Trans kids fear Alabama laws targeting medicine, bathrooms
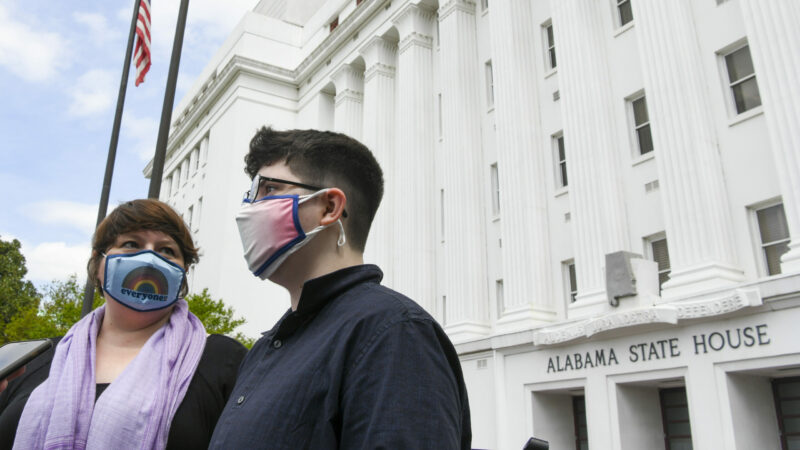
Trace Trice (L) and her son, Phineas Fleming-Smith, who is trans, speak to the media during a rally at the Alabama State House to draw attention to anti-transgender legislation introduced in Alabama on March 30, 2021 in Montgomery, Alabama.
MONTGOMERY, Ala. — Ninth grader Harleigh Walker, 15, spends her time after school like many girls her age: doing homework, listening to Taylor Swift, collecting records and hanging out with friends.
But this year, her spring break also included trying to persuade members of the state House and Senate to reject legislation banning gender-affirming medications for transgender kids like her under 19.
She was unsuccessful. On Thursday, Alabama lawmakers passed the measure, and Gov. Kay Ivey signed it into law on Friday, meaning Harleigh’s doctor would face prison time if she continued to prescribe her testosterone-blocking drugs.
“Honestly, I’m a little scared now,” Harleigh said Thursday after learning the bill had passed. “But we’re still going to fight, no matter what.”
She said she is holding out hope the bill will be blocked by a court.
Alabama is among multiple states with Republican-controlled legislatures that have advanced bills not only to block medical treatment but to ban transgender children from using school restrooms or playing on sports teams that don’t correspond with their sex at birth. The Alabama medication bill is one of the most far-reaching: It would put doctors in prison for up to 10 years for prescribing puberty blockers or hormonal treatment to trans kids under 19.
“I believe very strongly that if the Good Lord made you a boy, you are a boy, and if he made you a girl, you are a girl,” said Ivey, who faces a May primary with conservative opponents trying to outflank her on her right. “We should especially protect our children from these radical, life-altering drugs and surgeries when they are at such a vulnerable stage in life. Instead, let us all focus on helping them to properly develop into the adults God intended them to be.”
Ivey also signed a separate measure that requires students to use bathrooms that align with their original birth certificate and prohibits instruction of gender and sexual identity in kindergarten through fifth grades.
Cathryn Oakley, state legislative director and senior counsel for the Human Rights Campaign, a national advocacy group for the LGBTQ community, called the new laws “breathtakingly cruel and cowardly” and “the single most anti-transgender legislative package in history.” Groups on Friday vowed to quickly file a lawsuit challenging the measures in court.
Oakley and other opponents say transgender health is being used as a deliberate political wedge issue to motivate a voting base — in the same way they say bills about critical race theory have been employed. Critical race theory is a way of thinking about America’s history through the lens of racism. Numerous Republican-controlled legislatures have proposed bills to block its teaching in public schools.
The measures have prompted swift backlash from medical experts, Democratic President Joe Biden’s administration, the U.S. Department of Justice and the families of trans youth. Last month, the Justice department sent a letter to all 50 state attorneys general, warning them that blocking transgender and nonbinary youth from receiving gender-affirming care could be an infringement of federal constitutional protections.
