Hells Canyon, the deepest gorge in the U.S., is surprisingly young
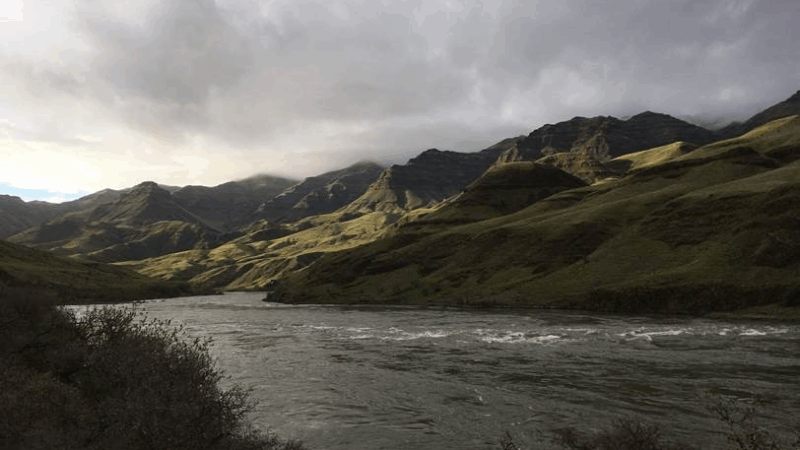
Hells Canyon, the deepest river gorge in the United States, likely got rapidly carved 2.1 million years ago when a shifting landscape in Idaho caused a giant lake to start overflowing.
That’s according to a new study that looked at ancient river sediments that have long been hidden away inside the canyon’s caves, which now lie high above today’s Snake River.
This new work is “brilliant because they realized that this really enigmatic canyon that people have wondered about for over a century could be dated using caves,” says Darryl Granger, a geoscientist at Purdue University who wasn’t part of the research team.
“They had the persistence to find the right caves that still had river sand and gravel inside, just as it was deposited millions of years ago,” he says.
Hells Canyon, which is on the border between Oregon and Idaho, is almost 8,000 feet deep. That makes it far deeper than the famous Grand Canyon of Arizona, which reaches a depth of about 6,000 feet and which has been well studied by geologists who want to know how and when it formed.
“The Hells Canyon, despite being a deeper canyon, has not really attracted as much modern scientific interest,” says Matthew Morriss, a geologist with the Utah Geological Survey.
He personally became interested back when he was 19 years old, and visited the canyon during a college field trip. It made him wonder how and when the canyon got created.
“As an Earth scientist and as just a citizen of this country, we have these big landscapes. And for people who visit them, it’s an important part of the natural history, to understand what formed the landscapes that inspire at such a scale,” he says.
He made multiple trips to the canyon, hiking up steep slopes and fighting poison ivy, trying to find places where the river might have left behind gravelly sediments back when it created the canyon by wearing through rock.
“You’re looking for pieces of evidence of where the river used to be,” says Morriss.
Sometimes, as a river carves down through rock to make a canyon, it can leave behind small rock shelves on the canyon’s walls. These flat terraces can end up covered with river sediments, and scientists have ways of figuring out how long the layers of sediment have been sitting there.
But in Hells Canyon, the rock walls close to the river were so steep, they didn’t have these shelves. So Morriss went looking for old river sediments someplace else: inside of caves.
Limestone caves that faced the river might have temporarily been filled with sediment-carrying water as the river carved the canyon, he figured.
Other river canyons have been dated this way in the past, says Granger, who first used this approach in the 1990’s.
“But it requires pretty special circumstances for it to work,” says Granger. “You have to have the right river, carrying the right minerals, and there have to be caves.”
Morriss teamed up with local spelunkers, who knew the area, to search for caves in Hells Canyon that might fit the bill.
