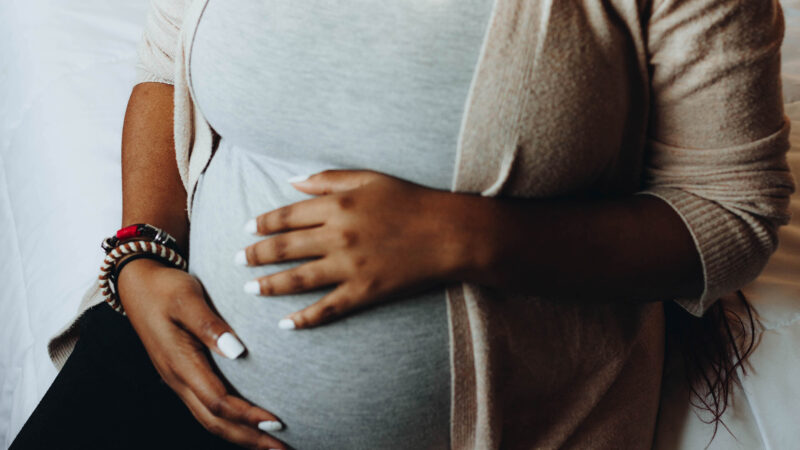
Alabama’s health care system for women ranks near the bottom of this new scorecard
The Commonwealth Fund has a new category in its annual scorecard of state health systems — reproductive and women’s health care.
The scorecard looks deeper at 12 new measures that evaluate and rank states on maternal and pregnancy-related outcomes, as well as women’s access to reproductive services and other care.
Mississippi, Alabama and Louisiana rank near the bottom in the report — released June 22 — with marked increases in preventable deaths, high uninsured rates and more preterm births across all three states.
Maternal deaths nearly doubled between 2018 and 2021 and the COVID-19 pandemic played a big role. The increase was especially high among Black and Indigenous mothers already impacted by poverty and poor access to maternal health care.
Louisiana, which ranked 38th out of the 50 states and the District of Columbia, saw an increase in its maternal morbidity rate between 2018 and 2020, and it did not improve in any of the key areas researchers examined.
In Alabama, which ranked 43rd, the infant mortality rate remained higher than the U.S. average but the state did improve its access to prenatal care.
Mississippi ranked second to last in reproductive and women’s health, with worsening rates of death for women of reproductive age, postpartum medical visits, and deaths from preventable and treatable causes. Mississippi also continues to have the highest rate of infant mortality in the country.
The report uses data from before and after Roe v. Wade was overturned, and notes that most of the states that ranked lowest in reproductive care and women’s health have some of the strictest abortion bans. These states — including Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana have fewer maternity care providers, and more women of color and their babies are dying.
The researchers recommended that states can work to improve poor reproductive outcomes, suggesting policies like extending postpartum Medicaid, funding community-based organizations and more.
You can read the full scorecard report here.
This story was produced by the Gulf States Newsroom, a collaboration between Mississippi Public Broadcasting, WBHM in Alabama, WWNOand WRKF in Louisiana and NPR. Support for reproductive health coverage comes from The Commonwealth Fund, but the news and the business departments operate independently.
In this Icelandic drama, a couple quietly drifts apart
Icelandic director Hlynur Pálmason weaves scenes of quiet domestic life against the backdrop of an arresting landscape in his newest film.
