Gov. Kay Ivey wants to give the state more time to carry out executions
MONTGOMERY, Ala. (AP) — Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey on Monday said she wants to give the state additional time to carry out an execution after a series of failed lethal injections.
The Republican governor sent a letter to the Alabama Supreme Court asking justices to alter a longstanding rule that limits execution warrants to a single date. It is the first change requested by Ivey after announcing a “top-to-bottom” review of execution procedures. The review is ongoing, Ivey spokeswoman Gina Maiola said Monday.
Alabama prison officials called off two recent scheduled lethal injections — for Kenneth Eugene Smith in November and Alan Miller in September — as a midnight deadline approached after last-minute legal appeals and difficulties by the execution team in connecting an IV line to each inmate.
Under Ivey’s proposal, the state corrections commissioner could immediately designate a new execution date if a last-minute stay or some other delay prevents the state from carrying out an execution on the original date listed on the death warrant. She said the federal government and the state of Kentucky have similar rules. Currently, if Alabama authorities can’t get the procedure underway by midnight, officials must ask the Alabama Supreme Court to set a new execution date.
“In several recent executions, last-minute gamesmanship by death row inmates and their lawyers has consumed a lot of valuable time, preventing the department from carrying out its execution protocol between the conclusion of all legal challenges in the federal courts and the expiration at the death warrant issued by your court,” Ivey wrote.
An alternative, Ivey wrote, would be for the court to allow a longer period for the execution to be carried out. California gives a 10-day window and Georgia allows seven days, the governor’s office wrote.
While Ivey blamed Alabama’s failed lethal injections on the single-day time frame and last-minute appeals, lawyers for inmates and advocacy groups have said the repeated difficulties show something is wrong with Alabama’s procedures.
“One of the Alabama Department of Corrections’ clear problems in carrying out executions has been the inability of the execution team to establish IV executions lines.” Robert Dunham, executive director of the Death Penalty Information Center wrote in an email.
Extending how long the state has to to carry out an execution certainly increases the probability that the execution team will eventually find a vein or perform an invasive procedure to set an IV line, he said, but “unfortunately, it doesn’t do anything to improve the performance of ADOC execution personnel to ensure that future executions are not also botched.”
In a court filing opposing the setting of a new execution date for Smith, his lawyers wrote that his treatment “does not fall within society’s standards for a constitutional execution. The botched execution was terrifying and extremely painful for Mr. Smith.”
Ivey last month requested a pause in executions after the state called off Smith’s lethal injection. It was the second time this year and the third time since 2018 that the state was unable to put an inmate to death. The state completed an execution in July, but only after a three-hour delay caused at least partly by trouble starting an IV line on Joe Nathan James Jr.
Ivey said the state is also looking at moving up the current 6 p.m. start time for executions to give the Department of Corrections more time. Corrections Commissioner John Hamm will make a recommendation to her for a new time, she told justices.
Hamm last month said “everything is on the table” in the review, including how the department trains staff and prepares for executions. Ivey said she agrees because she wants to make sure future executions go forward “to ensure those guilty of perpetrating the most heinous crimes in our society receive their just punishment.”
Memory loss: As AI gobbles up chips, prices for devices may rise
Demand for memory chips currently exceeds supply and there's very little chance of that changing any time soon. More chips for AI means less available for other products such as computers and phones and that could drive up those prices too.
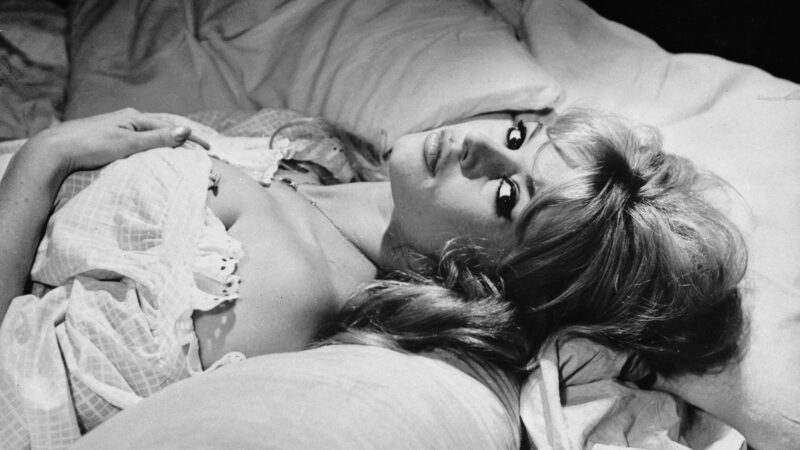
Brigitte Bardot, sex goddess of cinema, has died
Legendary screen siren and animal rights activist Brigitte Bardot has died at age 91. The alluring former model starred in numerous movies, often playing the highly sexualized love interest.
