Birmingham Revitalization: While Downtown Grows, Frustrated Citizens Feel Left Behind
On a March evening, more than 100 people gather in city council chambers to discuss a proposed (and since passed) law delineating the balance of power in city government.
But the conversation quickly turns to something else: frustration and anger over how Birmingham is changing.
Citizen after citizen expresses concerns, and there are many. They worry that too many newcomers, mainly wealthy people and white people, will move into Birmingham. There’s concern those newcomers will make it too expensive, change the culture, and open businesses that don’t serve the needs of their neighborhoods. Others say local leaders are focusing too much money and energy on the city center.
“Nothing is being done in the neighborhood,” Bonderia Lyons of Fountain Heights tells the crowd. “Everything that’s being done is geared toward downtown.”
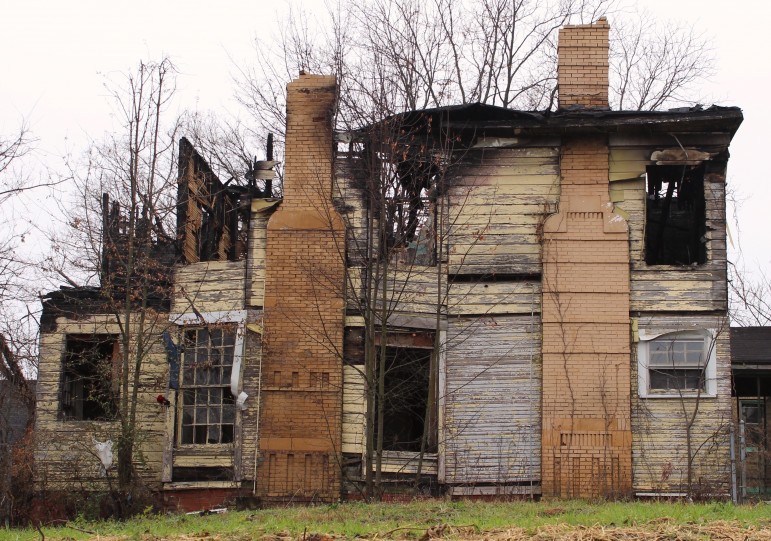
There’s an excitement in Birmingham that’s steadily building. Downtown Birmingham has seen almost 40 percent residential growth since 2000. Railroad Park and Regions Field have fueled the momentum. Today, construction cranes dot the skyline, historic buildings are being restored, and the city was recently named a top destination by Lonely Planet and by the Travel Channel, among others. Despite this, Birmingham’s revitalization has touched only part of the city, leaving many longtime residents feeling ignored.
Recent press on Birmingham overlooks this disparity. Glossy magazines and tech and culture websites have showered the city with accolades. But for people like Lyons, being Fast Company’s top city for Millennial entrepreneurs doesn’t mean squat.
“We are the forgotten people over there,” Lyons says. “The black people, we’ve been forgotten. They don’t do anything in our areas.”
Scott Douglas, head of the social service organization Greater Birmingham Ministries, was at the meeting too. He says years of frustration came to a head that evening. He understands Lyons. Her neighborhood, Fountain Heights, is just north of downtown.
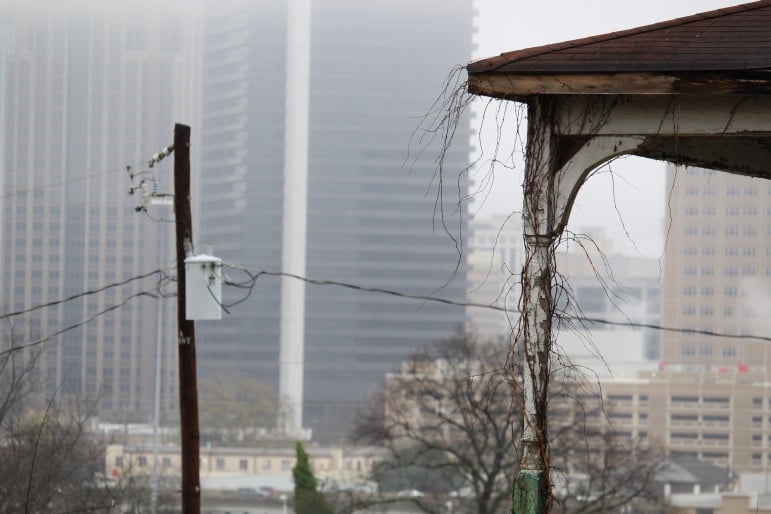
“So you can really be on the hill in Fountain Heights or Druid Hills, and look down on all the rising skyscrapers, just an interstate bridge away,” says Douglas. “But it’s not affecting you.”
Downtown’s growth isn’t unique to Birmingham. Census Bureau data shows more and more Americans are moving into cities. In a place like Birmingham, with its history of economic and racial injustice, the tension of this migration is stronger.
