Judges reject Alabama’s congressional lines, will draw new districts to increase Black voting power
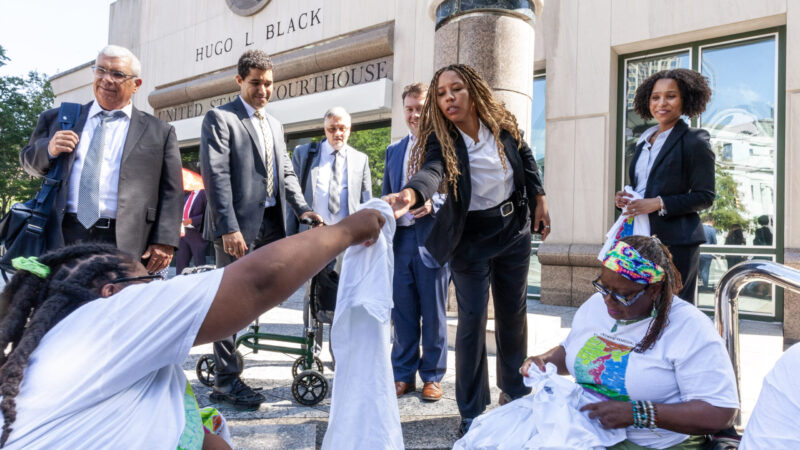
Plaintiffs in a high-profile redistricting case hand t-shirts to a group of their lawyers after a hearing on Monday, August 14, 2023, in Birmingham, Alabama.
MONTGOMERY, Ala. (AP) — Federal judges said Tuesday that they will draft new congressional lines for Alabama after lawmakers refused to create a second district where Black voters at least came close to comprising a majority, as suggested by the court.
The three-judge panel blocked use of the state’s newly drawn congressional map in next year’s elections. A special master will be tapped to draw new districts for the state, the judges said. Alabama is expected to appeal the decision to the U.S. Supreme Court.
“This is a significant step toward equal representation for Black Alabamians,” said former U.S. Attorney General Eric Holder, chairman of the National Democratic Redistricting Committee, which backed one of the court challenges that led to the decision.
The Republican-controlled Alabama Legislature hastily drew new lines this summer after the U.S. Supreme Court in June upheld the panel’s finding that the map — that had one majority-Black district out of seven in a state where 27% of residents are Black — likely violated the U.S. Voting Rights Act.
The three-judge panel, in striking down Alabama’s map in 2022, said the state should have two districts where Black voters have an opportunity to elect their preferred candidates. Because of racially polarized voting in the state, that map would need to include a second district where Black voters are the majority or “something quite close,” the judges wrote.
Alabama lawmakers in July passed a new map that maintained a single majority-Black district and boosted the percentage of Black voters in another district, District 2, from about 30% to almost 40%.
The three judges said Monday that they were “deeply troubled” that Alabama lawmakers enacted a map that ignored their finding that the state should have an additional majority-Black district “or an additional district in which Black voters otherwise have an opportunity to elect a representative of their choice.”
“We are not aware of any other case in which a state legislature — faced with a federal court order declaring that its electoral plan unlawfully dilutes minority votes and requiring a plan that provides an additional opportunity district — responded with a plan that the state concedes does not provide that district. The law requires the creation of an additional district that affords Black Alabamians, like everyone else, a fair and reasonable opportunity to elect candidates of their choice. The 2023 Plan plainly fails to do so,” the judges wrote.
In a hearing last month, all three judges pointedly questioned the state’s solicitor general about the state’s refusal to create a second majority-Black district.
“What I hear you saying is the state of Alabama deliberately chose to disregard our instructions to draw two majority-Black districts or one where minority candidates could be chosen,” Judge Terry Moorer said.
The state argued the map complied with the Voting Rights Act and the Supreme Court decision in the case. The state argued that justices did not require the creation of a second majority-Black district if doing so would mean violating traditional redistricting principles, such as keeping communities of interest together.
“District 2 is as close as you are going to get to a second majority-Black district without violating the Supreme Court’s decision,” Alabama Solicitor General Edmund LaCour replied to Moorer.
