Alabama to move forward with nitrogen gas execution in September after lawsuit settlement
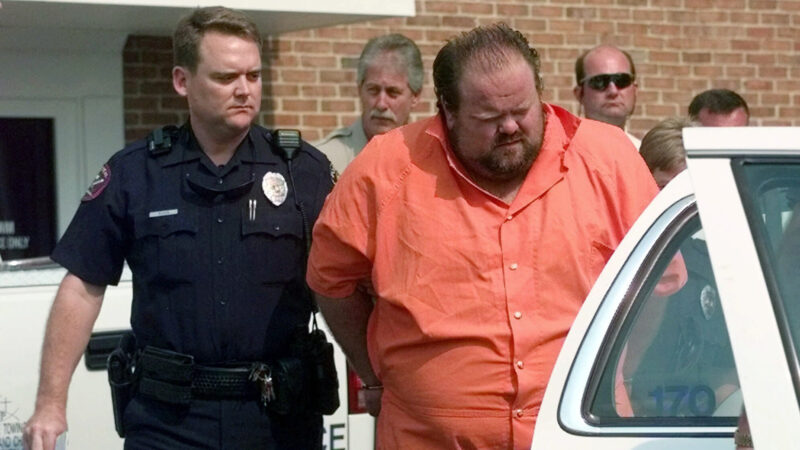
In this file photo, Officials escort Alan Eugene Miller away from the Pelham City Jail in Alabama, Aug. 5, 1999. Miller was the second person executed by nitrogen gas in the U.S. in September.
MONTGOMERY, Ala. (AP) — Alabama’s attorney general said Monday that another nitrogen gas execution will go forward in September after the state reached a settlement agreement with the inmate slated to be the second person put to death with the new method.
Alabama and attorneys for Alan Miller, who was convicted of killing three men, reached a “confidential settlement agreement” to end litigation filed by Miller, according to a court document filed Monday. Miller’s lawsuit cited witness descriptions of the January execution of Kenneth Smith with nitrogen gas as he sought to block the state from using the same protocol on him.
The court records did not disclose the terms of the agreement. Miller had suggested several changes to the state’s nitrogen gas protocol, including the use of medical grade nitrogen, having a trained professional supervise the gas flow and the use of sedative before the execution. Will Califf, a spokesman for Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said he could not confirm if the state had agreed to make changes to execution procedures.
“Miller entered into a settlement on favorable terms to protect his constitutional right to be free from cruel and unusual punishments,” Mara E. Klebaner, an attorney representing Miller wrote in an email Monday night.
Marshall described the settlement as a victory for the use of nitrogen gas as an execution method. His office said it will allow Miller’s execution to be carried out in September with nitrogen gas.
“The resolution of this case confirms that Alabama’s nitrogen hypoxia system is reliable and humane,” Marshall said in a statement.
“Miller’s complaint was based on media speculation that Kenneth Smith suffered cruel and unusual punishment in the January 2024 execution, but what the state demonstrated to Miller’s legal team undermined that false narrative. Miller’s execution will go forward as planned in September.”
Marshall’s office had titled a press release announcing the settlement that the attorney general “successfully defends constitutionality” of nitrogen executions. An attorney for Miller disputed Marshall’s assessment.
“No court upheld the constitutionality of the state’s proposed nitrogen hypoxia method of execution in Mr. Miller’s case, thus the state’s claim that it “successfully defend(ed)” that method’s “constitutionality” is incorrect. By definition, a settlement agreement does not involve a ruling on the merits of the underlying claim,” Klebaner wrote in an email.
The settlement was filed a day before a federal judge was scheduled to hold a hearing in Miller’s request to block his upcoming Sept. 26 execution. Klebaner said that by entering into a settlement agreement that the state avoided a public hearing in the case.
Alabama executed Smith in January in the first execution using nitrogen gas. The new execution method uses a respirator mask fitted over the inmate’s face to replace their breathing air with nitrogen gas, causing the person to die from lack of oxygen.
Attorneys for Miller had pointed to witness descriptions of Smith shaking in seizure-like spasms for several minutes during his execution. The attorneys argued that nation’s first nitrogen execution was “disaster” and the state’s protocol did not deliver the quick death that the state promised a federal court that it would.
The state argued that Smith had held his breath which caused the execution to take longer than anticipated.
Miller, a delivery truck driver, was convicted of killing three men — Terry Jarvis, Lee Holdbrooks and Scott Yancy — during back-to-back workplace shootings in 1999.
Alabama had previously attempted to execute Miller by lethal injection. But the state called off the execution after being unable to connect an IV line to the 351-pound inmate. The state and Miller agreed that any other execution attempt would be done with nitrogen gas.
Scientists make a pocket-sized AI brain with help from monkey neurons
A new study suggests AI systems could be a lot more efficient. Researchers were able to shrink an AI vision model to 1/1000th of its original size.
U.S. evacuates diplomats, shuts down some embassies as war enters fourth day
The United States evacuated diplomats across the Middle East and shut down some embassies as war with Iran intensified Tuesday while President Trump signaled the conflict could turn into extended war.
North Carolina and Texas have primary elections Tuesday. Here’s what you need to know
The midterm elections are officially underway and contests in Texas and North Carolina will be the first major opportunity for parties to hear from voters about what's important to them in 2026.
Trump promised the MAGA base no new wars. Then he went to war with Iran
President Trump promised his "Make America Great Again" voters an "America First" foreign policy. With the war in Iran, he's testing MAGA world's willingness to be flexible on one of its core beliefs.
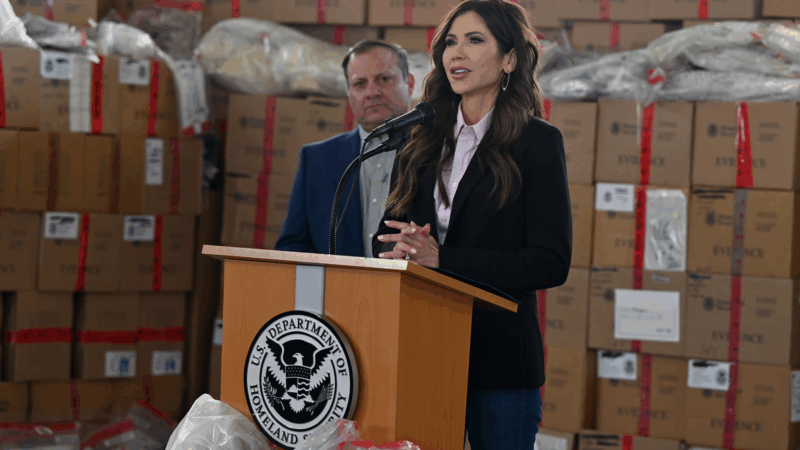
Kristi Noem set to face senators over DHS shutdown, immigration enforcement
The focus of the hearing is likely to be on how Kristi Noem is pursuing President Trump's mass deportation efforts in his second term, after two U.S. citizens were killed by immigration officers.
College students, professors are making their own AI rules. They don’t always agree
More than three years after ChatGPT debuted, AI has become a part of everyday life — and professors and students are still figuring out how or if they should use it.