Eating yogurt regularly may reduce the risk of colon cancer, a study finds
Humans have been consuming yogurt for millennia. Ancient texts dating back to 6,000 B.C. reference its health-promoting properties. Now, a new study finds one more benefit to a long-term yogurt habit: It may protect against certain types of aggressive colon cancer through changes in the gut microbiome.
In the study, researchers at Mass General Brigham looked at data from more than 150,000 people who were followed for at least three decades. They found that people who regularly ate two or more servings of yogurt a week had lower rates of certain types of colorectal cancer.
“Yogurt may be good for maintaining a good microbiome in our body,” says Dr. Tomotaka Ugai, a co-senior author of the study. He’s an investigator at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a department associate at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Specifically, the researchers found that the habitual yogurt eaters had lower rates of Bifidobacterium-positive proximal colon cancers. Proximal colon cancer is a type of colon cancer that occurs on the right side of the colon and can have worse survival outcomes than cancers that occur in the distal colon, which is on the left side.
Ugai says the bacteria in yogurt appear to promote an overall healthy balance of bacteria in the gut. And that, in turn, promotes a strong and healthy gut barrier, which is important, because when the gut barrier becomes too permeable, it can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of colon cancer.
“My message is, if you like yogurt, go for it,” Ugai says.
The findings are in line with prior studies that have linked yogurt intake to a lower risk of colon cancer, says Dr. Chris Damman, a gastroenterologist and professor at the University of Washington who studies the intersection of the microbiome and metabolic disease.
“It builds on the evidence that yogurt may be protective,” he says.
Other studies have linked regular yogurt consumption to other health benefits, including a lower risk of Type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis and of dying from cardiovascular disease.
Yogurt is a fermented food, meaning it is produced when microbes break down sugars in foods in a way that produces complex flavors and prevents them from spoiling. One randomized controlled trial found that people assigned to eat a diet rich in yogurt and other fermented foods — such as kefir, fermented cottage cheese, kimchi and kombucha tea — for 10 weeks had lower markers of inflammation and improved diversity of microbes in their gut.
Damman says that along with fiber, healthy fats and nutrients known as polyphenols found in plant-based foods, yogurt and other fermented foods are a staple of a healthy gut.
“These are the common denominators across culinary traditions and healthy eating,” he says.
From Middle Eastern cream cheese-like labneh to Persian abdoogh khiar soup and Indian raita, cultures around the world have long embraced yogurt as a culinary staple.
But before adding yogurt to your diet be sure to check the nutrition label. Research has found that, despite its health halo, many yogurts can be loaded with added sugar. Your best bet is to stick with yogurts without added sugar. Add some berries, bananas or other fruit if you miss that hint of sweetness.
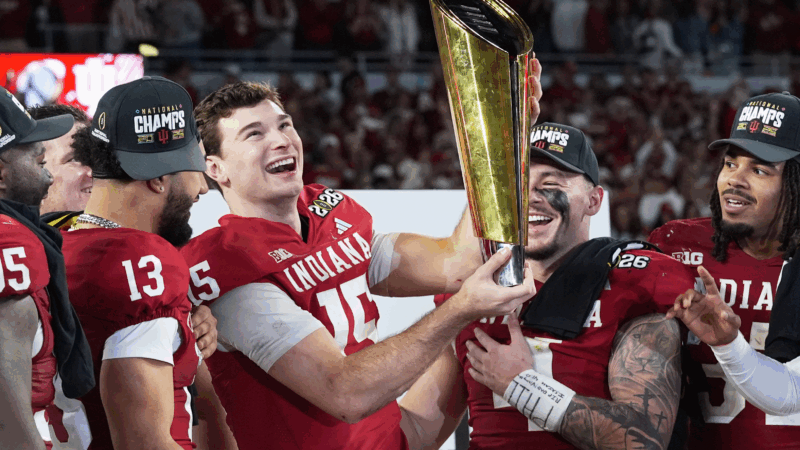
Indiana completes undefeated season and wins first national title, beating Miami
Indiana bullied its way into the history books Monday night, toppling Miami 27-21 to put the finishing touch on a rags-to-riches story, an undefeated season and the national title.
Top U.S. archbishops denounce American foreign policy
The three most-senior cardinals leading U.S. archdioceses issued the rebuke in a joint statement on Monday, saying recent policies have thrown America's "morale role in confronting evil" into question.
