What You Need To Know About Pregnancy, Fertility And The COVID-19 Vaccine
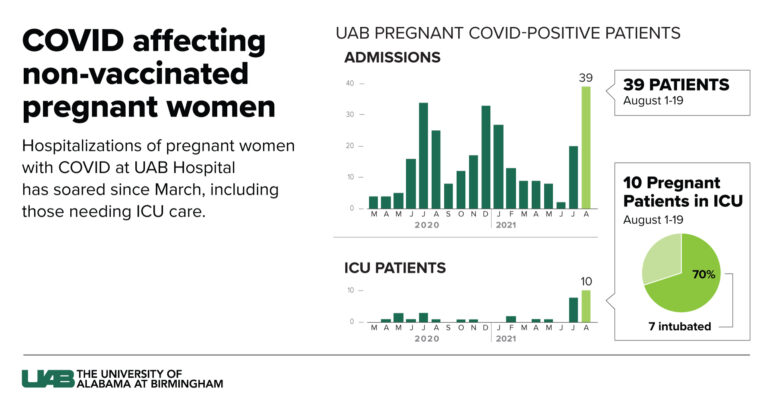
Roughly half of all pregnant women who have visited the maternity emergency room at the University of Alabama at Birmingham in the last two weeks have tested positive for COVID-19, according to Dr. Audra Williams from UAB’s Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
“We are just seeing numbers that we have not previously seen during this pandemic of rates of pregnant women being affected,” Williams said.
There aren’t enough nurses, so the hospital system is having to delay labor induction for patients who don’t have COVID, Williams said.
Meanwhile, health professionals are trying to combat misinformation surrounding the vaccine and pregnancy. WBHM spoke with two doctors from UAB. Here’s what we learned:
Is it safe to get the vaccine if I’m pregnant, breastfeeding or want to get pregnant?
Yes, according to guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
“The vaccine is safe, and there is no difference in pregnancy outcomes between women that are vaccinated and unvaccinated,” Williams said.
She said UAB Hospital is also “strongly, strongly” recommending that all pregnant women get vaccinated. She said the benefits of the vaccines outweigh the risks.
But what if I’m early in my pregnancy? Is it still safe for me to get the vaccine?
Yes, according to Williams.
“Even when a woman is contemplating getting pregnant is a good time to get the vaccine,” she said. “There is not an increased risk of miscarriage – regardless of which trimester the patient receives the vaccine.”
In fact, there have been studies that specifically looked at patients who were vaccinated before 20 weeks.
“[Those studies] did not show any adverse outcomes – no changes in the miscarriage rate, [which] is between 13 and 15% in both vaccinated and unvaccinated populations,” Williams said.
If a pregnant mother is sick with COVID-19 and ends up in the ICU, are there risks to the baby?
Yes, according to Williams.
“If a mom is not oxygenating her body well, then she’s not oxygenating her baby well, either,” Williams said.
She added that doctors may be inclined to induce labor early in an effort to protect the health of the mom and baby.
A California study released in July showed that mothers who are sick with COVID-19 are 60% more likely to have a very preterm birth, which occurs before 32 weeks of pregnancy. It also found that these mothers are 40% more likely to have a regular preterm, which occurs before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Williams said that there are a number of long-term life risks associated with preterm birth, including neurological and gastrointestinal, or GI, complications.
Can the vaccine make me infertile? Where did this rumor start?
“[No], it’s absolutely false,” said Dr. Jodie Dionne, associate director of UAB’s Global Health in the Center for Women’s Reproductive Health.
She said that this is “a lie” and has spread on social media “like wildfire.” Dionne said that it’s hard to pinpoint where the misinformation originated, but that there was one scientist who circulated the idea.
“They were talking about some of the receptors on the placenta and making a link between the risk in pregnancy of the vaccine and the receptor on the placenta.”
But Dionne says the receptor on the placenta is entirely different from the COVID receptor.
“It’s almost a willful, pseudo-scientific explanation for a side effect and a problem in a pregnant woman that is not the case.”
Dionne said that the idea of vaccines causing infertility is not new and is used against other vaccines like the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
“So it’s something that anti-vax groups have attached to vaccines in the past,” Dionne said.
She said that there are studies of vaccinated and unvaccinated people trying to conceive at infertility clinics.
“There’s no difference [between the vaccinated or unvaccinated] for the numbers of women who become pregnant with the infertility treatment [and] the number of successful live births with the fertility treatment,” Dionne said.
U.S. and Iran to hold a third round of nuclear talks in Geneva
Iran and the United States prepared to meet Thursday in Geneva for nuclear negotiations, as America has gathered a fleet of aircraft and warships to the Middle East to pressure Tehran into a deal.
FIFA’s Infantino confident Mexico can co-host World Cup despite cartel violence
FIFA President Gianni Infantino says he has "complete confidence" in Mexico as a World Cup co-host despite days of cartel violence in the country that has left at least 70 people dead.
Supreme Court appears split in tax foreclosure case
At issue is whether a county can seize homeowners' residence for unpaid property taxes and sell the house at auction for less than the homeowners would get if they put their home on the market themselves.
Top House Dem wants Justice Department to explain missing Trump-related Epstein files
After NPR reporting revealed dozens of pages of Epstein files related to President Trump appear to be missing from the public record, a top House Democrat wants to know why.
ICE won’t be at polling places this year, a Trump DHS official promises
In a call with top state voting officials, a Department of Homeland Security official stated unequivocally that immigration agents would not be patrolling polling places during this year's midterms.
Cubans from US killed after speedboat opens fire on island’s troops, Havana says
Cuba says the 10 passengers on a boat that opened fire on its soldiers were armed Cubans living in the U.S. who were trying to infiltrate the island and unleash terrorism. Secretary of State Marco Rubio says the U.S. is gathering its own information.






