A telescope’s powerful new tool may offer a better way to predict solar storms
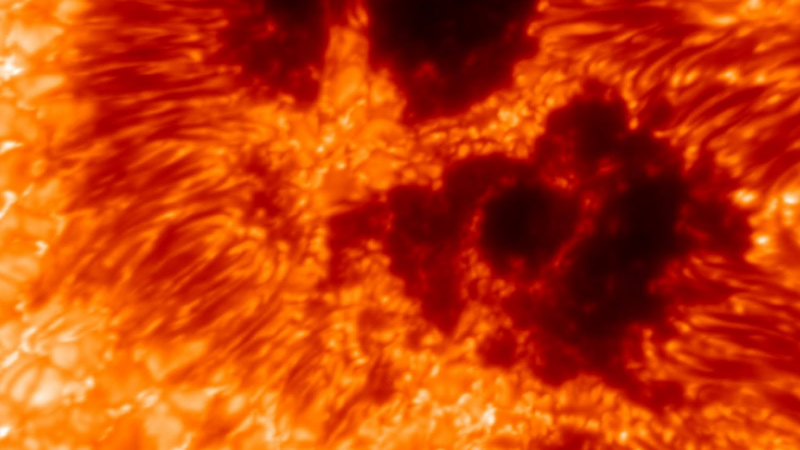
The most powerful solar telescope in the world has recorded a major milestone atop an active volcano in Hawaii, capturing a detailed image of a cluster of sunspots with the telescope’s new Visible Tunable Filter (VTF).
Scientists hope that in the future the instrument will help predict powerful and potentially damaging solar storms.
The Daniel K. Inouye Telescope snapped the photo of the roaring star late last month from the summit of the Haleakalā volcano in Maui.
The National Solar Observatory (NSO), which operates the telescope, said that the image was taken during technical testing and that the VTF is not yet even fully operational. But the fact that the telescope was able to capture such an image at this phase shows how powerful the device will eventually be.

The NSO describes sunspots as “areas of intense magnetic activity” that can trigger solar flares and coronal mass ejections — phenomena that can have damaging effects on Earth’s radio communications and electrical grids.
“After all these years of work, VTF is a great success for me,” said Thomas Kentischer, co-principal investigator at Germany’s Leibniz Institute for Solar Physics, where the VTF was designed.
“I hope this instrument will become a powerful tool for scientists to answer outstanding questions on solar physics,” Kentischer added.

Matthias Schubert, a project scientist at the institute, spoke poetically of the highly technical device.
“The significance of the technological achievement is such that one could easily argue the VTF is the Inouye Solar Telescope’s heart, and it is finally beating at its forever place,” he said.
The NSO described the sun as “a plasma laboratory right on our doorstep” and said that the VTF’s image gives promise that with time, the telescope will help scientists better predict when powerful solar storms are coming toward Earth in order to mitigate the damage these geomagnetic disturbances might cause.
While the team of researchers hailed the success of the telescope, the road to its construction was marked by years of protests against the placement of yet another massive device on what many native Hawaiians view as sacred land.

