budget proposal, along with the first bills starting to make their way through the legislative process. We talk about that with Todd Stacy, host of Capital Journal on Alabama Public Television.
Canada agrees to cut tariff on Chinese EVs in return for lower tariffs on Canadian farm products
Breaking with the United States, Canada has agreed to cut its 100% tariff on Chinese electric cars in return for lower tariffs on Canadian farm products, Prime Minister Mark Carney said Friday.