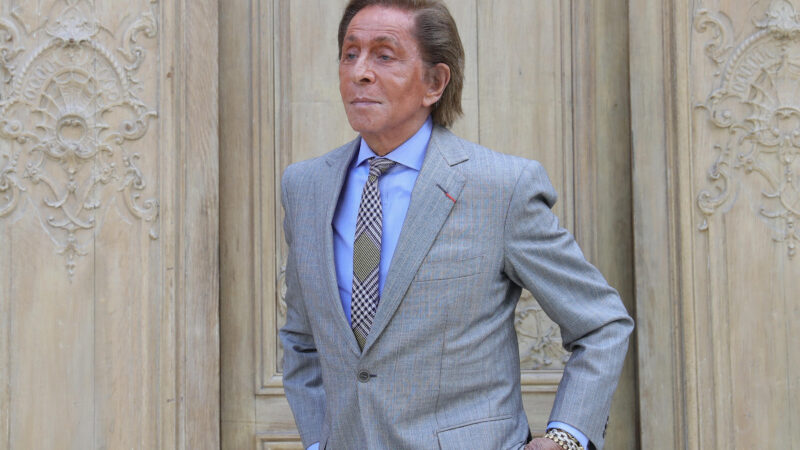
Italian fashion designer Valentino dies at 93
Garavani built one of the most recognizable luxury brands in the world. His clients included royalty, Hollywood stars, and first ladies.
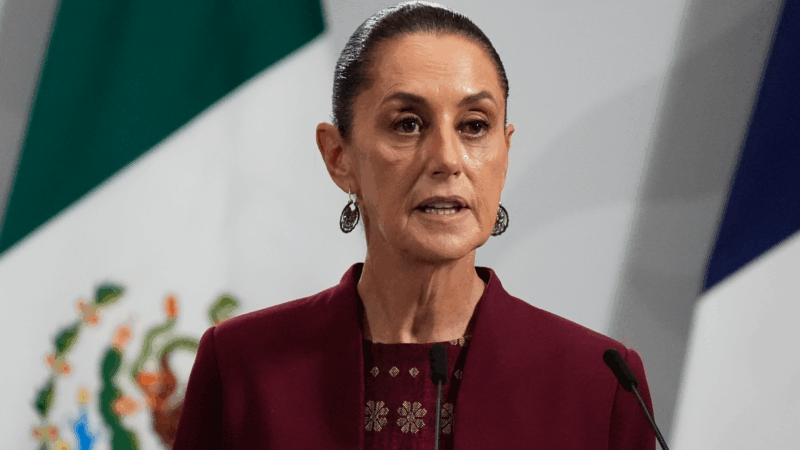
Sheinbaum reassures Mexico after US military movements spark concern
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum quelled concerns on Monday about two recent movements of the U.S. military in the vicinity of Mexico that have the country on edge since the attack on Venezuela.
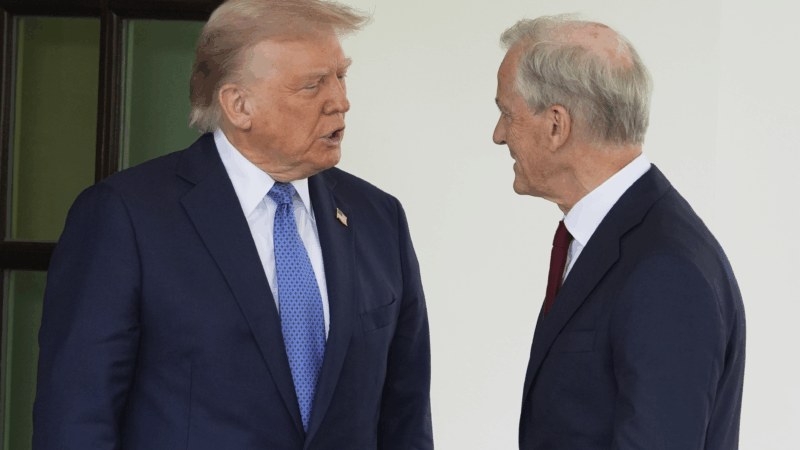
Trump says he’s pursuing Greenland after perceived Nobel Peace Prize snub
"Considering your Country decided not to give me the Nobel Peace Prize… I no longer feel an obligation to think purely of Peace," Trump wrote in a message to the Norwegian Prime Minister.
Can exercise and anti-inflammatories fend off aging? A study aims to find out
New research is underway to test whether a combination of high-intensity interval training and generic medicines can slow down aging and fend off age-related diseases. Here's how it might work.