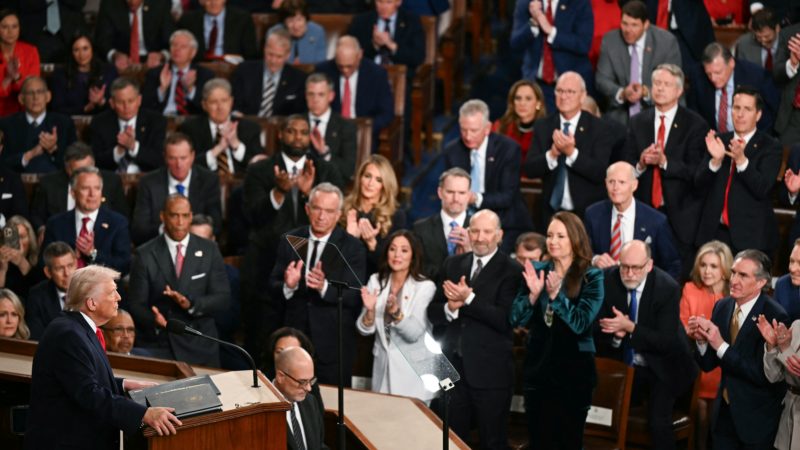
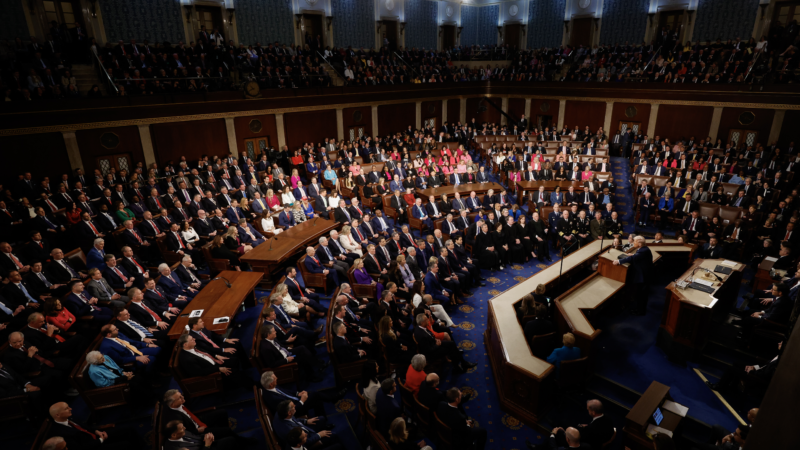
Read NPR’s annotated fact check of President Trump’s State of the Union
As President Trump delivers his State of the Union address, reporters from across NPR's newsroom will fact check his speech and offer context.
President Trump set to deliver first State of the Union address of his second term
Facing low approval ratings and ahead of midterm elections in November, President Trump delivers the first State of the Union address of his second term as president Tuesday night.
U.S. House rejects aviation safety bill after Pentagon abruptly withdraws support
The House of Representatives narrowly rejected a bipartisan aviation safety bill that was spurred by the deadly midair collision near Washington, D.C. after the Pentagon abruptly withdrew its support.
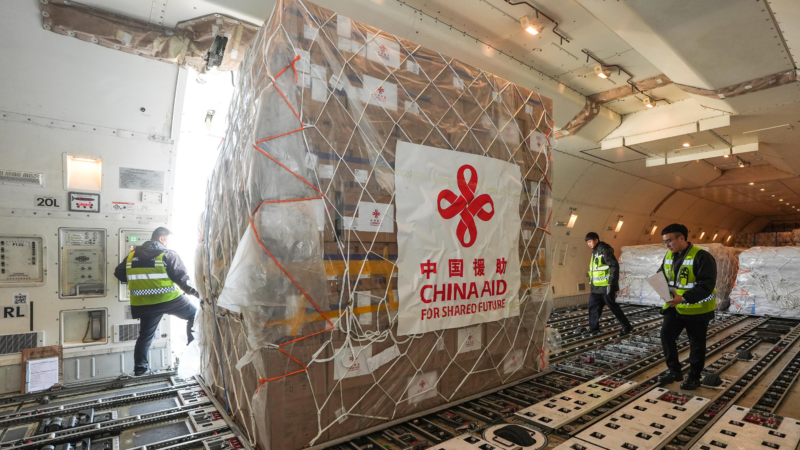
China and the US alter foreign aid strategies
China's foreign aid strategy has shifted in the last few decades and now its model may be the one the US is adopting as China moves away from it.
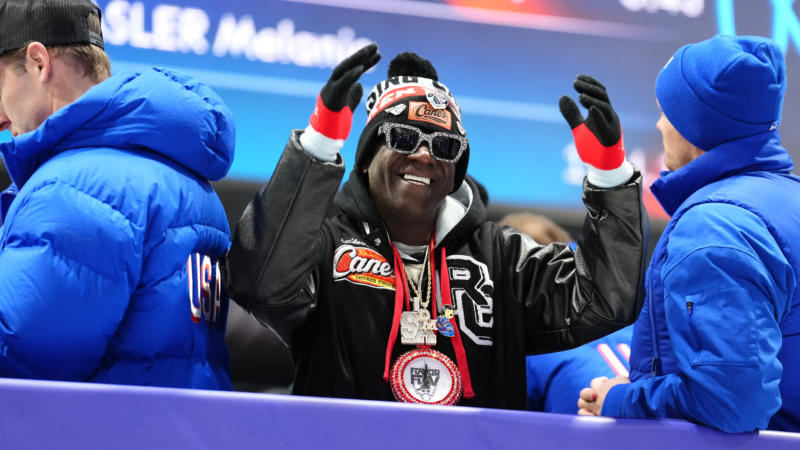
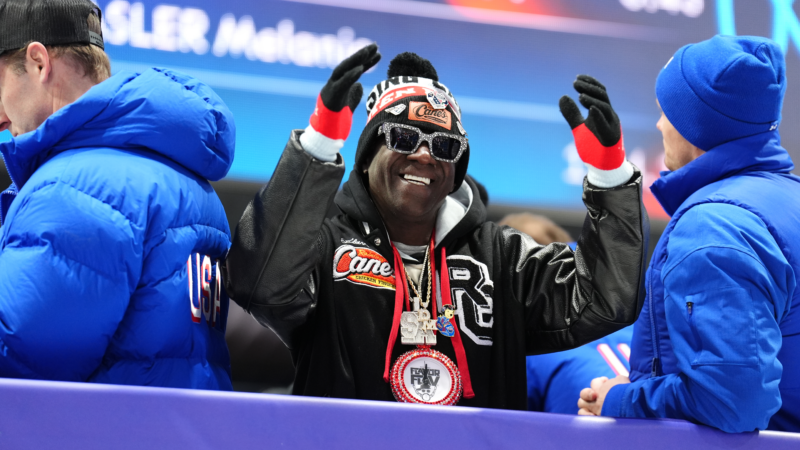
Flavor Flav is among women’s hockey team fans outraged by presidential snub
The rapper, who also serves as the official "hype man" for multiple U.S. Olympic teams, invited the female hockey players to Las Vegas for a "real celebration."
Flavor Flav is among women’s hockey team fans outraged by presidential snub
The rapper, who also serves as the official "hype man" for multiple U.S. Olympic teams, invited the female hockey players to Las Vegas for a "real celebration."