Mexican ranchers struggle to adapt as a parasite ravages cattle exports to the U.S.
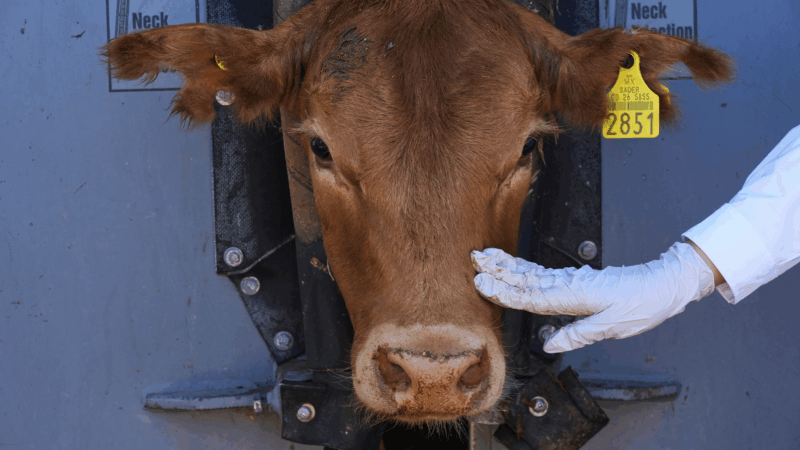
HERMOSILLO, Mexico — The United States’ suspension of live cattle imports from Mexico hit at the worst possible time for rancher Martín Ibarra Vargas, who after two years of severe drought had hoped to put his family on better footing selling his calves across the northern border.
Like his father and grandfather before him, Ibarra Vargas has raised cattle on the parched soil of Sonora, the state in northwestern Mexico that shares a long border with the United States, particularly Arizona. His family has faced punishing droughts before but has never before had to contend with the economic hit of a new scourge: the New World Screwworm, a flesh-eating parasite.
U.S. agriculture officials halted live cattle crossing the border in July – the third suspension of the past eight months — due to concerns about the flesh-eating maggot which has been found in southern Mexico and is creeping north.
The screwworm is a larva of the Cochliomyia hominivorax fly that can invade the tissues of any warm-blooded animal, including humans. The parasite enters animals’ skin, causing severe damage and lesions that can be fatal. Infected animals are a serious threat to herds.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture calls it a “devastating pest” and said in June that it poses a threat to “our livestock industry, our economy, and our food supply chain.” It has embarked on other steps to keep it out of the United States, which eradicated it decades ago.
As part of its strategy the U.S. is preparing to breed billions of sterile flies and release them in Mexico and southern Texas. The aim is for the sterile males to mate with females in the wild who then produce no offspring.
The U.S. ban on live cattle also applies to horses and bison imports. It hit a ranching sector already weakened by drought and specifically a cattle export business that generated $1.2 billion for Mexico last year. This year, Mexican ranchers have exported fewer than 200,000 head of cattle, which is less than half what they historically send in the same period.
For Ibarra Vargas, considered a comparatively small rancher by Sonora’s beef-centric standards, the inability to send his calves across the border has made him rethink everything.
The repeated bans on Mexican cows by U.S. authorities has pushed his family to branch into beekeeping, raising sheep and selling cow’s milk. What he earns is just a fraction of what he earned by exporting live cattle, but he is trying to hold on through the lean times.
“Tiempos de vacas flacas” — times of the lean cows — as he calls them.
“At least it lets us continue” ranching, the 57-year-old said with a white cowboy hat perched on his head.
Reinvent to survive
Even as ranchers in Sonora intensify their efforts to make sure the parasitic fly never makes it into their state, they’ve had to seek new markets.
In the past two months, they’ve sold more than 35,000 mature cows within Mexico at a significant loss.
“We couldn’t wait any longer,” said Juan Carlos Ochoa, president of the Sonora Regional Cattle Union. Those sales, he said, came at a “35% lower price difference compared with the export value of a cow.”
That’s hard to stomach when beef prices in the U.S. are rising.
The U.S. first suspended cattle imports last November. Since then, more than 2,258 cases of screwworm have been identified in Mexico. Treatment requires a mix of manually removing the maggots, healing the lesions on the cows and using anti-parasite medicine.
Some ranchers have also started retail beef sales through luxury butcher shops referred to as “meat boutiques.”
There are other foreign markets, for example Japan, but selling vacuum sealed steaks across the Pacific is a dramatically different business than driving calves to U.S. feedlots. The switch is not easy.
An uncertain future
With his calves mooing as they ran from one end of a small corral to the other waiting to be fed, Ibarra Vargas said he still hasn’t figured out how he will survive an extended period of not being able to send them to the U.S.