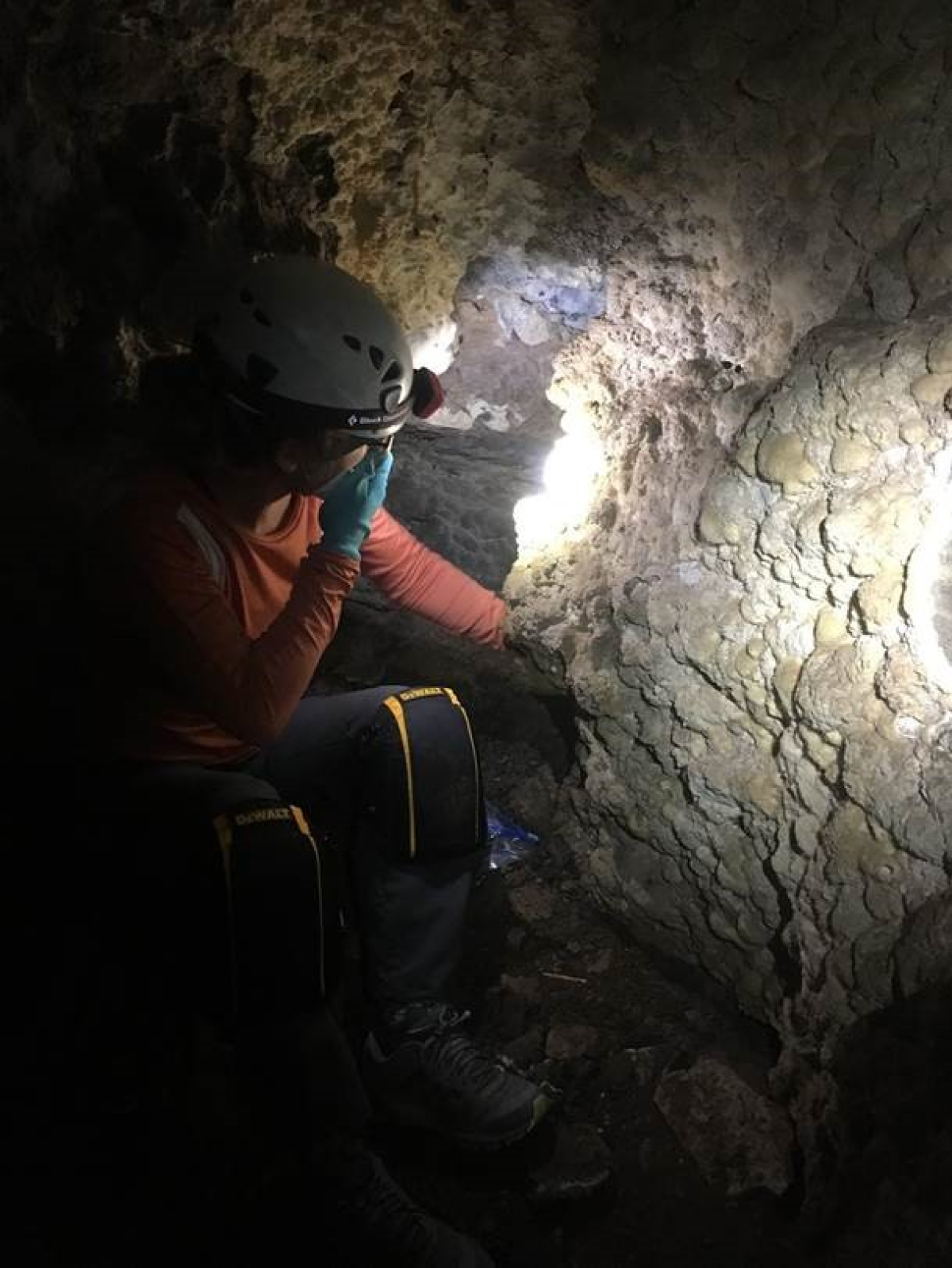

“Lo and behold, the first cave we went in together, we did find a lot of gravel we were able to sample,” he says, noting that this cave is about 1,200 feet above the modern-day Snake River.
Eventually, by exploring over 30 caves, they found old river sediments in a couple other caves, too.
Then the research team used a dating technique on the sediment samples to reveal how long it had been since the river stashed these minerals underground in these caves. There, the minerals were protected from incoming cosmic rays that would have otherwise changed their chemical makeup over time.
The results, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, indicate that “the river is carving a new course that is 2.1 million years old,” says Morriss. “There was no river canyon there before 2.1 million years ago.”
The researchers believe that the canyon emerged when a huge lake in what’s now Idaho drained away and disappeared from the landscape.
Geologic changes and melting glaciers around this lake would have resulted in a lot more water heading into it, explains Morriss, leading to a “fill and spill” episode that seems to have supplied the water needed to carve out Hells Canyon.
He was surprised by the age of the canyon.
“This is younger than the youngest reported age for the Grand Canyon,” he says, noting that the Grand Canyon’s youngest stretches are about 5 million years old. “Hells Canyon’s incision is much more recent.”
And he was glad to finally be able to answer the question he wondered about as a teenager on that field trip to Hells Canyon.
“It was nice to put that to rest and also be able to email my college professors and say, ‘See, I told you I’d find out how old this was’ and be able to share that excitement with them,” says Morriss. “It was really fun.”
British Columbia to make daylight saving time permanent
The Canadian province is permanently ending the biannual time shifts for more light at the day's end. But research shows daylight saving increases health risks.
