Asian Soybean Rust
It’s a sunny but cold Mid November Saturday in Dothan. The cold is what’s
killing a big bed of kudzu between cotton fields and the passing cars on
highway 431. But not all the plants are dead, and some of those are
host to a devastating little devil-the Asian Soybean rust spore. The spore sucks
the life out of kudzu, which wouldn’t bother many horticulturalists… but
the spore also has a taste for another legume – Soy beans. Infected plants can’ t mature-meaning, smaller harvests and smaller revenues for farmers. And it’s
difficult to contain the fungi because it moves with the wind.
The spore originates in Asia and took the scenic route over to the states,
stopping off in Africa and South America. Before the diseased arrived, climatologists believed it would take the perfect storm to scoop up the spores in
Brazil and carry them over the ocean before dumping them along the Gulf Coast.
That perfect storm came in the form of Hurricane Ivan, which dumped millions upon millions of rust spores in the southeast. Shortly after the storm, scientists detected spores in Louisiana. Soon after, they found them in Georgia, Alabama, Florida, and within a year the range of the spores stretched from Texas to North Carolina.
“It’s certainly important to know the where the spores are and how widespread the disease is.
That’s Dr. Robert Wisner, an economist and grain-marketing specialist at
Iowa State University. Wisner sits on the Iowa Soybean Rust Task Force, which is
charged with protecting that state’s $2 billion soy crop. So far rust spores haven’t made their way up to the Midwest. But Wisner says eventually they will, and farmers in Iowa need to know what’s going on in Alabama and the rest of the southeast.
“That gives us some clues as to the likely hood of those spores blowing in to Iowa.
Currently, farmers fight the disease with expensive fungicides that have to
be applied at a specific time to be effective. If a farmer is late to spot the rust, and has to spray the crops twice, that could eliminate any profit the soybeans would have been brought in. So while climatologists watch the wind patterns, plant pathologists like Auburn University’s Ed Sikora are watching the ground. Sikora is a leading figure in the fight against spores. He’s also set the record for the most spore discoveries in a single day.
“My competitive juices were running because Georgia was getting ahead of us. So over about a 24-hour period, I traveled up the eastern edge of Alabama going county to county and looking at kudzu patches and soybean fields and I managed to find rust in ten counties along that edge.
The Alabama-Georgia Border is ground zero for the rust spores, and there’s
lots of friendly competition between scientists from the two states. University of Georgia researchers say they were in awe of Sikora’s mad dash to track the spore. But the Georgia researchers are also gaining attention for their work in the fields.
“I think the only thing more boring than rating plots is you watching me rate plots.”
He may think it’s boring, but Dr. Bob Kemeriat’s work could save farmers billions of dollars. On a windy weekday afternoon, Kemeriat is in Attapulgus, Georgia, looking over soy leaves. He’s interested in how quickly the plants succumb to the
fungi.
“You can see it starts in the lower canopy; a few leaves are
dropping, as you move up to towards the top of the plant it’s not there.
Kemerait is searching for the spores-which look like little balls of rust
you’d find on an old washing machine or tin can.
“Unless you knew what you were looking for, you’d never see it. Especially if you were scouting a field driving by in your pick-up truck, it’d be tough.
Kemeriat is joined in the field by Dr. Leila Skonyers. They’re searching with hopes of finding what they call the Holy Grail of soy – a rust proof plant.
“So far we haven’t been able to find that Holy Grail plant. Most
Legumes we come across have some sort of susceptibility to rust. But if we do
find it will be of great help to the grower.
But for now, the biggest help to farmers isn’t scientists with a friendly
AL-GA rivalry. It’s mother nature. Growers are hoping it gets cold enough in
places like Dothan, to kill the kudzu, and the soybean rust spore.
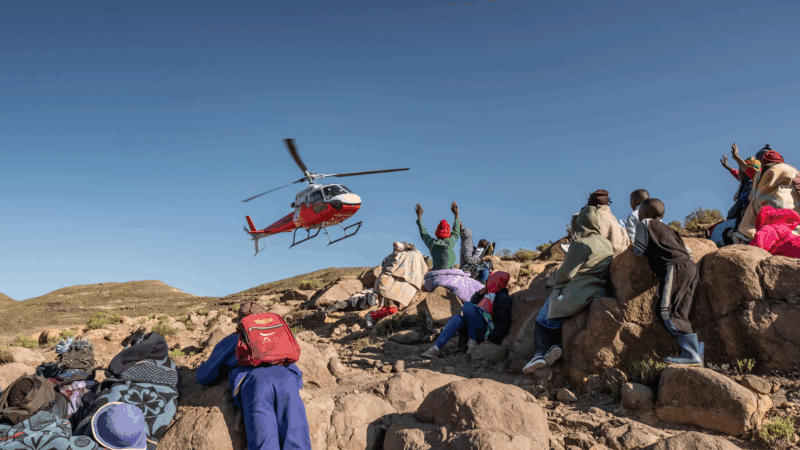
Photos: The flying doctors of Lesotho won’t let their wings be clipped
This band of airborne health workers bring essential medical care to isolated communities in the southern African nation. In addition to turbulence, they face a new obstacle: budget cuts.