The recent two-year drought reduced his cattle stocks and forced him to take on debt to save the small family ranch that has survived for three generations.
Juan Carlos Anaya, director of Agricultural Markets Consulting Group, attributed a 2% drop in Mexico’s cattle inventory last year to the drought.
Anaya said Mexican ranchers who export are trying to get the U.S. to separate what happens in southern Mexico from the cattle exporting states in the north where stricter health and sanitation measures are taken, “but the damage is already done.”
“We’re running out of time,” said Ibarra Vargas, who already laments that his children are not interested in carrying on the family business. For a rancher who “doesn’t have a market or money to continue feeding his calves, it’s a question of time before he says: ‘you know what, this is as far as I go.'”
Mideast clashes breach Olympic truce as athletes gather for Winter Paralympic Games
Fighting intensified in the Middle East during the Olympic truce, in effect through March 15. Flights are being disrupted as athletes and families converge on Italy for the Winter Paralympics.
A U.S. scholarship thrills a teacher in India. Then came the soul-crushing questions
She was thrilled to become the first teacher from a government-sponsored school in India to get a Fulbright exchange award to learn from U.S. schools. People asked two questions that clouded her joy.
Sunday Puzzle: Sandwiched
NPR's Ayesha Rascoe plays the puzzle with WXXI listener Jonathan Black and Weekend Edition Puzzlemaster Will Shortz.
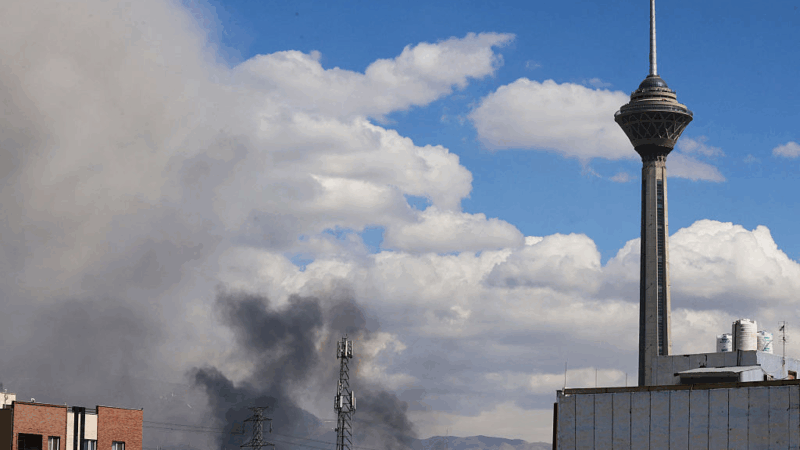
U.S.-Israeli strikes in Iran continue into 2nd day, as the region faces turmoil
Israel said on Sunday it had launched more attacks on Iran, while the Iranian government continued strikes on Israel and on U.S. targets in Gulf states, Iraq and Jordan.
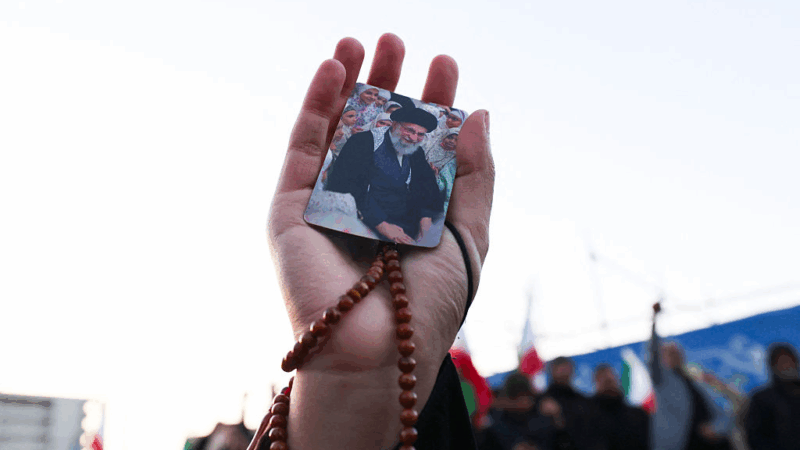
Trump warns Iran not to retaliate after Ayatollah Ali Khamenei is killed
The Iranian government has announced 40 days of mourning. The country's supreme leader was killed following an attack launched by the U.S. and Israel on Saturday against Iran.
Iran fires missiles at Israel and Gulf states after U.S.-Israeli strike kills Khamenei
Iran fired missiles at targets in Israel and Gulf Arab states Sunday after vowing massive retaliation for the killing of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei by the United States and Israel.