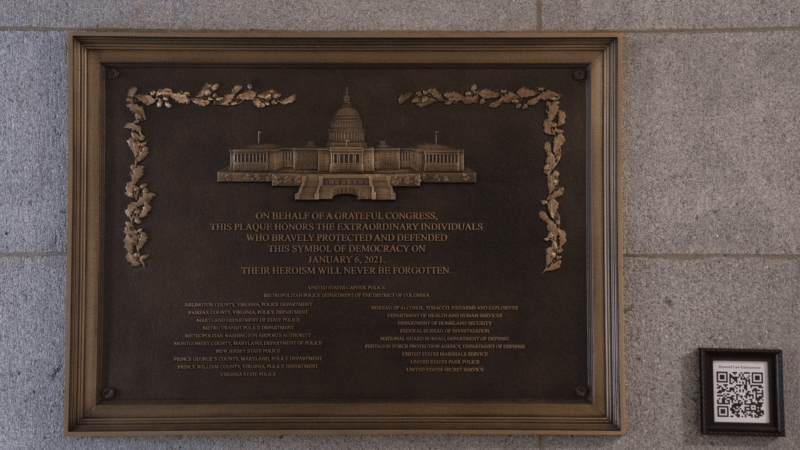
Jan. 6 plaque honoring police officers is now displayed at the Capitol after a 3-year delay
Visitors to the Capitol in Washington now have a visible reminder of the siege there on Jan. 6, 2021, and the officers who fought and were injured that day.
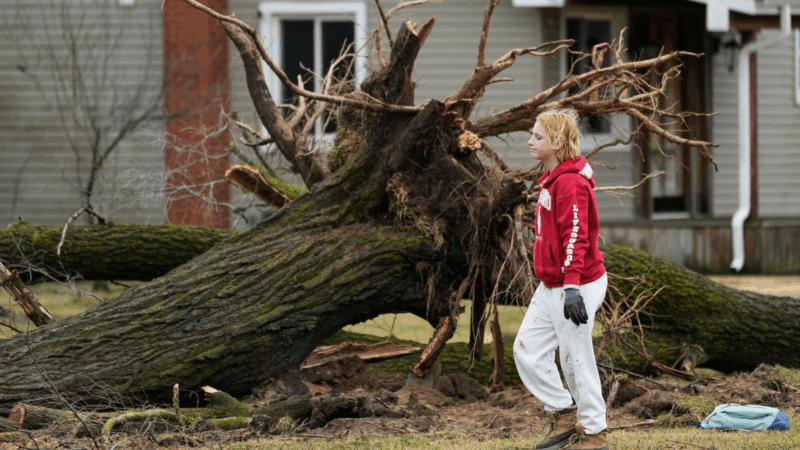
Authorities searching debris after suspected tornadoes kill 6 in Michigan, Oklahoma
A 12-year-old boy is reported to be among the dead following powerful storms that stretched across the middle of the country.
Opinion: The immorality of betting on war
Traders on prediction markets bet on nearly anything. One made more than half a million dollars betting on the U.S. strike against Iran. But should people wager on human suffering?
Alabama man facing execution for deadly robbery asks for clemency as he didn’t kill victim
Charles “Sonny” Burton is scheduled to be executed March 12 for his role in a 1991 robbery in which a man was fatally shot. His supporters and attorney are asking the governor for clemency, arguing that his life should be spared because Burton didn’t fire the gun or witness the killing.
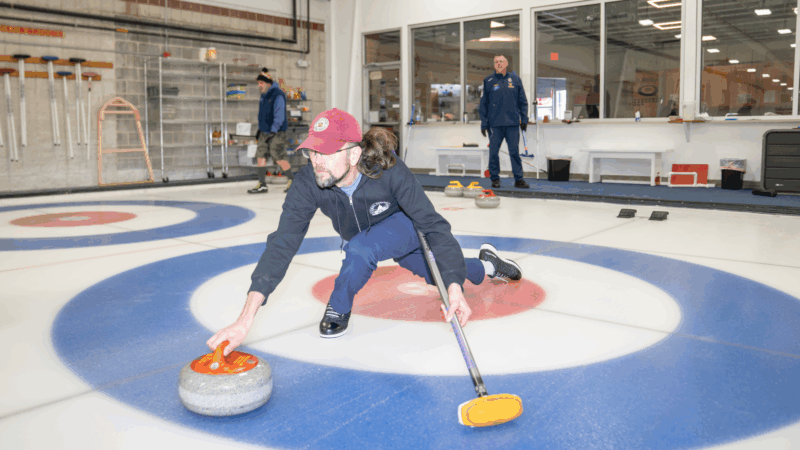
Curling had its moment at the Olympics and now Paralympics. It sparked a curling bonanza in America
Hundreds of people become interested in curling every four years and the 2026 numbers already show that boom.