UAB Using Whole Blood to Improve Trauma Care
When someone is experiencing severe blood loss, that blood needs to be replaced as soon as possible. Most doctors deliver this transfusion as a “balanced resuscitation,” combining equal amounts of red blood cells, plasma and platelets, which is how blood is separated and delivered to most U.S. hospitals. But a balanced resuscitation is not the same thing as using whole blood that has never been separated, according to Dr. Marisa Marques, medical director of transfusion services at UAB Hospital.
“You’re not able to reconstitute whole blood just mixing the other components,” Marques says, “because each one of them is somewhat diluted with anticoagulant and other substances.”
Most of the research on whole blood transfusions comes from the military and treating injured soldiers in war zones. It suggests that transfusing actual whole blood to care for hemorrhaging patients can lead to better outcomes. Patients may require less blood to be transfused, and they often recover faster. UAB trauma surgeon Dr. Daniel Cox says another advantage of using whole blood, rather than separated components, is that it saves time.
“For the very seriously injured patient, this has the potential to significantly improve the chances of that person surviving,” says Cox.
UAB Hospital recently joined a growing number of hospitals across the country that use whole blood to treat severe trauma patients. Dr. Marques says finding a supply was not easy. It is not available from the local American Red Cross (ARC), where UAB gets most of its blood products. The hospital ended up having to get it from an ARC blood bank in Oklahoma.
Marques says whole blood has to meet strict requirements. To ensure that the product can be used for most patients, she says donors have to be male with low-antigen, type O blood. And timing is key, as whole blood has a shelf life of about three weeks, which is about half that of packed red blood cells.
UAB receives 12 units every week, which is less than 5% of the hospital’s total blood supply. UAB trauma doctors say that since they started receiving the whole blood in August they have used just about every drop.
Offshore wind developer prevails in U.S. court as Trump calls wind farms ‘losers’
A federal judge ruled Monday that work on a major offshore wind farm can resume, handing the industry at least a temporary victory as President Trump seeks to shut it down.
Minnesota officials sue to block Trump’s immigration crackdown as enforcement intensifies
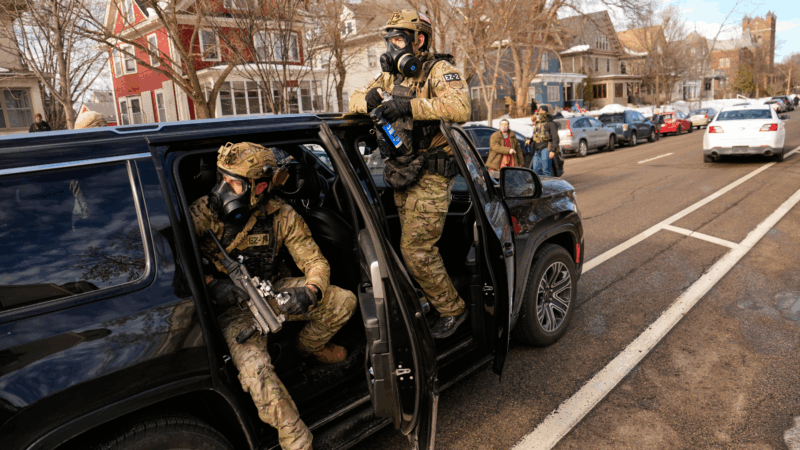
More than 2,000 federal immigration agents are in Minnesota, and that number is expected to increase. On Monday, an NPR reporter witnessed multiple instances where immigration agents drove around Minneapolis — and in parking lots of big box stores — and randomly questioned people about their immigration status.
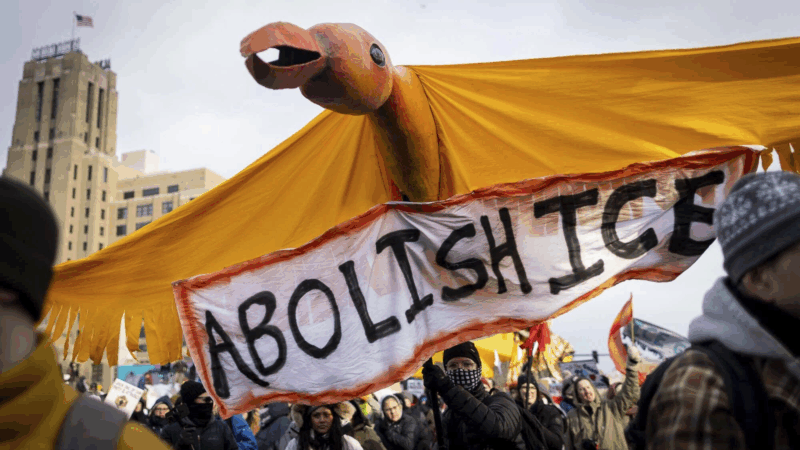
In photos: A week of protests against ICE
People across the country gathered to protest against ICE over the past week.
Elon Musk’s X faces bans and investigations over nonconsensual bikini images
After the social media app's AI chatbot started generating sexualized images of women and children, two countries have blocked it and several more have launched investigations.
Trump administration tells states to end ‘orphan tax’ on foster kids
There's a growing move to end what some call "the orphan tax" and stop states from taking benefit checks from children and youth in foster care.
Flu shot recommendation for kids dropped just as the illness rages
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention dropped its advice that kids get an annual flu shot at a time when flu cases and hospitalizations are surging.