Hundreds of Rwandans who fled to Congo after the 1994 genocide return home
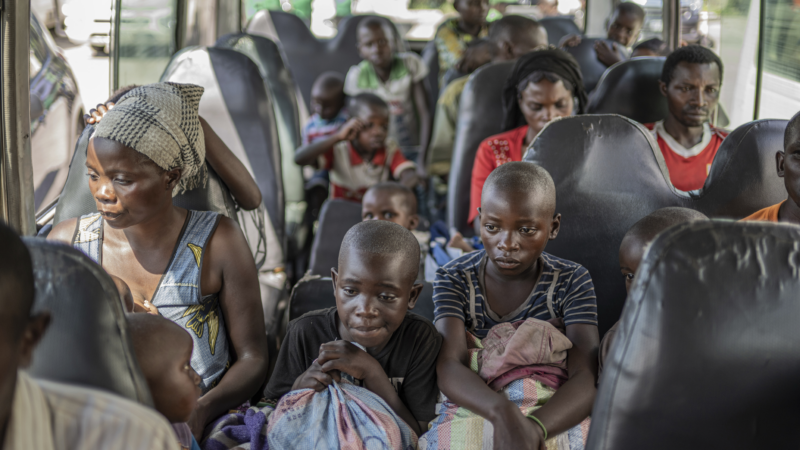
GOMA, Congo — Hundreds of Rwandan refugees who were living in eastern Congo since the 1994 genocide in Rwanda were repatriated on Saturday, the U.N. refugee agency said, after Rwandan-backed rebels seized key parts of the region.
Most of the refugees were women and children, and 360 of them crossed the border in buses provided by Rwandan authorities and were escorted by the U.N. High Commissioner for Refugees, and aid group Save the Children, local authorities said. The goal is to repatriate 2,000 people, UNHCR said.
“We are happy to welcome our compatriots. They are a valuable workforce for the country’s development,” said Prosper Mulindwa, the Rwandan mayor of Rubavu, during a brief ceremony at the border.
The returnees were transported to a transit center where they will receive emergency assistance and support for reintegration.
They were among the hundreds of thousands of Hutus who fled Rwanda after the state-sponsored 1994 genocide that left up to a million minority Tutsis and moderate Hutus dead. Most had returned when Tutsi-led Rwandan troops first invaded Congo in 1996. But Rwandan authorities said thousands of Hutu militiamen and ex-soldiers had stayed and joined Congo’s army to destabilize Rwanda.
For decades, mineral-rich eastern Congo has been ripped apart by violence from government forces and different armed groups, including the Rwanda-backed M23, whose recent resurgence has escalated the conflict and worsened an already acute humanitarian crisis.
The rebels are supported by about 4,000 troops from neighboring Rwanda, according to U.N. experts.
Among the Rwandan returnees, personal testimonies highlighted journeys marked by exile and a deep connection to a homeland some have never known.
Nyirakajumba Twizere was born in 1996 in Congo and had never seen Rwanda.
“I never thought this day would come,” he said. “I’m finally going back to the land of my ancestors.”
The repatriation is based on a tripartite agreement between Rwanda, Congo and UNHCR that has been in place for more than a decade. According to Rwandan authorities, more than 101,000 refugees have already been repatriated, including 1,500 since the beginning of 2025.
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
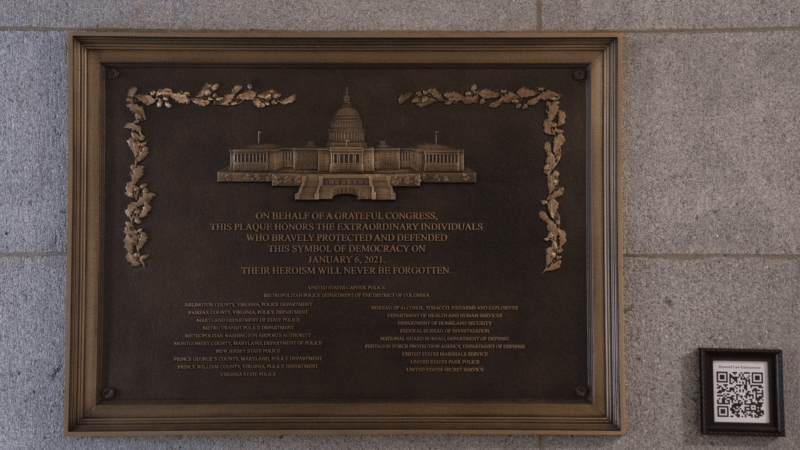
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
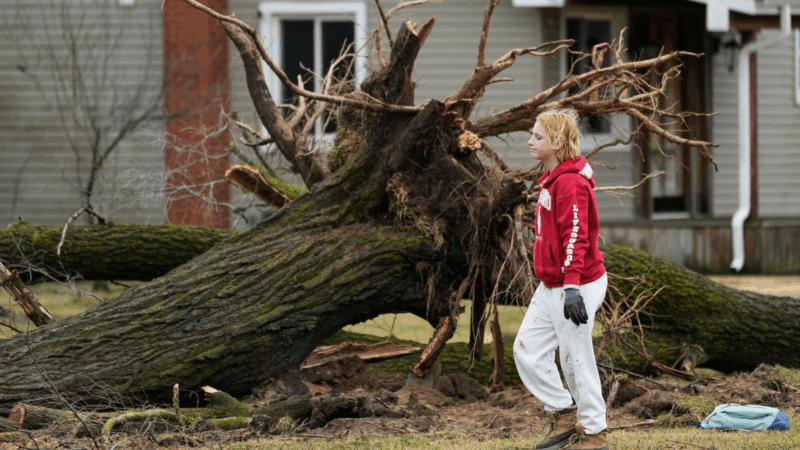
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
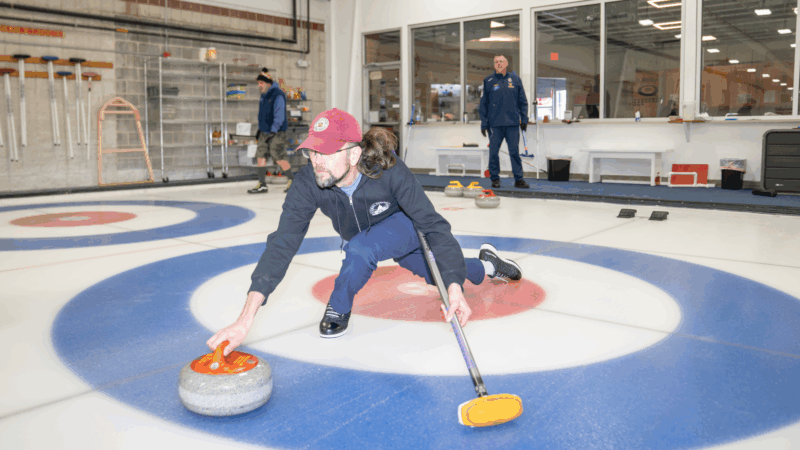
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.