Doctors remove pig kidney from an Alabama woman after a record 130 days
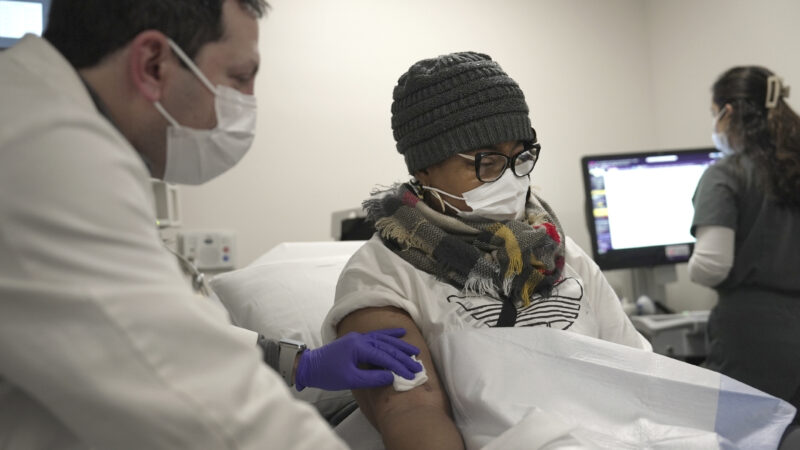
Towana Looney, a pig kidney transplant recipient, gets a morning check-up with Dr. Jeffrey Stern at NYU Langone Health in New York, Friday, Jan. 24, 2025.
By Lauran Neergaard
WASHINGTON (AP) — An Alabama woman who lived with a pig kidney for a record 130 days had the organ removed after her body began rejecting it and is back on dialysis, doctors announced Friday – a disappointment in the ongoing quest for animal-to-human transplants.
Towana Looney is recovering well from the April 4 removal surgery at NYU Langone Health and has returned home to Gadsden, Alabama. In a statement, she thanked her doctors for “the opportunity to be part of this incredible research.”
“Though the outcome is not what anyone wanted, I know a lot was learned from my 130 days with a pig kidney – and that this can help and inspire many others in their journey to overcoming kidney disease,” Looney added.
Scientists are genetically altering pigs so their organs are more humanlike to address a severe shortage of transplantable human organs. More than 100,000 people are on the U.S. transplant list, most who need a kidney, and thousands die waiting.
Before Looney’s transplant only four other Americans had received experimental xenotransplants of gene-edited pig organs – two hearts and two kidneys that lasted no longer than two months. Those recipients, who were severely ill before the surgery, died.
Now researchers are attempting these transplants in slightly less sick patients, like Looney. A New Hampshire man who received a pig kidney in January is faring well and a rigorous study of pig kidney transplants is set to begin this summer. Chinese researchers also recently announced a successful kidney xenotransplant.
Looney had been on dialysis since 2016 and didn’t qualify for a regular transplant – her body was abnormally primed to reject a human kidney. So she sought out a pig kidney and it functioned well – she called herself “superwoman” and lived longer than anyone with a gene-edited pig organ before, from her Nov. 25 transplant until early April when her body began rejecting it.
NYU xenotransplant pioneer Dr. Robert Montgomery, Looney’s surgeon, said what triggered that rejection is being investigated. But he said Looney and her doctors agreed it would be less risky to remove the pig kidney than to try saving it with higher, riskier doses of anti-rejection drugs.
“We did the safe thing,” Montgomery told The Associated Press. “She’s no worse off than she was before (the xenotransplant) and she would tell you she’s better off because she had this 4½ month break from dialysis.”
Shortly before the rejection began, Looney had suffered an infection related to her prior time on dialysis and her immune-suppressing anti-rejection drugs were slightly lowered, Montgomery said. At the same time, her immune system was reactivating after the transplant. Those factors may have combined to damage the new kidney, he said.
Rejection is a common threat after transplants of human organs, too, and sometimes cost patients their new organ. Doctors face a balancing act in tamping down patients’ immune systems just enough to preserve the new organ while allowing them to fight infection.
It’s an even bigger challenge with xenotransplantation. While these pig organs have been altered to help prevent immediate rejection, patients still require immune-suppressing drugs. Which drugs are best to prevent different, later forms of rejection isn’t clear, said Dr. Tatsuo Kawai of Massachusetts General Hospital, another xenotransplant pioneer. Different research groups are using different combinations, he said.
“When we have more experience, we’ll know what kind of immunosuppression is really necessary for xenotransplant,” Kawai said
Montgomery said Looney’s experience offers valuable lessons for the upcoming clinical trial.
Making xenotransplant ultimately work “is going to be won with singles and doubles, not swinging for the fence every time we do one of these,” he said.
House Dem. Leader Jeffries responds to air strikes on Iran by U.S. and Israel
NPR's Emily Kwong speaks to House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries (D-NY), who is still calling for a vote on a war powers resolution following a wave of U.S.- and Israel-led airstrikes on Iran.
Iran’s Ayatollah Ali Khamenei is killed in Israeli strike, ending 36-year iron rule
Khamenei, the Islamic Republic's second supreme leader, has been killed. He had held power since 1989, guiding Iran through difficult times — and overseeing the violent suppression of dissent.
Found: The 19th century silent film that first captured a robot attack
A newly rediscovered 1897 short by famed French filmmaker Georges Méliès is being hailed as the first-ever depiction of a robot in cinema.
‘One year of failure.’ The Lancet slams RFK Jr.’s first year as health chief
In a scathing review, the top US medical journal's editorial board warned that the "destruction that Kennedy has wrought in 1 in office might take generations to repair."
Here’s how world leaders are reacting to the US-Israel strikes on Iran
Several leaders voiced support for the operation – but most, including those who stopped short of condemning it, called for restraint moving forward.
How could the U.S. strikes in Iran affect the world’s oil supply?
Despite sanctions, Iran is one of the world's major oil producers, with much of its crude exported to China.