For the first time, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has lowered the recommended age for those who should get a pneumococcal vaccine — down to 50, from 65.
“Lowering the age for pneumococcal vaccination gives more adults the opportunity to protect themselves from pneumococcal disease at the age when risk of infection substantially increases,” the CDC said in a statement.
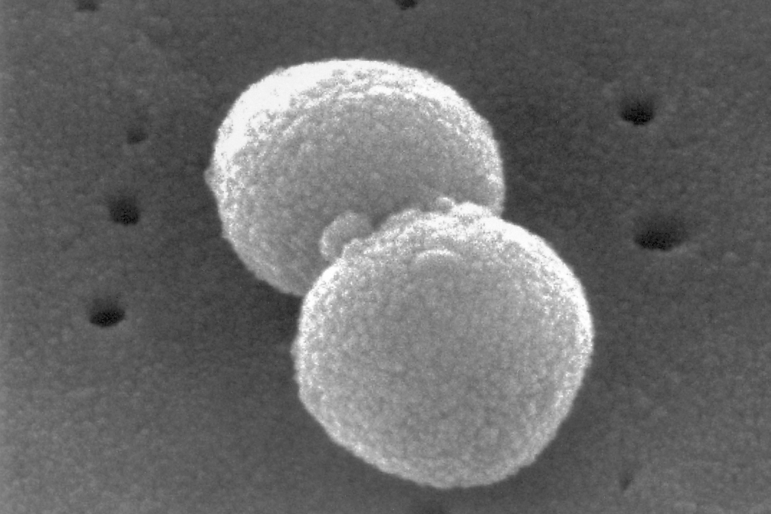
“Pneumococcal bacteria can also cause serious illnesses, including pneumonia, meningitis, and bloodstream infections, and older adults are at increased risk for pneumococcal disease.”
Wednesday’s recommendation comes as respiratory infections caused by the bacteria mycoplasma pneumoniae are rising across the U.S., especially in children, according to the CDC. That marks a change from previous years, when most cases involved older children and adolescents.
This year, the number of people who have been diagnosed with the pneumonia-causing bacteria or with bronchitis has increased over the past six months and peaked in August, the agency says.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes respiratory infections such as pneumonia and can be spread in droplets through sneezing and coughing. Symptoms depend on the type of infection, but fatigue, fever and a cough are a few common symptoms, the CDC says. Diarrhea, runny nose and vomiting may be seen in children 5 years old or younger.
Some people may have the infection but not have symptoms. Those who have pneumonia and don’t need bed rest or treatment at the hospital may have a milder form of the infection known as “walking pneumonia.” A person can also develop pneumonia more than once.
About 2 million infections caused by mycoplasma pneumoniae are diagnosed each year, although the actual number is likely higher.
Treatment for pneumonia can include antibiotics and some people recover without medicine, according to the CDC. There are currently two types of vaccines aimed at preventing pneumonia available in the United States. There are four vaccines in the U.S. that target 15 or more strains of pneumococcal bacteria.
The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices also voted on Wednesday in favor of recommending that those 65 years old and older who are moderately or severely immunocompromised receive an additional updated COVID-19 booster six months after their first one.
“This vote allows people to make the best decisions possible to keep themselves and their loved ones safe from COVID-19,” CDC Director Dr. Mandy Cohen said in a statement. “CDC will continue to educate the public on how and when to get their updated vaccinations so they can risk less severe illness and do more of what they love.”
The number of COVID-19 cases is declining across the U.S., according to data from the CDC.