Federal trade court blocks Trump from imposing tariffs under emergency powers law
WASHINGTON — A federal trade court on Wednesday blocked President Donald Trump from imposing sweeping tariffs on imports under an emergency-powers law.
The ruling from a three-judge panel at the New York-based Court of International Trade came after several lawsuits arguing Trump has exceeded his authority, left U.S. trade policy dependent on his whims and unleashed economic chaos.
“The Worldwide and Retaliatory Tariff Orders exceed any authority granted to the President by IEEPA to regulate importation by means of tariffs,” the court wrote, referring to the 1977 International Emergency Economic Powers Act.
The White House did not immediately respond to a message seeking comment. The Trump administration is expected to appeal.
At least seven lawsuits are challenging the levies, the centerpiece of Trump’s trade policy.
Tariffs must typically be approved by Congress, but Trump says he has the power to act because the country’s trade deficits amount to a national emergency. He imposed tariffs on most of the countries in the world at one point, sending markets reeling.
The plaintiffs argued that the emergency powers law does not authorize the use of tariffs, and even if it did, the trade deficit does not meet the law’s requirement that an emergency be triggered only by an “unusual and extraordinary threat.” The U.S. has run a trade deficit with the rest of the world for 49 consecutive years.
Trump imposed tariffs on most of the countries in the world in an effort to reverse America’s massive and longstanding trade deficits. He earlier plastered levies on imports from Canada, China and Mexico to combat the illegal flow of immigrants and the synthetic opioids across the U.S. border.
His administration argues that courts approved then-President Richard Nixon’s emergency use of tariffs in 1971, and that only Congress, and not the courts, can determine the “political” question of whether the president’s rationale for declaring an emergency complies with the law.
Trump’s Liberation Day tariffs shook global financial markets and led many economists to downgrade the outlook for U.S. economic growth. So far, though, the tariffs appear to have had little impact on the world’s largest economy.
The lawsuit was filed by a group of small businesses, including a wine importer, V.O.S. Selections, whose owner has said the tariffs are having a major impact and his company may not survive.
A dozen states also filed suit, led by Oregon. “This ruling reaffirms that our laws matter, and that trade decisions can’t be made on the president’s whim,” Attorney General Dan Rayfield said.
___
Associated Press writers Zeke Miller and Paul Wiseman contributed to this story.
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
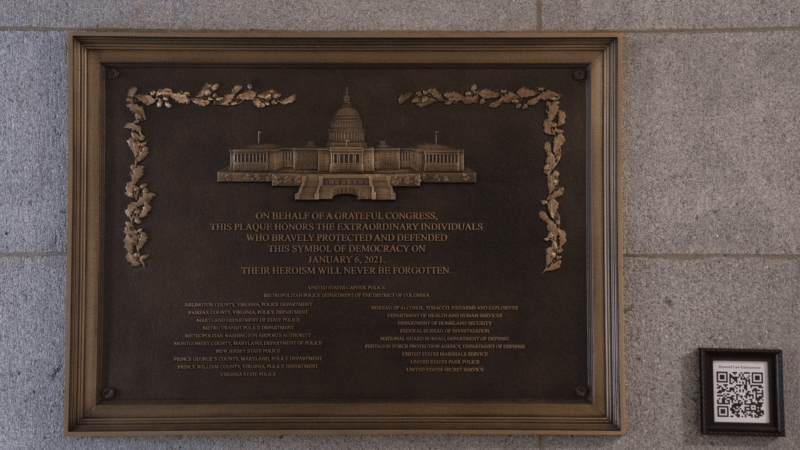
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
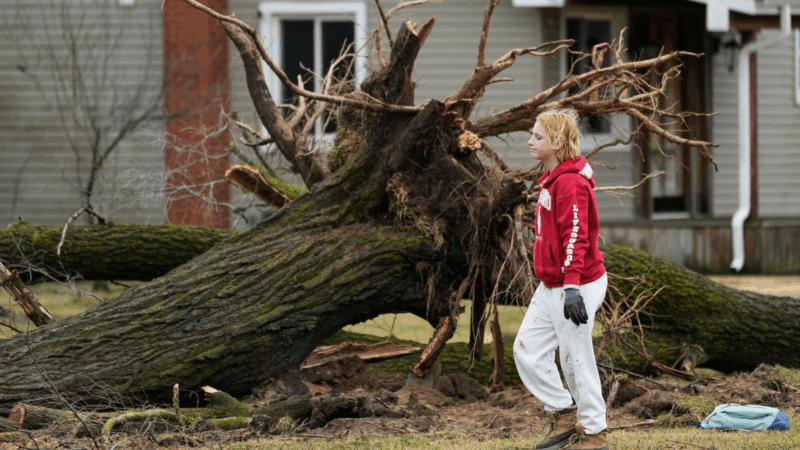
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
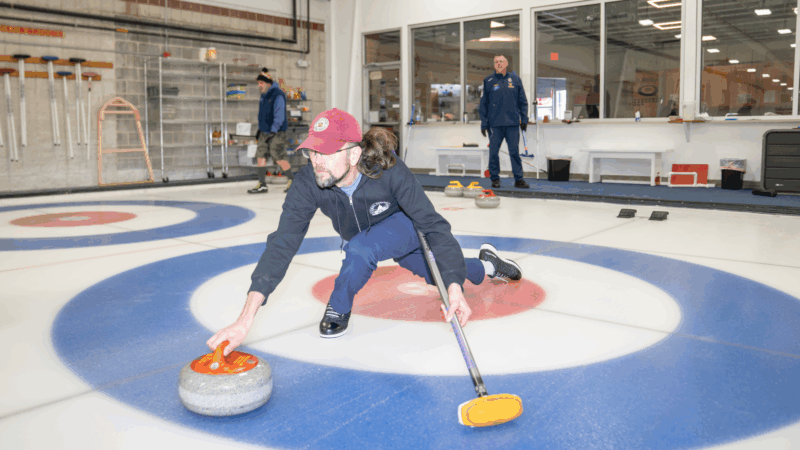
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.