Supreme Court Justice Questions Landmark Ruling from Alabama
Recently, the U.S. Supreme Court declined to hear a defamation case against comedian Bill Cosby. Perhaps more interesting than the rejection was a comment from Justice Clarence Thomas. He wrote the court should re-examine a landmark First Amendment case that originated in Alabama.
In 1960, the New York Times ran an ad from a civil rights group criticizing how authorities treated demonstrators, including those in Montgomery. The ad got some details wrong.
It misstated how many times the Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. had been arrested in Alabama. It mischaracterizes the police response to student protests at the state capitol.
“One of the more petty examples of something not being accurate was [the ad] said that the students had sung ‘My Country ‘Tis of Thee’ on the steps of the Capitol but it was actually the national anthem,” says Steven Brown, an Auburn University political science professor.
Montgomery’s Police Commissioner, L.B. Sullivan, argued the errors meant the ad defamed him as a public official. He sued and won a half-million dollar award in Alabama. The case, New York Times v. Sullivan, went on to the U.S. Supreme Court.
In a unanimous ruling in 1964, the Supreme Court said it took more than factual errors to constitute libel. You have to show “actual malice.”
“Which the court defined as knowing falsity or reckless disregard of the truth,” Samford University law professor William Ross says.
In other words, the media can’t knowingly print information about a public official that’s wrong or in a way that’s reckless. It’s considered a seminal case ensuring freedom of the press.
Justice Clarence Thomas questioned that precedent. He wrote this libel standard isn’t in the Constitution and that the states are capable of striking the appropriate balance between “public discourse” and “reputational harm.”
Ross says it’s not unusual for justices to publicly call for revisiting precedents, and Thomas’ comments fall in line with how he interprets the Constitution
Thomas’ words have gained extra attention because President Donald Trump on multiple occasions has suggested libel law be rewritten. But Ross says the Sullivan decision is not partisan in its effect.
“Every person at some point has some reason to criticize the government and criticize public officials,” Ross says.
Brown says the case might be reconsidered, but in light of today’s online and social media landscape.
“You have so much more speech that’s out there,” Brown says. “So many more ways that people say unkind and perhaps defamatory things about each other. Should the same standard apply?”
Who is a public figure on Facebook? Who is a publisher on Twitter? Those questions weren’t before the court in the 1960s.
The Sullivan case, along with seven others from Alabama, are highlighted in an exhibit created by Brown. It’s on display at Vulcan Park & Museum through May 9th.
Photo by Mark Fischer
EDITOR NOTE: Vulcan Park & Museum is a sponsor of WBHM programming. WBHM’s news and business departments operate separately.
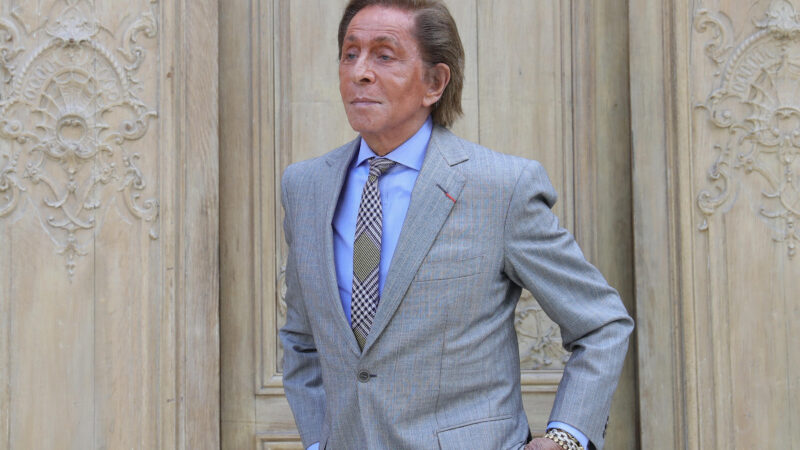
Italian fashion designer Valentino dies at 93
Garavani built one of the most recognizable luxury brands in the world. His clients included royalty, Hollywood stars, and first ladies.
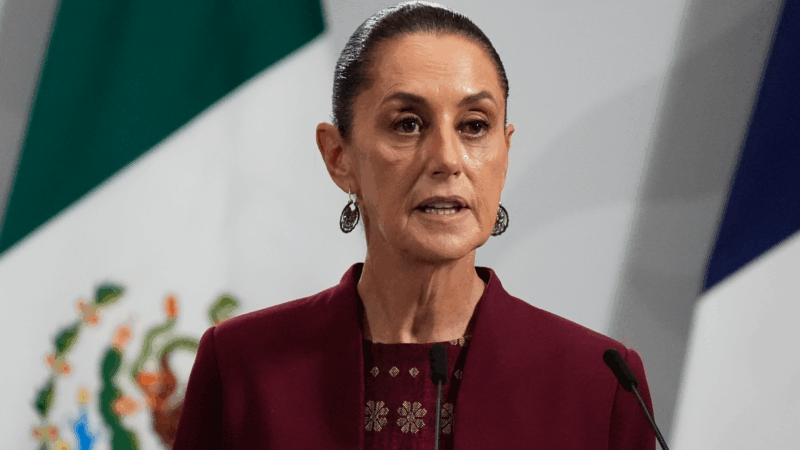
Sheinbaum reassures Mexico after US military movements spark concern
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum quelled concerns on Monday about two recent movements of the U.S. military in the vicinity of Mexico that have the country on edge since the attack on Venezuela.
Trump says he’s pursuing Greenland after perceived Nobel Peace Prize snub
"Considering your Country decided not to give me the Nobel Peace Prize… I no longer feel an obligation to think purely of Peace," Trump wrote in a message to the Norwegian Prime Minister.
Trump has rolled out many of the Project 2025 policies he once claimed ignorance about
Some of the 2025 policies that have been implemented include cracking down on immigration and dismantling the Department of Education.
U.S. lawmakers wrap reassurance tour in Denmark as tensions around Greenland grow
A bipartisan congressional delegation traveled to Denmark to try to deescalate rising tensions. Just as they were finishing, President Trump announced new tariffs on the country until it agrees to his plan of acquiring Greenland.
Can exercise and anti-inflammatories fend off aging? A study aims to find out
New research is underway to test whether a combination of high-intensity interval training and generic medicines can slow down aging and fend off age-related diseases. Here's how it might work.