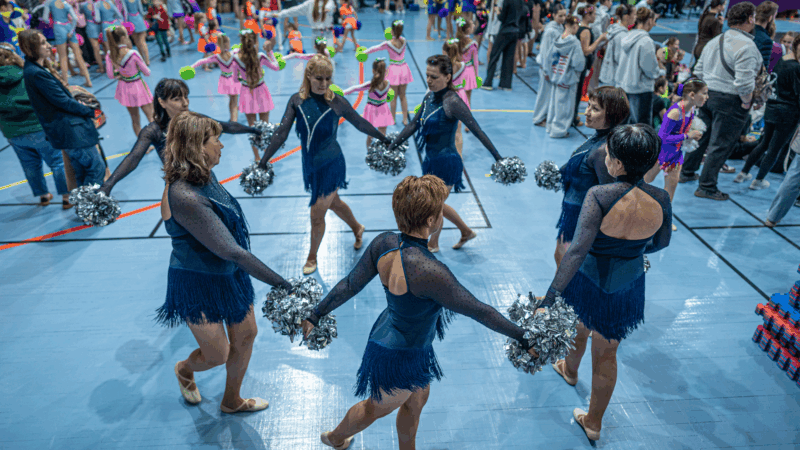Trump’s efforts to defund NPR and PBS playing out in Congress and the courts
The Trump administration is trying to cut federal funding for public broadcasting on multiple fronts. One of those efforts is an executive order, issued in May, that instructs federal agencies to cease funding for NPR and PBS.
Another is an attempt to claw back $1.1 billion that had already been allocated by Congress to the Corporation for Public Broadcasting – money that would flow to local stations along with the two networks.
Theodore Boutrous is an attorney, representing NPR in a lawsuit against the Trump White House over the president’s executive order. He said one of the main reasons Trump and his Republican allies want to cut funding is because they say the two networks are biased.
Boutrous disagrees that the content is politically one-sided, but said Trump’s objections to the content make the networks’ case stronger.
“This executive order could not be clearer in its intent to directly interfere with the independence of NPR,” Boutrous said. “It is absolutely blatant and clear that’s its goal, that it’s based on the fact that the president and members of his administration do not like the content.
“It flies in the face of the First Amendment,” Boutrous continued. “Viewpoint discrimination by the government [is] one of the worst offenses you can have under the Constitution, and the Public Broadcasting Act, which was meant to insulate the public broadcasting system from interference from the government.”
Boutrous added the request to rescind funding – the effort to take back money already appropriated – is cut from the same cloth.
“It’s retaliatory with respect to NPR and PBS and their content. And that, again, is unconstitutional,” he said.
Wayne Reid is the executive director of Alabama Public Television. He agreed the executive order and rescission request are clear-cut attempts to interfere with public broadcasting, and they run counter to the very reason Congress created the CPB.
“Nobody should dictate over what the programming is,” Reid said. “That’s at the station’s discretion, as long as it fits within the FCC guidelines.”
Reid added that if the order is allowed to stand, almost every national program APT gets through PBS would be in jeopardy. On top of that, if the rescission request passes, APT and the NPR member station it owns in Huntsville – WLRH – would lose a total of about $3 million, or about 10 percent of its annual funding.
“It’s quite a substantial amount of money,” Reid said. “We would have to take a deep look at our budget. So, we are doing everything we can to prepare for what-if scenarios and have a plan in place.”
WBHM, Birmingham’s NPR member station, would also lose about 10 percent of its annual funding, according to Will Dahlberg, the station’s executive director.
On Thursday, the House passed the rescission resolution 214-212 on a mostly party-line vote. It now moves to the Senate.
WBHM reached out to both of Alabama’s senators asking whether they will vote for rescission. Only U.S. Senator Tommy Tuberville replied.
While he did not answer the question directly, Tuberville told WBHM through a spokesperson that he is “100 percent supportive of the Trump administration’s efforts to claw back wasteful spending.”
Boutrous, the attorney representing NPR, says a ruling in the court case over the executive order could come as early as this summer. As for the rescission request, the Senate has until July 18 to act on Trump’s request. If the body doesn’t approve the rescission by that deadline, the White House is required to spend the money, under a decades-old law enacted to block presidents from withholding federal funds Congress has already allocated.
This story was reported and written by WBHM’s Richard Banks and edited by Managing Editor Andrew Yeager. In following NPR’s protocol for reporting on itself, no WBHM executive reviewed this story before it was posted publicly.
Forget the State of the Union. What’s the state of your quiz score?
What's the state of your union, quiz-wise? Find out!
A team of midlife cheerleaders in Ukraine refuses to let war defeat them
Ukrainian women in their 50s and 60s say they've embraced cheerleading as a way to cope with the extreme stress and anxiety of four years of Russia's full-scale invasion.
As the U.S. celebrates its 250th birthday, many Latinos question whether they belong
Many U.S.-born Latinos feel afraid and anxious amid the political rhetoric. Still, others wouldn't miss celebrating their country
SNL mocked her as a ‘scary mom.’ In the Senate, Katie Britt is an emerging dealmaker
Sen. Katie Britt, Republican of Alabama, is a budding bipartisan dealmaker. Her latest assignment: helping negotiate changes to immigration enforcement tactics.
Nancy Guthrie case: How do families of missing people cope with the uncertainty?
When a loved one goes missing, relatives can feel guilty simply for eating, says Charlie Shunick, whose sister was kidnapped. Shunick now helps others navigate a nightmare "nobody is prepared for."
This community festival embraces the joys of a frozen lake — while it still has one
As climate change accelerates, local experts say the date Wisconsin's Lake Mendota freezes over is getting later, making safe conditions for activities that rely on snow and ice harder to predict.