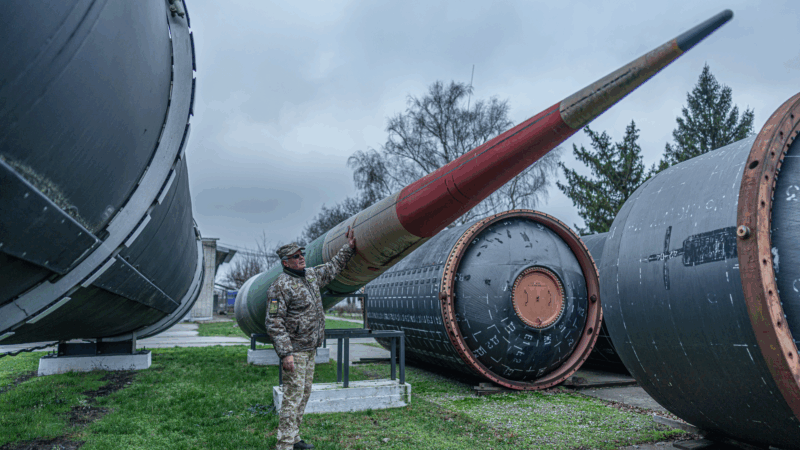
For Ukrainians, a nuclear missile museum is a bitter reminder of what the country gave up
The Museum of Strategic Missile Forces tells the story of how Ukraine dismantled its nuclear weapons arsenal after independence in 1991. Today many Ukrainians believe that decision to give up nukes was a mistake.
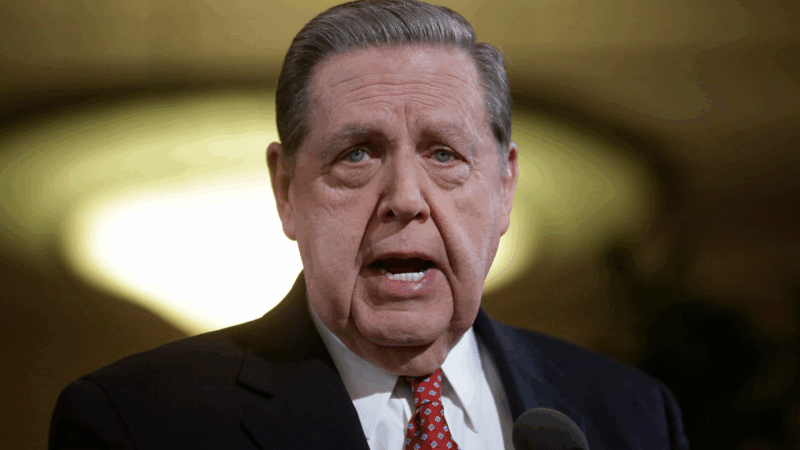
Jeffrey R. Holland, next in line to lead Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, dies at 85
Jeffrey R. Holland led the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles, a key governing body. He was next in line to become the church's president.
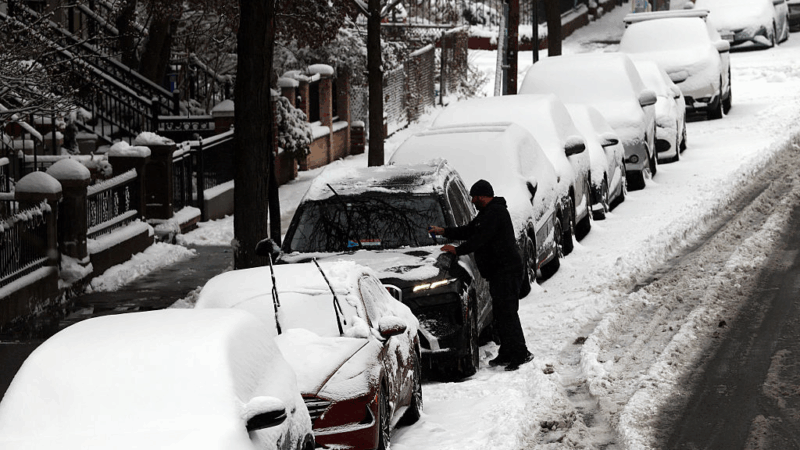
Winter storm brings heavy snow and ice to busy holiday travel weekend
A powerful winter storm is impacting parts of the U.S. with major snowfall, ice, and below zero wind chills. The conditions are disrupting holiday travel and could last through next week.
Disability rights advocate Bob Kafka dead at 79
Bob Kafka was an organizer with ADAPT (American Disabled for Attendant Programs Today), a group which advocates for policy change to support people with disabilities.