“My child is not a political tool. This is not a fair fight to pick on vulnerable children,” said Vanessa Finney Tate, the mother of a 13-year-old trans boy in Birmingham, Alabama, after testifying at a public legislative hearing on bill that would block students from using bathrooms corresponding to their gender.
Harleigh’s father, Jeff Walker notes that many of the same Alabama lawmakers who supported the ban on gender-affirming medical treatment recently argued, ‘It’s your body and your choice’ regarding coronavirus vaccinations. He said the family is now scrambling to find another state where it can continue Harleigh’s medical care.
“We just don’t want people meddling in our medical care,” he said.
Medical groups including The American Academy of Pediatrics have publicly opposed efforts to outlaw gender-affirming care.
“Gender-affirming care benefits the health and psychological functioning of transgender and gender-diverse youth,” the Endocrine Society said in a statement. “When an individual’s gender identity is not respected and they cannot access medical care, it can result in higher psychological problem scores and can raise the person’s risk of committing suicide or other acts of self-harm.”
The organization notes that only reversible puberty blockers are recommended for younger adolescents, while older adolescents might qualify for hormone therapy.
Harleigh received the medication — which stops her from going through male puberty — only after consulting with a team of doctors for years. She said it’s “weird” to see lawmakers with no medical experience call her medication “child abuse,” when six doctors have agreed she should have it.
Angus, a 16-year-old trans teen who requested that his last name not be used because of the bullying he has received in his north Alabama town, said he knew at puberty that the mirror reflected “a body that wasn’t my own.”
After coming out to his mother, he began slowly testing the waters: dressing as a man, changing his name. Only after years of talking to a team of doctors, was he able to recently get medications to stop his periods. The next step, which he is eager to start, would be a small dose of testosterone.
“I have been waiting for seven years to finally become a man, the man that I’ve always known I am,” Angus said.
He said bills to block such treatments are harming, not protecting trans youth.
“The government is saying, ‘Oh, parents are abusing their children by letting them transition,'” he said. “Actually, it’s more child abuse to not let them transition if they come out. What these bills really are doing is putting trans youth lives at risk because these suicide rates will spike exponentially. And a lot of families will lose their children.”
Similar bans are moving forward in other states.
In Texas, Republican Gov. Greg Abbott has ordered the state’s child welfare agency to investigate as abuse reports of gender-confirming care for kids. And a law in Arkansas bans gender-affirming medications. That law has been blocked by a court, however.
Trans youth in many red states say they feel attacked, angry, betrayed and scared by the wave of legislation aimed at them.
“It feels like a back-stab,” Harleigh said. “I’ve lived in this state my whole life. For them to just say, ‘Well, you know what, this is an issue that’s really popular on my side of the aisle so I’m just going to raise it up and support it because it’ll help me win my election’ — It just hurts to see them do that.”
US military used laser to take down Border Protection drone, lawmakers say
The U.S. military used a laser to shoot down a Customs and Border Protection drone, members of Congress said Thursday, and the Federal Aviation Administration responded by closing more airspace near El Paso, Texas.
Deadline looms as Anthropic rejects Pentagon demands it remove AI safeguards
The Defense Department has been feuding with Anthropic over military uses of its artificial intelligence tools. At stake are hundreds of millions of dollars in contracts and access to some of the most advanced AI on the planet.
Pakistan’s defense minister says that there is now ‘open war’ with Afghanistan after latest strikes
Pakistan's defense minister said that his country ran out of "patience" and considers that there is now an "open war" with Afghanistan, after both countries launched strikes following an Afghan cross-border attack.
Hillary Clinton calls House Oversight questioning ‘repetitive’ in 6 hour deposition
In more than seven hours behind closed doors, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton answered questions from the House Oversight Committee as it investigates Jeffrey Epstein.
Chicagoans pay respects to Jesse Jackson as cross-country memorial services begin
Memorial services for the Rev. Jesse Jackson Sr. to honor his long civil rights legacy begin in Chicago. Events will also take place in Washington, D.C., and South Carolina, where he was born and began his activism.
In reversal, Warner Bros. jilts Netflix for Paramount
Warner Bros. says Paramount's sweetened bid to buy the whole company is "superior" to an $83 billion deal it struck with Netflix for just its streaming services, studios, and intellectual property.