“It’s not even fear of personal loss but fear that progress might pass me by,” says Douglas. “Here it is, things are happening better in the city and I’m not included in it. I’m being left out.”
So far, the city says its attention downtown has paid off. Birmingham’s business tax revenue increased by more than $16 million dollars since 2013. But State Representative Patricia Todd suggests a more expansive approach.
“What city leadership sometimes forgets is, they see the immediate revenue generator of an urban core being developed, but, in reality, look what we’ve done in Avondale!” says Todd.
Todd represents Avondale, which has seen an explosion of investment and rising real estate prices. Last year, Thrillist.com named it the “Brooklyn” of Alabama.
As in the real Brooklyn, Todd says, longtime residents can get shorted when ex-suburbanites move in.
“I have constituents who don’t have running water, can’t pay their electric bills. You know, they’re trapped,” says Todd. “You’ve got to be sensitive to that when you’re going in to do some development.”
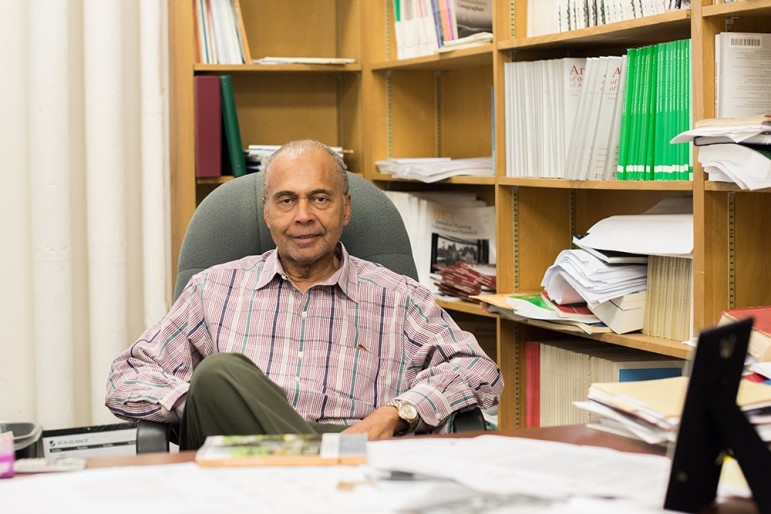
Despite complaints about high rents on lofts downtown, Birmingham is not San Francisco or New York City. After seeing decades of gentrification there, former University of Alabama social geography professor Bobby Wilson says mid-sized cities like Birmingham can do revitalization, even gentrification, better.
“It’s very controversial, but if done right, it can benefit everybody,” says Wilson. Wilson lectured on urban revitalization and social justice for more than 40 years. But, his academic credentials aside, as an area resident, he says he’s just excited to see new life in the city.
“Who would have ever thought about 10 years ago a significant number of people would be moving into the city, fixing up these houses?” Wilson asks. “I study the thing, and I was surprised!”
While there’s no unified plan for making sure Birmingham’s rising tide raises all ships, efforts are moving forward. The Birmingham City Council has put an emphasis on tackling blight this year. New affordable housing units are going up in Woodlawn and other places. On the west side of the city, the CrossPlex sports complex leaves residents hopeful for more stores, restaurants and improved infrastructure.
It’s not perfect, but, as Representative Patricia Todd says, “We should just be glad anyone wants to move to Birmingham … and celebrate that.”
WBHM continues our series on Birmingham revitalization tomorrow. We’ll visit with real estate developers in the city’s fastest-growing areas, and tour two neighborhoods whose residents claim the city has forgotten them.
Pentagon tightens controls over Stars and Stripes after calling it “woke”
The new rules for the independent military newspaper are the Defense Department's latest effort to put extraordinary restrictions on journalists covering the agency.
‘War of the Worlds’ remake sinks to the bottom at this year’s Razzie Awards
The surveillance industry version of HG Wells' 1898 classic sci-fi novel stars Ice Cube, and won accolades for worst picture, actor, director and more.
Russian strike on Kyiv region kills 4 and wounds 15, with peace talks stalled
The strikes comes after the United States paused ceasefire talks between Russia and Ukraine due to the war with Iran.
As the risk of measles grows, why are parents so divided on vaccines?
In South Carolina, some parents embrace vaccines, others opt out. Why do people make such different choices? A mix of politics, distrust and misinformation is pushing neighbors apart.
Brazil’s ex-President Bolsonaro is in intensive care with pneumonia, hospital says
One of Bolsonaro's doctor's described the former Brazilian president's medical condition as "serious."
Opinion: An ancient, sophisticated palate
Researchers looking at foodcrusts on the pottery shards of ancient humans say there's evidence of a wide variety of ingredients, indicating that they may have been experimenting with "recipes."