Abha Khanna, an attorney representing one group of plaintiffs in the case, argued during the hearing that Alabama chose “defiance over compliance” and urged the judges to reject the state’s map.
“Alabama has chosen instead to thumb its nose at this court and to thumb its nose at the nation’s highest court and to thumb its nose at its own Black citizens,” Khanna said.
In this Icelandic drama, a couple quietly drifts apart
Icelandic director Hlynur Pálmason weaves scenes of quiet domestic life against the backdrop of an arresting landscape in his newest film.
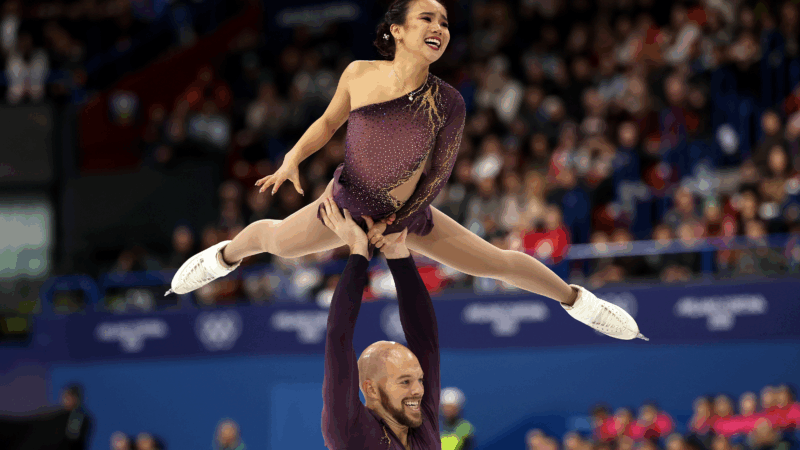
After the Fall: How Olympic figure skaters soar after stumbling on the ice
Olympic figure skating is often seems to take athletes to the very edge of perfection, but even the greatest stumble and fall. How do they pull themselves together again on the biggest world stage? Toughness, poise and practice.
They’re cured of leprosy. Why do they still live in leprosy colonies?
Leprosy is one of the least contagious diseases around — and perhaps one of the most misunderstood. The colonies are relics of a not-too-distant past when those diagnosed with leprosy were exiled.
This season, ‘The Pitt’ is about what doesn’t happen in one day
The first season of The Pitt was about acute problems. The second is about chronic ones.
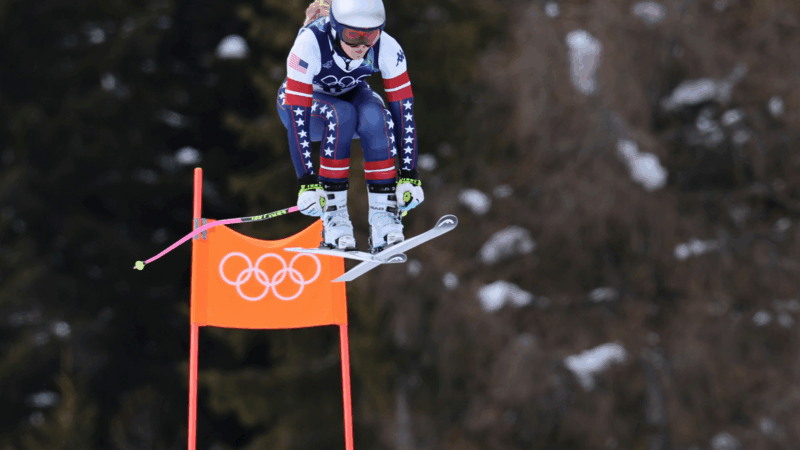
Lindsey Vonn is set to ski the Olympic downhill race with a torn ACL. How?
An ACL tear would keep almost any other athlete from competing -- but not Lindsey Vonn, the 41-year-old superstar skier who is determined to cap off an incredible comeback from retirement with one last shot at an Olympic medal.
Trump promised a crypto revolution. So why is bitcoin crashing?
Trump got elected promising to usher in a crypto revolution. More than a year later, bitcoin's price has come tumbling down. What happened?