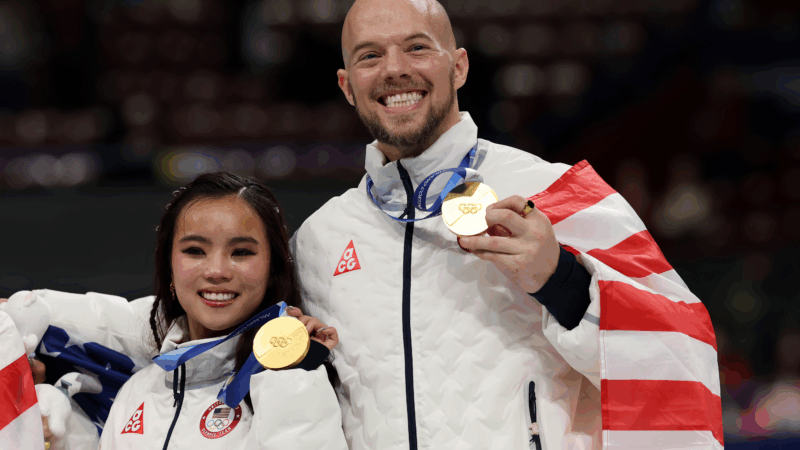
For U.S. pairs skater Danny O’Shea, these Olympics are 30 years in the making
Danny O'Shea turned 35 at his first Olympics, after three decades of skating and two reversed retirements.
Want a mortgage for under 3% in 2026? Meet the ‘assumable mortgage’
Low mortgage rates from the COVID era might still be attainable for homebuyers, if they find the right house and have the cash.
Epstein files fallout takes down elite figures in Europe, while U.S. reckoning is muted
Unlike in Europe, officials in the U.S. with ties to Epstein have largely held their positions of power.
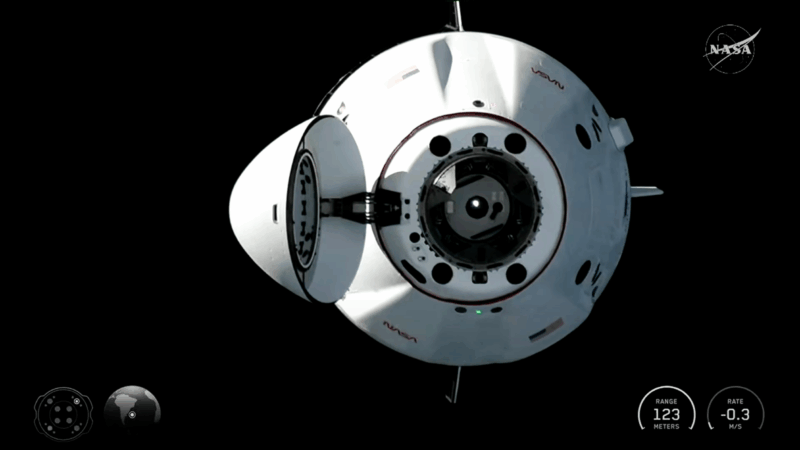
Four people on NASA’S Crew-12 arrive at the International Space Station
The crew will spend the next eight months conducting experiments to prepare for human exploration beyond Earth's orbit.
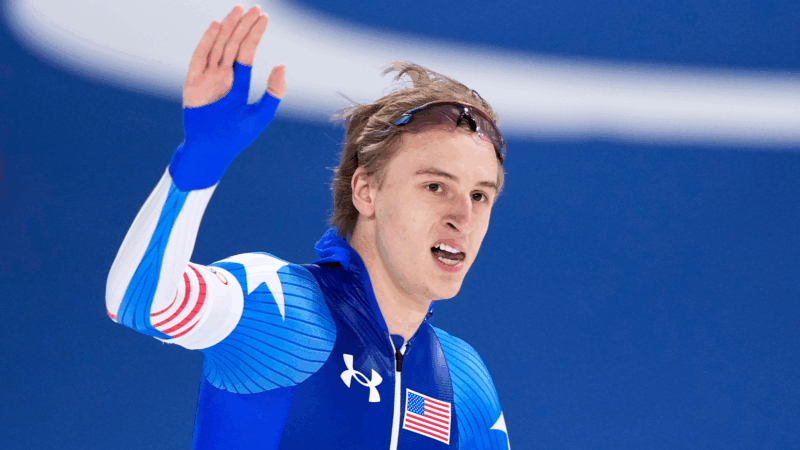
American speedskater Jordan Stolz wins second Olympic gold with 500-meter race victory
With the win, Stolz joins Eric Heiden as the only skaters to take gold in both the 500 and 1,000 at the same Olympics.