EXPLAINER: What’s known about sudden liver disease in kids
By LINDSEY TANNER AP Medical Writer
A puzzling outbreak of sudden liver disease in nearly 200 children has health authorities in Europe and the U.S. racing to find answers.
The illnesses have no known connection, although a possible link with a virus that can cause colds is being investigated. At least one child died and several others have required liver transplants.
What’s known so far:
The Basics
Previously healthy children are suddenly developing hepatitis, or liver inflammation often caused by viruses. Jaundice, diarrhea and abdominal pain are among reported symptoms. Children aged 1 month to 16 years have been affected.
Most cases have occurred in Europe. The first U.K. cases were recorded in January. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in a nationwide health alert last week that the first U.S. cases were identified in October in Alabama.
The Disease
Hepatitis is usually caused by one of several contagious hepatitis viruses that have not been found in the affected children. Sometimes the disease is mild and requires no specific treatment. But severe cases require hospitalization and can lead to liver failure.
The Cause
Authorities are uncertain what is causing the outbreak. Nine children in the Alabama cluster tested positive for adenovirus. Some types of the virus can cause colds but authorities are also looking at a version that can cause digestive problems. It is unknown whether that virus is a cause or is somehow contributing to the outbreak.
Locations
Cases have been reported in at least a dozen countries, including Denmark, England, France, Ireland, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Scotland, Spain, and the United Kingdom. In the United States, cases have also occurred in Illinois and North Carolina.
The CDC says all physicians should be on the lookout for symptoms and report any suspected case of what’s called hepatitis of unknown origin.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
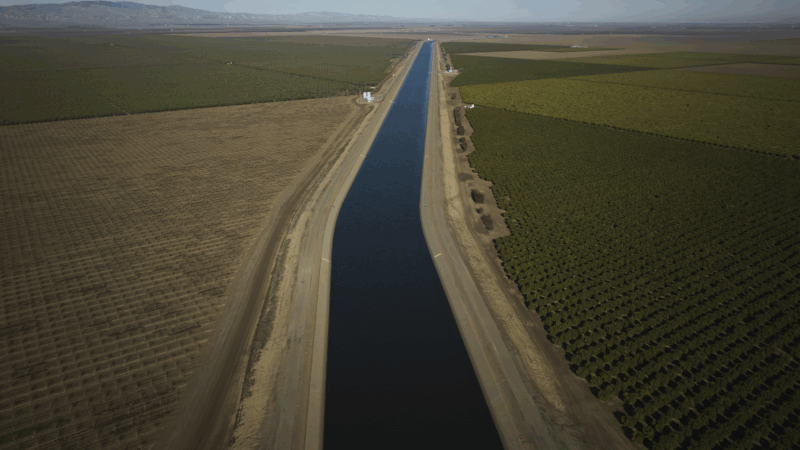
Why farmers in California are backing a giant solar farm
Many farmers have had to fallow land as a state law comes into effect limiting their access to water. There's now a push to develop some of that land… into solar farms.
Every business wants your review. What’s with the feedback frenzy?
Customers want to read reviews and businesses need reviews to attract customers. But the constant demand for reviews could be creating a feedback backlash, experts say.
Can’t get a prescription renewed? Here’s how to cope with prior authorizations
These health care hurdles can stand in the way of getting treatment your doctor says you need. Here's what to know about how to deal with them.
‘Get back to integrity’: Oklahoma’s Kevin Stitt on Republicans after Trump
NPR's Steve Inskeep asks Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt about his spat with President Trump, immigration and the future of the Republican Party.
Civil rights leaders say the racial progress Jesse Jackson fought for is under threat
Activists say racial progress won by the Rev. Jesse Jackson is under threat, as a new generation of leaders works to preserve hard-fought civil rights gains.
Tariffs cost American shoppers. They’re unlikely to get that money back
After the Supreme Court declared the emergency tariffs illegal, the refund process will be messy and will go to businesses first.