Supreme Court rules in favor of Black voters in Alabama redistricting case
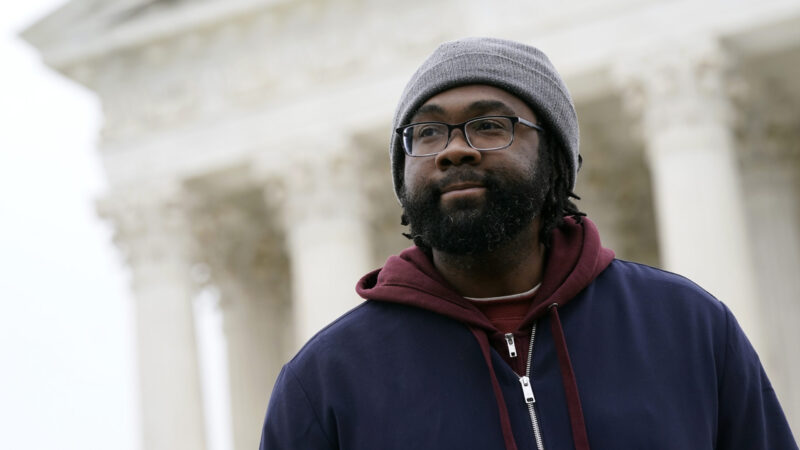
Evan Milligan, plaintiff in Merrill v. Milligan, an Alabama redistricting case, listens to a reporter's question following oral arguments outside the Supreme Court on Capitol Hill in Washington, Oct. 4, 2022. The Supreme Court on Thursday, June 8, 2023, issued a surprising ruling in favor of Black voters in a congressional redistricting case, ordering the creation of a second district with a large Black population.
By Mark Sherman
WASHINGTON (AP) — The Supreme Court on Thursday issued a surprising 5-4 ruling in favor of Black voters in a congressional redistricting case from Alabama, with two conservative justices joining liberals in rejecting a Republican-led effort to weaken a landmark voting rights law.
Chief Justice John Roberts and Justice Brett Kavanaugh aligned with the court’s liberals in affirming a lower-court ruling that found a likely violation of the Voting Rights Act in an Alabama congressional map with one majority Black seat out of seven congressional districts in a state where more than one in four residents is Black. The state now will have to draw a new map for next year’s elections.
The decision was closely watched for its potential effect on control of the closely divided U.S. House of Representatives. Because of the ruling, new maps are likely in Alabama and Louisiana that could allow Democratic-leaning Black voters to elect their preferred candidates in two more congressional districts.
The outcome was unexpected in that the court had allowed the challenged Alabama map to be used for the 2022 elections, and in arguments last October the justices appeared willing to make it harder to challenge redistricting plans as racially discriminatory under the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
The chief justice himself suggested last year that he was open to changes in the way courts weigh discrimination claims under the part of the law known as section 2. But on Thursday, Roberts wrote that the court was declining “to recast our section 2 case law as Alabama requests.”
Roberts also was part of conservative high-court majorities in earlier cases that made it harder for racial minorities to use the Voting Rights Act in ideologically divided rulings in 2013 and 2021.
The other four conservative justices dissented Thursday. Justice Clarence Thomas wrote that the decision forces “Alabama to intentionally redraw its longstanding congressional districts so that black voters can control a number of seats roughly proportional to the black share of the State’s population. Section 2 demands no such thing, and, if it did, the Constitution would not permit it.”
The Biden administration sided with the Black voters in Alabama.
Attorney General Merrick Garland applauded the ruling: “Today’s decision rejects efforts to further erode fundamental voting rights protections, and preserves the principle that in the United States, all eligible voters must be able to exercise their constitutional right to vote free from discrimination based on their race.”
Evan Milligan, a Black voter and the lead plaintiff in the case, said the ruling was a victory for democracy and people of color.
“We are grateful that the Supreme Court upheld what we knew to be true: that everyone deserves to have their vote matter and their voice heard. Today is a win for democracy and freedom not just in Alabama but across the United States,” Milligan said.
Alabama Republican Party Chairman John Wahl said in a statement that state lawmakers would comply with the ruling.
“Regardless of our disagreement with the Court’s decision, we are confident the Alabama Legislature will redraw district lines that ensure the people of Alabama are represented by members who share their beliefs, while following the requirements of applicable law,” Wahl said.
The case stems from challenges to Alabama’s seven-district congressional map, which included one district in which Black voters form a large enough majority that they have the power to elect their preferred candidate. The challengers said that one district is not enough, pointing out that overall, Alabama’s population is more than 25% Black.
A three-judge court, with two appointees of former President Donald Trump, had little trouble concluding that the plan likely violated the Voting Rights Act by diluting the votes of Black Alabamians. The panel ordered a new map drawn.
But the state quickly appealed to the Supreme Court, where five conservative justices prevented the lower-court ruling from going forward. At the same time, the court decided to hear the Alabama case.
The National Redistricting Foundation said in a statement that its pending lawsuits in Georgia and Texas also could be affected.
Separately, the Supreme Court in the fall will hear South Carolina’s appeal of a lower-court ruling that found Republican lawmakers stripped Black voters from a district to make it safer for a Republican candidate. That case also could lead to a redrawn map in South Carolina, where six U.S. House members are Republicans and one is a Democrat.
Partisan politics also underlies the Alabama case. Republicans who dominate elective office in Alabama have been resistant to creating a second district with a Democratic-leaning Black majority, or close to one, that could send another Democrat to Congress.
The judges found that Alabama concentrated Black voters in one district, while spreading them out among the others to make it much more difficult to elect more than one candidate of their choice.
Alabama’s Black population is large enough and geographically compact enough to create a second district, the judges found.
Denying discrimination, Alabama argued that the lower court ruling would have forced it to sort voters by race and insisted it was taking a “race neutral” approach to redistricting.
At arguments in October, Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson scoffed at the idea that race could not be part of the equation. Jackson, the court’s first Black woman, said that constitutional amendments passed after the Civil War and the Voting Rights Act a century later were intended to do the same thing, make Black Americans “equal to white citizens.”
___
Associated Press writer Kim Chandler contributed to this report from Montgomery, Alabama.
The candy heir vs. chocolate skimpflation
The grandson of the Reese's Peanut Butter Cups creator has launched a campaign against The Hershey Company, which owns the Reese's brand. He wants them to stop skimping on ingredients.
Scientists make a pocket-sized AI brain with help from monkey neurons
A new study suggests AI systems could be a lot more efficient. Researchers were able to shrink an AI vision model to 1/1000th of its original size.
U.S. evacuates diplomats, shuts down some embassies as war enters fourth day
The United States evacuated diplomats across the Middle East and shut down some embassies as war with Iran intensified Tuesday while President Trump signaled the conflict could turn into extended war.
North Carolina and Texas have primary elections Tuesday. Here’s what you need to know
The midterm elections are officially underway and contests in Texas and North Carolina will be the first major opportunity for parties to hear from voters about what's important to them in 2026.
Kristi Noem set to face senators over DHS shutdown, immigration enforcement
The focus of the hearing is likely to be on how Kristi Noem is pursuing President Trump's mass deportation efforts in his second term, after two U.S. citizens were killed by immigration officers.
College students, professors are making their own AI rules. They don’t always agree
More than three years after ChatGPT debuted, AI has become a part of everyday life — and professors and students are still figuring out how or if they should use it.