Alabama to Close Most of Holman Prison
The Alabama Department of Corrections is accelerating plans to close most of Holman Correctional Facility in Atmore. Officials made the announcement Wednesday, citing growing maintenance costs and safety concerns at the 51-year-old prison.
Holman opened in 1969 and has faced high levels of violence, overcrowding and understaffing over the years. The maximum security prison houses the state’s only execution chamber, which officials say will remain in use. Other parts of the prison will also remain open to house more than 150 death row inmates and around 150 “low-risk” inmates serving life without parole.
Most of Holman’s main facility will close, including the cafeteria, medical unit, administrative suite and housing units. Officials say those inmates who remain at the facility will receive health and food services from Fountain Correctional Facility, located about one mile away. They will also continue to work at Holman’s auto tag and clothing plants, which will remain open.
More than 600 inmates will be transferred to other state prisons, which already face high levels of overcrowding and understaffing. In a statement, lawyers with the Southern Poverty Law Center and the Alabama Disabilities Advocacy Program called the move a “band-aid solution.” Both groups are plaintiffs in a class-action lawsuit against the ADOC regarding mental health and medical care of inmates.
“The movement of people at Holman to other facilities will only exacerbate the already deadly levels of overcrowding and the understaffing of correctional officers and mental health professionals at those facilities,” said attorney CJ Sandley.
Prison officials did not release a timeline for the move, citing security concerns. In a statement, corrections commissioner Jeff Dunn said officials will make “appropriate modifications” to ease the transition.
“We currently are working hard to identify and implement measures to account for the impact of increased populations across the correctional system,” Dunn said, “and to ensure continued access to health, educational, and rehabilitative services and programs for our inmate population.”
Dunn said daily maintenance at Holman has become too risky and unsustainable to continue. He said across the state, Alabama’s prison infrastructure “is failing.”
“We are now projecting upwards of $800 million in deferred maintenance costs alone,” Dunn said. “This unavoidable issue reinforces the critical importance of Governor Ivey’s transformative and necessary plan to build three new correctional facilities.”
Gov. Kay Ivey is awaiting proposals from approved developers for a plan to build three new regional prisons to replace more than a dozen facilities that house male inmates. Officials say they expect to have construction proposals by the end of April.
This Small Alabama Town Was Part of the Manhattan Project. Now It May Host a Hyperscale Data Center.
A town of less than 5,000 could be the site of a $6 billion data center project, its mayor says. Would the project be a boon or a burden?
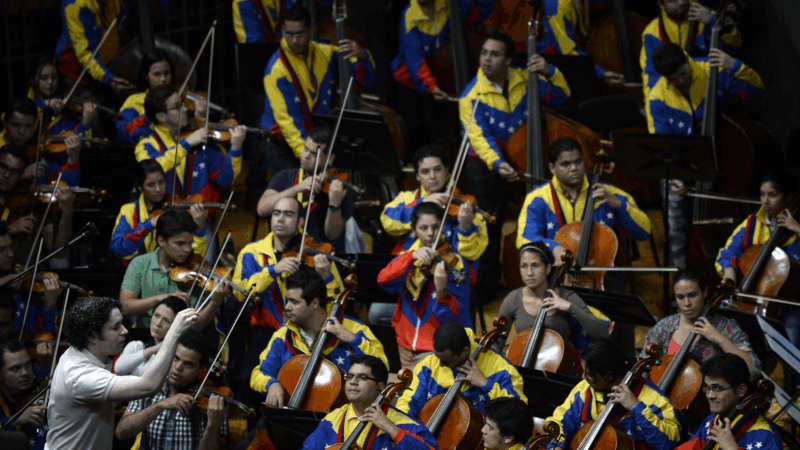
As Venezuela’s future remains uncertain, its symphony orchestra reaches a new milestone
The Simón Bolívar Symphony Orchestra's recording of Ravel's Boléro is up for a Grammy nomination for best orchestral performance. The recognition comes at a turbulent moment for Venezuela, but the orchestra remains focused on the music.
Meta, TikTok and YouTube are on trial over whether their apps hurt children
A trial kicking off in a Los Angeles courtroom marks the first time a jury will hear claims that social media companies knowingly hook young users and cause harm.
In China, AI is no longer optional for some kids. It’s part of the curriculum
While debate rages in the U.S. about the merits and risks of AI in schools, it's become a state-mandated part of the curriculum in China, as the authorities try to create a pool of AI-savvy professionals.
Trump to hold de facto midterm kickoff in Iowa focused on the economy, energy prices
President Trump's rally in Iowa on Tuesday brings his message to a state disproportionately affected by his economic policies and whose voters could help determine control of Congress.
Minneapolis killings put a focus on use of body cameras
Federal immigration enforcement authorities are facing scrutiny and criticism over their tactics, including the lack of body-worn cameras, following the killing of two U.S. citizens in Minneapolis.