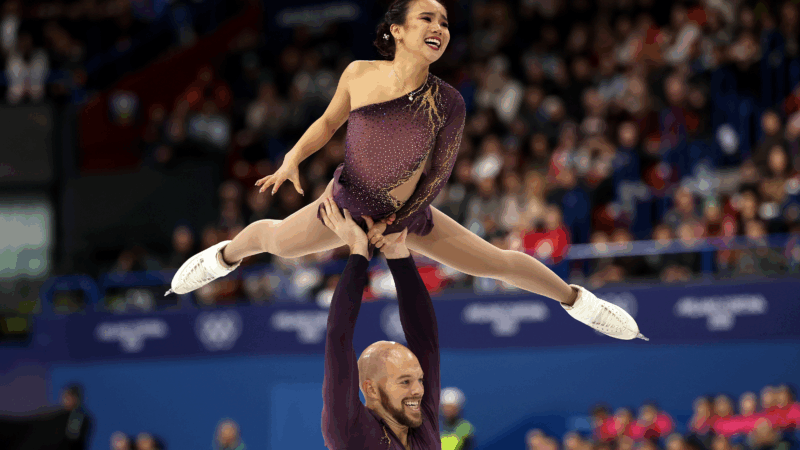
After the Fall: How Olympic figure skaters soar after stumbling on the ice
Olympic figure skating is often seems to take athletes to the very edge of perfection, but even the greatest stumble and fall. How do they pull themselves together again on the biggest world stage? Toughness, poise and practice.
They’re cured of leprosy. Why do they still live in leprosy colonies?
Leprosy is one of the least contagious diseases around — and perhaps one of the most misunderstood. The colonies are relics of a not-too-distant past when those diagnosed with leprosy were exiled.
This season, ‘The Pitt’ is about what doesn’t happen in one day
The first season of The Pitt was about acute problems. The second is about chronic ones.
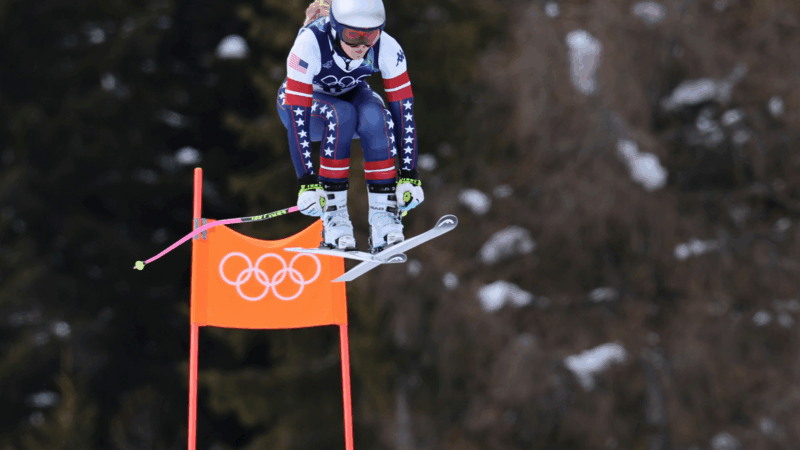
Lindsey Vonn is set to ski the Olympic downhill race with a torn ACL. How?
An ACL tear would keep almost any other athlete from competing -- but not Lindsey Vonn, the 41-year-old superstar skier who is determined to cap off an incredible comeback from retirement with one last shot at an Olympic medal.
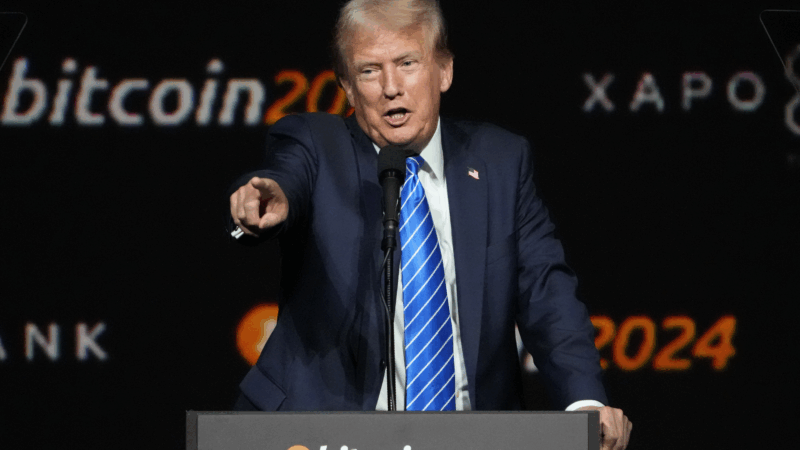
Trump promised a crypto revolution. So why is bitcoin crashing?
Trump got elected promising to usher in a crypto revolution. More than a year later, bitcoin's price has come tumbling down. What happened?